Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program
This commit is contained in:
commit
7050b83c77
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# 02 C#语言基本语法结构
|
||||
# 01 C#语言基本语法结构
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# 03 C#面向对象设计 I
|
||||
# 02 C#面向对象设计 I
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 04 C#面向对象设计 II
|
||||
# 03 C#面向对象设计 II
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# 绪论
|
||||
# 01 绪论
|
||||
|
||||
知识结构:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
# 09 栈与递归
|
||||
# 03 栈与递归
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
插入(入栈)和删除(出栈)操作只能在一端(栈顶)进行的线性表。即先进后出(First In Last Out)的线性表。
|
||||
|
||||
例1 :线性表`$(a_0,a_1,?,a_{n-1)}$`进栈与出栈演示。
|
||||
例1 :线性表 $(a_0,a_1,?,a_{n-1)}$ 进栈与出栈演示。
|
||||
|
||||
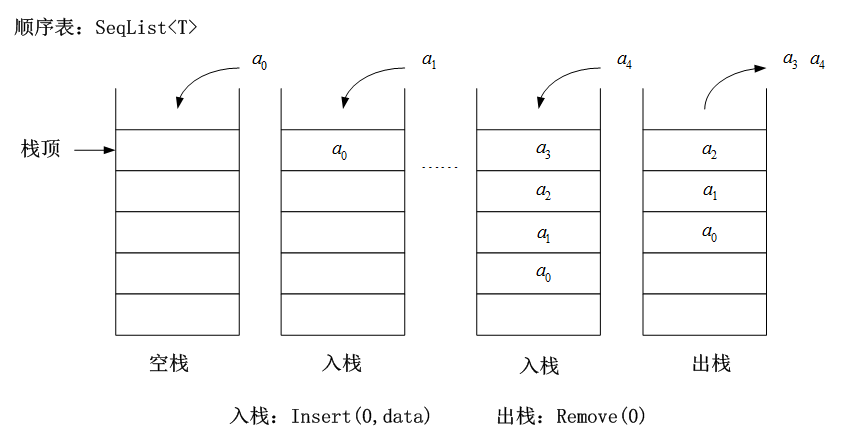
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# 10 队列与多线程
|
||||
# 04 队列与多线程
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,791 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# Leetcode同步练习(一)
|
||||
|
||||
## 题目01:两数之和
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:1
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组 `nums` 和一个目标值 `target`,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 <b>两个整数</b>,并返回他们的数组下标。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例1:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
|
||||
|
||||
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,所以返回 [0, 1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例2:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定 nums = [230, 863, 916, 585, 981, 404, 316, 785, 88, 12, 70, 435, 384, 778, 887, 755, 740, 337, 86, 92, 325, 422, 815, 650, 920, 125, 277, 336, 221, 847, 168, 23, 677, 61, 400, 136, 874, 363, 394, 199, 863, 997, 794, 587, 124, 321, 212, 957, 764, 173, 314, 422, 927, 783, 930, 282, 306, 506, 44, 926, 691, 568, 68, 730, 933, 737, 531, 180, 414, 751, 28, 546, 60, 371, 493, 370, 527, 387, 43, 541, 13, 457, 328, 227, 652, 365, 430, 803, 59, 858, 538, 427, 583, 368, 375, 173, 809, 896, 370, 789], target = 542
|
||||
|
||||
因为 nums[28] + nums[45] = 221 + 321 = 542,所以返回 [28, 45]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:直接利用暴力匹配算法。
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:432 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 65.82% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:30.8 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 8.67% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int[] TwoSum(int[] nums, int target)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int[] result = new int[2];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length - 1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int find = target - nums[i];
|
||||
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.Length; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (find == nums[j])
|
||||
{
|
||||
result[0] = i;
|
||||
result[1] = j;
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目02:删除排序数组中的重复项
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:26
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个 **排序数组**,你需要在 **原地** 删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
|
||||
|
||||
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 **原地修改输入数组** 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定数组 nums = [1,1,2],
|
||||
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2。
|
||||
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定 nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
|
||||
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4。
|
||||
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,输入数组是以“**引用**”方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以想象内部操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参做任何拷贝
|
||||
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
|
||||
|
||||
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
|
||||
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中该长度范围内的所有元素。
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
|
||||
print(nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:双索引法,就是一个快索引一个慢索引,`j`快`i`慢,当`nums[j] == nums[i]`时,`j++`就可以跳过重复项,不相等时,让`i++`并让`nums[i] = nums[j]`,把值复制过来继续执行到末尾即可,时间复杂度为`O(n)`。
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:300 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 64.43% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:33.5 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.48% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int RemoveDuplicates(int[] nums)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (nums.Length < 2)
|
||||
return nums.Length;
|
||||
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j < nums.Length; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (nums[j] != nums[i])
|
||||
{
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
nums[i] = nums[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目03:移除元素
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:27
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组`nums`和一个值`val`,你需要**原地**移除所有数值等于`val`的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度。
|
||||
|
||||
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在**原地修改输入数组**并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
|
||||
|
||||
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定 nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
|
||||
|
||||
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。
|
||||
|
||||
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定 nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
|
||||
|
||||
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。
|
||||
|
||||
注意这五个元素可为任意顺序。
|
||||
|
||||
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 3:**
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:[] value = 0
|
||||
|
||||
输出:0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 4:**
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:[1] value = 1
|
||||
|
||||
输出:0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 5:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:[4,5] value = 5
|
||||
|
||||
输出:1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**说明:**
|
||||
|
||||
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,输入数组是以“**引用**”方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以想象内部操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参作任何拷贝
|
||||
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
|
||||
|
||||
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
|
||||
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中该长度范围内的所有元素。
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
|
||||
print(nums[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:双索引法,利用双索引`i`和`j`,`i`为慢索引拖后,`j`为快索引向前冲。如果`nums[j]!=val`,将`num[j]`的值赋给`num[i]`,循环结束后,`i`指针前面的元素,即为需要保留的元素,从而达到了移除元素的目的,时间复杂度为 `O(n)`。
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:272 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 94.41% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:29.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.21% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int RemoveElement(int[] nums, int val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < nums.Length; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (nums[j] != val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
nums[i] = nums[j];
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目04:最大子序和
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:53
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数数组`nums`,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
|
||||
输出: 6
|
||||
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [-2,1],
|
||||
输出: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>进阶</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经实现复杂度为`O(n)`的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的分治法求解。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:利用暴力算法。
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 596 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 14.18% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24.5 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.88% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int MaxSubArray(int[] nums) {
|
||||
int len = nums.Length;
|
||||
if (len == 0)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
if (len == 1)
|
||||
return nums[0];
|
||||
int max = int.MinValue;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int sum = nums[i];
|
||||
if (sum > max)
|
||||
{
|
||||
max = sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
sum += nums[j];
|
||||
if (sum > max)
|
||||
{
|
||||
max = sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return max;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目05:盛最多水的容器
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:11
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/container-with-most-water/
|
||||
|
||||
给定`n`个非负整数`a1,a2,...,an`,每个数代表坐标中的一个点`(i, ai)`。在坐标内画`n`条垂直线,垂直线`i` 的两个端点分别为`(i, ai)`和`(i, 0)`。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与`x`轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:你不能倾斜容器,且`n`的值至少为 2。
|
||||
|
||||
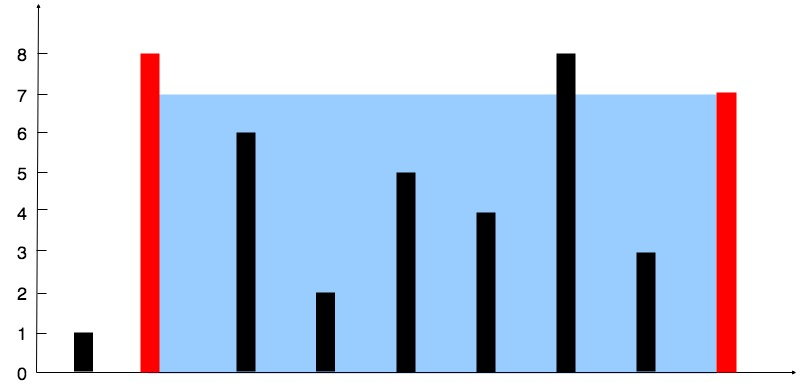
|
||||
|
||||
图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
|
||||
输出: 49
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:利用双索引的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
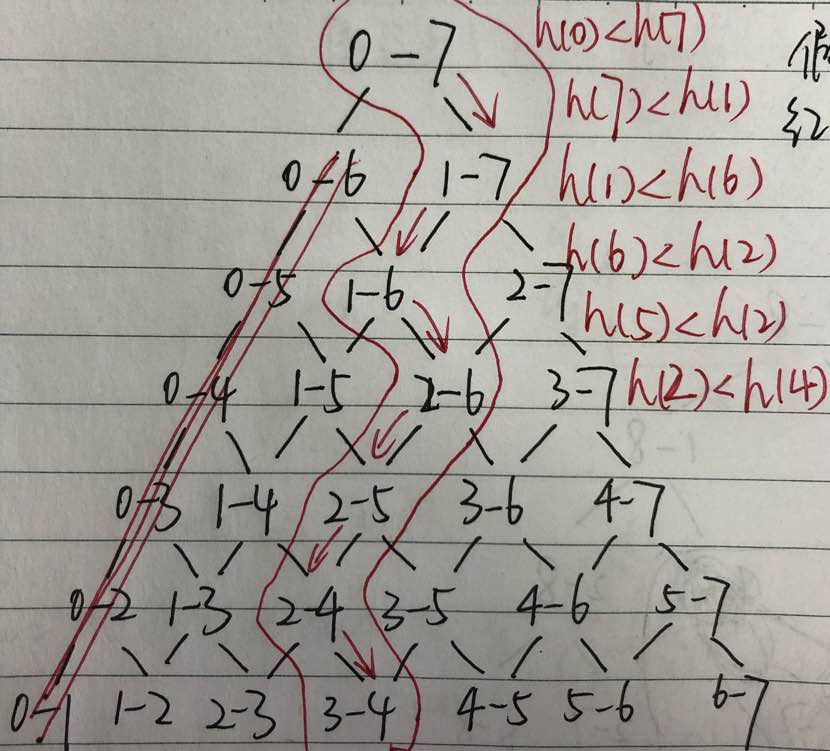
|
||||
|
||||
以0-7走到1-7这一步为例,解释为什么放弃0-6这一分支:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
用h(i)表示第i条线段的高度,S(ij)表示第i条线段和第j条线段圈起来的面积。
|
||||
|
||||
已知 h(0) < h(7),从而S(07) = h(0) * 7。
|
||||
|
||||
有S(06) = min(h(0), h(6)) * 6。
|
||||
|
||||
当h(0) <= h(6),有S(06) = h(0) * 6;
|
||||
当h(0) > h(6),有S(06) = h(6) * 6,S(06) < h(0) * 6。
|
||||
|
||||
由此可知,S(06)必然小于S(07)。
|
||||
```
|
||||
把每一棵子树按照同样的方法分析,很容易可以知道,双索引法走的路径包含了最大面积。
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 50 / 50 个通过测试用例
|
||||
- 执行用时: 144 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 99.64% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 26.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.45% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int MaxArea(int[] height)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = 0, j = height.Length - 1;
|
||||
int max = int.MinValue;
|
||||
while (i < j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int temp = (j - i) * Math.Min(height[i], height[j]);
|
||||
if (temp > max)
|
||||
{
|
||||
max = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (height[i] < height[j])
|
||||
{
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return max;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目06:搜索旋转排序数组
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:33
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/
|
||||
|
||||
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
|
||||
|
||||
( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
|
||||
|
||||
搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
你的算法时间复杂度必须是`O(log n)`级别。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
|
||||
输出: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
|
||||
输出: -1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: nums = [5,1,3], target = 5
|
||||
输出: 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 4</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: nums = [4,5,6,7,8,1,2,3], target = 8
|
||||
输出: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 5</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: nums = [3,1], target = 1
|
||||
输出: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:利用二分法。
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 128 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.17% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 23.8 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 12.00% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int Search(int[] nums, int target)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = 0, j = nums.Length - 1;
|
||||
while (i <= j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int mid = (i + j) / 2;
|
||||
if (nums[mid] == target)
|
||||
return mid;
|
||||
|
||||
if (nums[mid] >= nums[i])
|
||||
{
|
||||
//左半部分有序
|
||||
if (target > nums[mid])
|
||||
{
|
||||
i = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (target == nums[i])
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
|
||||
if (target > nums[i])
|
||||
j = mid - 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
i = mid + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (target < nums[mid])
|
||||
{
|
||||
j = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (target == nums[j])
|
||||
return j;
|
||||
if (target < nums[j])
|
||||
i = mid + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
j = mid - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目07:数组中的第K个最大元素
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:215
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
|
||||
|
||||
在未排序的数组中找到第 `k` 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 `k` 个最大的元素,而不是第 `k` 个不同的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
|
||||
输出: 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4
|
||||
输出: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你可以假设 `k` 总是有效的,且 `1 ≤ k ≤ 数组的长度`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:利用排序的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 152 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 76.47% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.55% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int FindKthLargest(int[] nums, int k)
|
||||
{
|
||||
nums = nums.OrderBy(a => a).ToArray();
|
||||
return nums[nums.Length - k];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目08:除自身以外数组的乘积
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:238
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/product-of-array-except-self/
|
||||
|
||||
给定长度为`n`的整数数组`nums`,其中`n > 1`,返回输出数组`output`,其中`output[i]`等于 `nums`中除`nums[i]`之外其余各元素的乘积。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [1,2,3,4]
|
||||
输出: [24,12,8,6]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>: 请不要使用除法,且在`O(n)` 时间复杂度内完成此题。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>进阶</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在常数空间复杂度内完成这个题目吗?( 出于对空间复杂度分析的目的,输出数组不被视为额外空间。)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:乘积 = 当前数左边的乘积 * 当前数右边的乘积
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
[1, 2, 3, 4]
|
||||
左边的乘积 [1, 1, 2, 6]
|
||||
右边的乘积 [24,12,4, 1]
|
||||
结果 = 左*右 [24,12,8, 6]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 304 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 34.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int[] ProductExceptSelf(int[] nums)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int len = nums.Length;
|
||||
int[] output1 = new int[len];//正向乘积
|
||||
int[] output2 = new int[len];//反向乘积
|
||||
output1[0] = 1;
|
||||
output2[len - 1] = 1;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
output1[i] = output1[i - 1]*nums[i - 1];
|
||||
output2[len - i - 1] = output2[len - i]*nums[len - i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
output1[i] *= output2[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return output1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目09:寻找两个有序数组的中位数
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:4
|
||||
> - 难度:困难
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个大小为`m`和`n`的有序数组`nums1`和`nums2`。
|
||||
|
||||
请你找出这两个有序数组的中位数,并且要求算法的时间复杂度为`O(log(m + n))`。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以假设`nums1`和`nums2`不会同时为空。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
nums1 = [1, 3]
|
||||
nums2 = [2]
|
||||
|
||||
则中位数是 2.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
nums1 = [1, 2]
|
||||
nums2 = [3, 4]
|
||||
|
||||
则中位数是 (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:利用二分策略。
|
||||
|
||||
中位数:用来将一个集合划分为两个长度相等的子集,其中一个子集中的元素总是大于另一个子集中的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
由于题目要求时间复杂度为`O(log(m + n))`,所以不能从两个有序数组的首尾挨个遍历来找到中位数(复杂度 `O(m + n)`);而是要通过二分策略,通过每次比较,能够直接按比例的刷掉一组数字,最后找到中位数(复杂度`O(log(m + n))`)。
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
nums1: [a1,a2,a3,...am]
|
||||
nums2: [b1,b2,b3,...bn]
|
||||
|
||||
[nums1[:i],nums2[:j] | nums1[i:], nums2[j:]]
|
||||
|
||||
nums1 取 i 个数的左半边
|
||||
nums2 取 j = (m+n+1)/2 - i 的左半边
|
||||
```
|
||||
只要保证左右两边 <b>个数</b> 相同,中位数就在 `|` 这个边界旁边产生,从而可以利用二分法找到合适的`i`。
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 160 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 99.18% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 26.8 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.05% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public double FindMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
|
||||
int m = nums1.Length;
|
||||
int n = nums2.Length;
|
||||
if (m > n)
|
||||
return FindMedianSortedArrays(nums2, nums1);
|
||||
|
||||
int k = (m + n + 1)/2;
|
||||
int left = 0;
|
||||
int right = m;
|
||||
while (left < right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = (left + right)/2;
|
||||
int j = k - i;
|
||||
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j - 1])
|
||||
left = i + 1;
|
||||
else
|
||||
right = i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int m1 = left;
|
||||
int m2 = k - left;
|
||||
int c1 = Math.Max(m1 == 0 ? int.MinValue : nums1[m1 - 1],
|
||||
m2 == 0 ? int.MinValue : nums2[m2 - 1]);
|
||||
|
||||
if ((m + n)%2 == 1)
|
||||
return c1;
|
||||
|
||||
int c2 = Math.Min(m1 == m ? int.MaxValue : nums1[m1],
|
||||
m2 == n ? int.MaxValue : nums2[m2]);
|
||||
return (c1 + c2)*0.5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目10:缺失的第一个正数
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:41
|
||||
> - 难度:困难
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-missing-positive/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个未排序的整数数组,找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例1</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [1,2,0]
|
||||
输出: 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例2</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [3,4,-1,1]
|
||||
输出: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [7,8,9,11,12]
|
||||
输出: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例4</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [1,1]
|
||||
输出: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>实例5</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: []
|
||||
输出: 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你的算法的时间复杂度应为O(n),并且只能使用常数级别的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
思路:把数组进行一次“排序”,“排序”的规则是:如果这个数字`i`落在“区间范围里”,`i`就应该放在索引为`i - 1`的位置上。
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:100 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 93.75% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:24.2 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.44% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int FirstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
|
||||
int len = nums.Length;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
while (nums[i] != i + 1 && nums[i] <= len && nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1])
|
||||
{
|
||||
int temp = nums[i];
|
||||
nums[i] = nums[temp - 1];
|
||||
nums[temp - 1] = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (nums[i] != i + 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return i + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return len + 1; //nums.Length = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# 12 数组与稀疏矩阵
|
||||
# 05 数组与稀疏矩阵
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# 13 字符串与整数集合
|
||||
# 06 字符串与整数集合
|
||||
|
||||
**知识点:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,759 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# Leetcode同步练习(二)
|
||||
|
||||
## 题目01:回文数
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:9
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-number/
|
||||
|
||||
判断一个整数是否是回文数。回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 121
|
||||
输出: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: -121
|
||||
输出: false
|
||||
解释: 从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不是一个回文数。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 10
|
||||
输出: false
|
||||
解释: 从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**填写代码**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public bool IsPalindrome(int x)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>进阶</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你能不将整数转为字符串来解决这个问题吗?
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 76 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 98.90% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 14.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 85.12% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public bool IsPalindrome(int x) {
|
||||
if (x < 0)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
int bit = 1;
|
||||
while (x / bit >= 10)
|
||||
{
|
||||
bit = bit * 10;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (x > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int left = x % 10;
|
||||
int right = x / bit;
|
||||
if (left != right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = (x % bit) / 10;
|
||||
bit = bit / 100;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目02:x 的平方根
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:69
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sqrtx/
|
||||
|
||||
实现 `int sqrt(int x)` 函数。
|
||||
|
||||
计算并返回`x`的平方根,其中`x`是非负整数。
|
||||
|
||||
由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数的部分,小数部分将被舍去。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 4
|
||||
输出: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 8
|
||||
输出: 2
|
||||
说明: 8 的平方根是 2.82842..., 由于返回类型是整数,小数部分将被舍去。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:利用牛顿迭代法。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 48 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 13.7 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.40% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int MySqrt(int x) {
|
||||
if (x < 0)
|
||||
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
|
||||
|
||||
double error = 1.0e-5;
|
||||
double cur = x;
|
||||
while (Math.Abs(cur*cur - x) > error)
|
||||
{
|
||||
cur = (cur + 1.0*x/cur)/2.0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (int)cur;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目03:爬楼梯
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:70
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/
|
||||
|
||||
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
|
||||
|
||||
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
|
||||
|
||||
<b>注意</b>:给定 n 是一个正整数。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 2
|
||||
输出: 2
|
||||
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
|
||||
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
|
||||
2. 2 阶
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 3
|
||||
输出: 3
|
||||
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
|
||||
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
|
||||
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
|
||||
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 44
|
||||
输出: 1134903170
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:利用循环
|
||||
|
||||
分析这个题目:
|
||||
- 1 阶,f(1) = 1 种方案
|
||||
- 2 阶,f(2) = 2 种方案
|
||||
- 3 阶,f(3) = 3 种方案
|
||||
- 4 阶,f(4) = 5 种方案
|
||||
- ……
|
||||
- n 阶,f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) 种方案
|
||||
|
||||
即,该问题可以转换为斐波那契数列问题。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 52 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.87% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 13.7 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.98% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int ClimbStairs(int n) {
|
||||
if (n <= 2)
|
||||
return n;
|
||||
|
||||
int first = 1;
|
||||
int second = 2;
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
result = first + second;
|
||||
first = second;
|
||||
second = result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目04:买卖股票的最佳时机
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:121
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你最多只允许完成一笔交易(即买入和卖出一支股票),设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
|
||||
|
||||
注意你不能在买入股票前卖出股票。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
|
||||
输出: 5
|
||||
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
|
||||
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
|
||||
输出: 0
|
||||
解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:如果今天把股票卖掉能够赚最多钱的最大值,即为最大利润。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 132 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.33% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.62% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int MaxProfit(int[] prices)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (prices.Length <= 1)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int min = prices[0];
|
||||
int max = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < prices.Length; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int earn = prices[i] - min;
|
||||
if (earn > max)
|
||||
{
|
||||
max = earn;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (prices[i] < min)
|
||||
{
|
||||
min = prices[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return max;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目05:买卖股票的最佳时机 II
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:122
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
|
||||
|
||||
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>注意</b>:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
|
||||
输出: 7
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 3 天(股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。
|
||||
随后,在第 4 天(股票价格 = 3)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-3 = 3 。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [1,2,3,4,5]
|
||||
输出: 4
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5-1 = 4 。
|
||||
注意你不能在第 1 天和第 2 天接连购买股票,之后再将它们卖出。
|
||||
因为这样属于同时参与了多笔交易,你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
|
||||
输出: 0
|
||||
解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:贪心算法
|
||||
|
||||
贪心策略:只要后一天价格比前一天高,就在前一天买进后一天卖出。
|
||||
|
||||
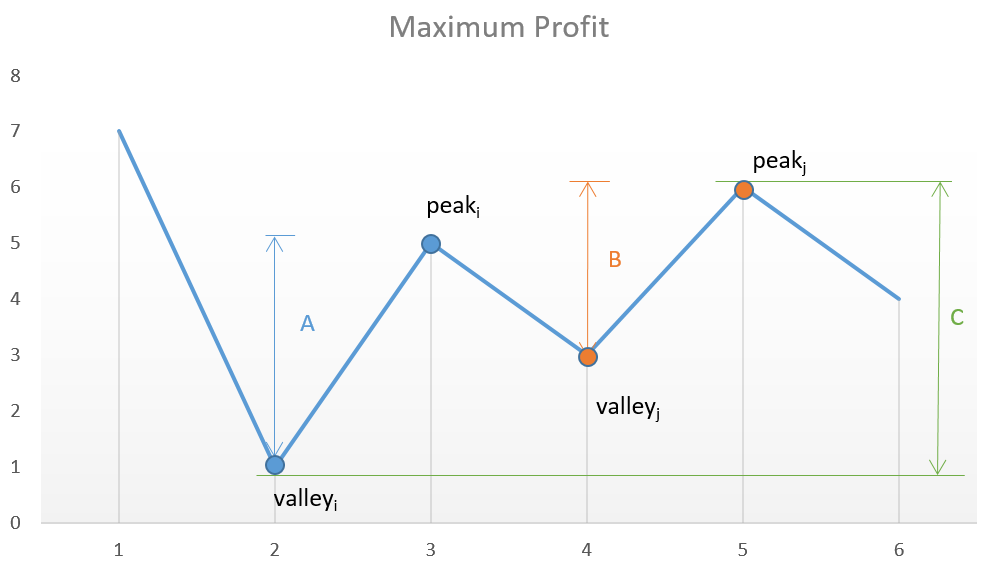
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
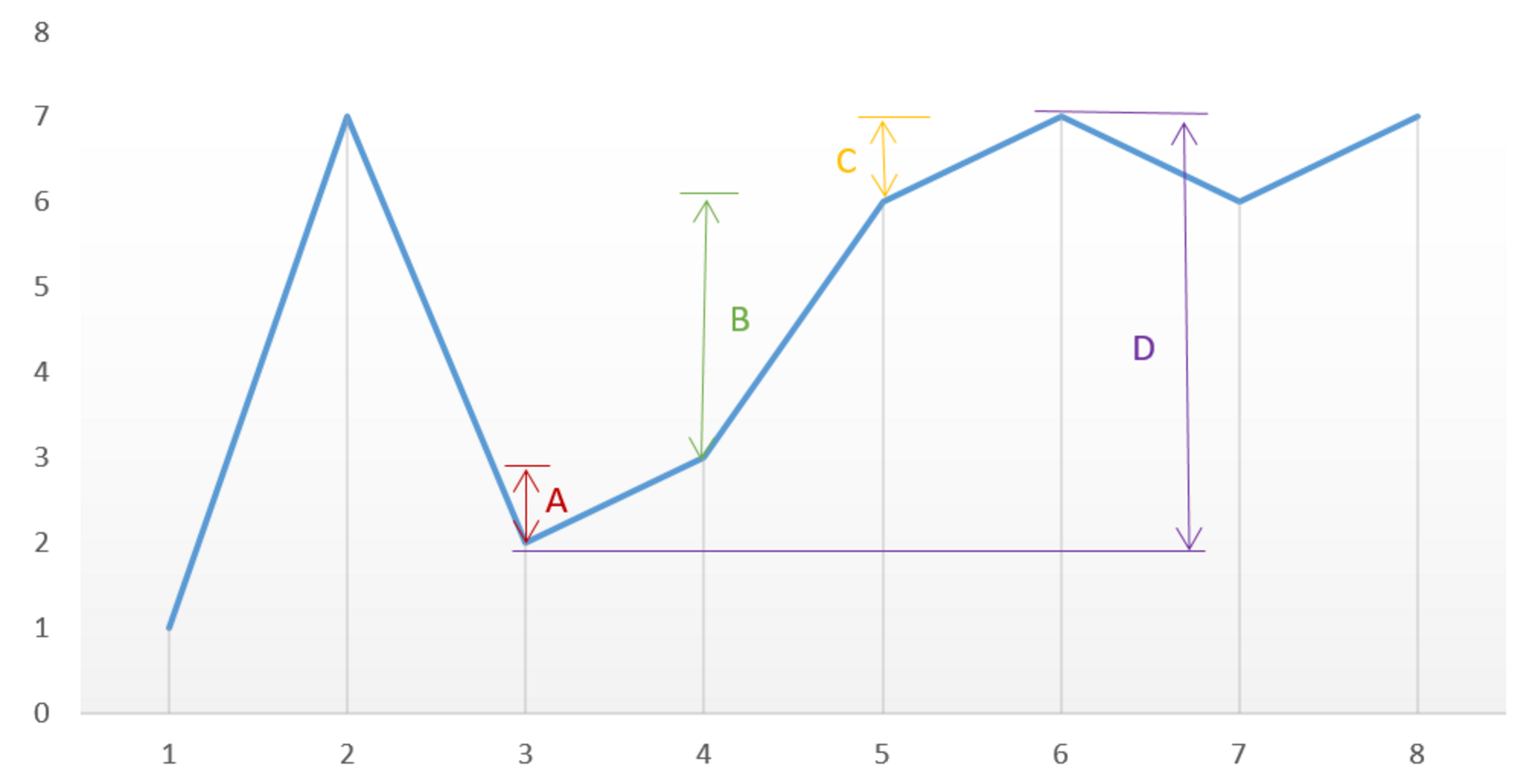
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 140 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 72.02% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24.2 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.36% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int MaxProfit(int[] prices)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int earn = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < prices.Length-1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
earn += Math.Max(prices[i + 1] - prices[i], 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return earn;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目06:跳跃游戏
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:55
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
|
||||
|
||||
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
|
||||
|
||||
判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
|
||||
输出: true
|
||||
解释: 我们可以先跳 1 步,从位置 0 到达 位置 1, 然后再从位置 1 跳 3
|
||||
步到达最后一个位置。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: [3,2,1,0,4]
|
||||
输出: false
|
||||
解释: 无论怎样,你总会到达索引为 3 的位置。但该位置的最大跳跃长度是 0,
|
||||
所以你永远不可能到达最后一个位置。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 3:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:[0]
|
||||
输出:true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路:贪心算法**
|
||||
|
||||
贪心策略:每次记录能跳到点的最大值,如果当前点超出最大值,返回false,如果最大值达到最后一个位置,返回true。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:120 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 57.32% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:26.2 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 6.67% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public bool CanJump(int[] nums)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int maxlength = 0; //记录所能到达的最远点
|
||||
for (int i = 0; maxlength < nums.Length-1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (i > maxlength)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return false;//若此点已不能到达,返回false
|
||||
}
|
||||
maxlength = Math.Max(i + nums[i], maxlength);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目07:三数之和
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:15
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个包含`n`个整数的数组`nums`,判断`nums`中是否存在三个元素`a,b,c`,使得`a + b + c = 0`?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
|
||||
|
||||
满足要求的三元组集合为:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[-1, 0, 1],
|
||||
[-1, -1, 2]
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**思路:利用 排序 + 三索引 的方法。**
|
||||
|
||||
为了避免三次循环,提升执行效率。首先,对`nums`进行排序。然后,固定3个索引`i,l(left),r(right)`,`i`进行最外层循环,`l`指向`nums[i]`之后数组的最小值,`r`指向`nums[i]`之后数组的最大值。模仿快速排序的思路,如果`nums[i] > 0`就不需要继续计算了,否则计算`nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]`是否等于零并进行相应的处理。如果大于零,向`l`方向移动`r`指针,如果小于零,向`r`方向移动`l`索引,如果等于零,则加入到存储最后结果的result链表中。当然,题目中要求这个三元组不可重复,所以在进行的过程中加入去重就好。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:348 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 99.54% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:35.8 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 6.63% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public IList<IList<int>> ThreeSum(int[] nums)
|
||||
{
|
||||
IList<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>();
|
||||
|
||||
nums = nums.OrderBy(a => a).ToArray();
|
||||
int len = nums.Length;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < len - 2; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (nums[i] > 0)
|
||||
break; // 如果最小的数字大于0, 后面的操作已经没有意义
|
||||
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i])
|
||||
continue; // 跳过三元组中第一个元素的重复数据
|
||||
|
||||
int l = i + 1;
|
||||
int r = len - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (l < r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r];
|
||||
if (sum < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
l++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (sum > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
r--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
result.Add(new List<int>() {nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]});
|
||||
// 跳过三元组中第二个元素的重复数据
|
||||
while (l < r && nums[l] == nums[l + 1])
|
||||
{
|
||||
l++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 跳过三元组中第三个元素的重复数据
|
||||
while (l < r && nums[r - 1] == nums[r])
|
||||
{
|
||||
r--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
l++;
|
||||
r--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目08:最接近的三数之和
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:16
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum-closest/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个包括`n`个整数的数组`nums`和一个目标值`target`。找出`nums`中的三个整数,使得它们的和与`target`最接近。返回这三个数的和。假定每组输入只存在唯一答案。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b> :
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
例如,给定数组 nums = [-1,2,1,-4], 和 target = 1.
|
||||
与 target 最接近的三个数的和为 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<b>思路:利用 排序 + 三索引 的方法</b>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 132 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.55% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int ThreeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target)
|
||||
{
|
||||
nums = nums.OrderBy(a => a).ToArray();
|
||||
int result = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length - 2; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int start = i + 1, end = nums.Length - 1;
|
||||
while (start < end)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int sum = nums[start] + nums[end] + nums[i];
|
||||
if (Math.Abs(target - sum) < Math.Abs(target - result))
|
||||
result = sum;
|
||||
if (sum > target)
|
||||
end--;
|
||||
else if (sum < target)
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目09:螺旋矩阵 II
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:59
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n^2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 3
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
|
||||
[ 8, 9, 4 ],
|
||||
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 296 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.67% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 25 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 11.11% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int[][] GenerateMatrix(int n)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int[][] matrix = new int[n][];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[i] = new int[n];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int start = 0;//起始位置
|
||||
int end1 = n - 1;//最左边位置
|
||||
int end2 = n - 1;//最下边位置
|
||||
int count = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (start < end1 && start < end2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
LeftToRight(start, end1, start, matrix, ref count);
|
||||
TopToBottom(start + 1, end2, end1, matrix, ref count);
|
||||
RightToLeft(end1 - 1, start, end2, matrix, ref count);
|
||||
BottomToTop(end2 - 1, start + 1, start, matrix, ref count);
|
||||
start++;
|
||||
end1 = n - 1 - start;
|
||||
end2 = n - 1 - start;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (n%2 == 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[start][start] = count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return matrix;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private void LeftToRight(int start, int end, int rowIndex, int[][] matrix, ref int from)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[rowIndex][i] = from;
|
||||
from++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private void TopToBottom(int start, int end, int colIndex, int[][] matrix, ref int from)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[i][colIndex] = from;
|
||||
from++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private void RightToLeft(int start, int end, int rowIndex, int[][] matrix, ref int from)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = start; i >= end; i--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[rowIndex][i] = from;
|
||||
from++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private void BottomToTop(int start, int end, int colIndex, int[][] matrix, ref int from)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = start; i >= end; i--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
matrix[i][colIndex] = from;
|
||||
from++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 题目10:不同路径
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:62
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/
|
||||
|
||||
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
|
||||
|
||||
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
|
||||
|
||||
问总共有多少条不同的路径?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
例如,上图是一个7 x 3 的网格。有多少可能的路径?
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:m 和 n 的值均不超过 100。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: m = 3, n = 2
|
||||
输出: 3
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
从左上角开始,总共有 3 条路径可以到达右下角。
|
||||
1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下
|
||||
2. 向右 -> 向下 -> 向右
|
||||
3. 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: m = 7, n = 3
|
||||
输出: 28
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: m = 23, n = 12
|
||||
输出: 193536720
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>思路:</b>利用动态规划。
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划表格01:
|
||||
|
||||
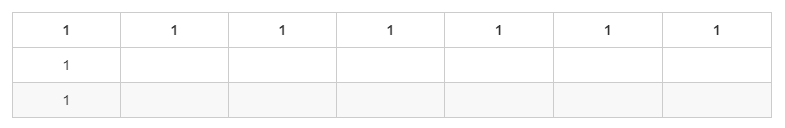
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划表格02:
|
||||
|
||||
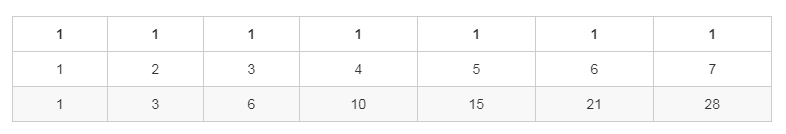
|
||||
|
||||
动态规划的最优子结构为:`d[i,j] = d[i-1,j] + d[i,j-1]`
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 62 / 62 个通过测试用例
|
||||
- 执行用时: 52 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 93.18% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 13.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 17.65% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public int UniquePaths(int m, int n)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int[,] memo = new int[m, n];
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (i == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
memo[i, j] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (j == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
memo[i, j] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
memo[i, j] = memo[i - 1, j] + memo[i, j - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return memo[m - 1, n - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# 15 树
|
||||
# 07 树
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,794 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# Leetcode同步练习(三)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 题目01:合并两个有序链表
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:21
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
|
||||
|
||||
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
|
||||
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:108 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 83.80% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:25.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.85% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode pHead = new ListNode(int.MaxValue);
|
||||
ListNode temp = pHead;
|
||||
|
||||
while (l1 != null && l2 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (l1.val < l2.val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp.next = l1;
|
||||
l1 = l1.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp.next = l2;
|
||||
l2 = l2.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
temp = temp.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (l1 != null)
|
||||
temp.next = l1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (l2 != null)
|
||||
temp.next = l2;
|
||||
|
||||
return pHead.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目02:删除排序链表中的重复元素
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:83
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 1->1->2
|
||||
输出: 1->2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
|
||||
输出: 1->2->3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:利用双指针的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
`p1`作为前面的指针探路,`p2`作为后面的指针跟进,如果遇到重复元素,`p2.next`跳过去,`p1`跑完整个链表所有重复元素都被摘下来。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:160 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.23% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:25.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.72% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode DeleteDuplicates(ListNode head)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (head == null)
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode p1 = head.next;
|
||||
ListNode p2 = head;
|
||||
while (p1 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (p1.val == p2.val)
|
||||
p2.next = p1.next;
|
||||
else
|
||||
p2 = p2.next;
|
||||
p1 = p1.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目03:环形链表
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:141
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
|
||||
|
||||
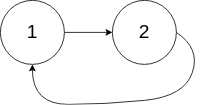
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数`pos` 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果`pos`是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
|
||||
输出:true
|
||||
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
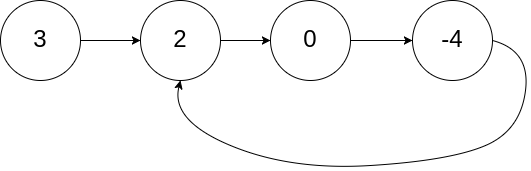
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
|
||||
输出:true
|
||||
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 3</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
|
||||
输出:false
|
||||
解释:链表中没有环。
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<b>进阶</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:利用双指针的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
通常情况下,判断是否包含了重复的元素,我们使用`Hash`的方式来做。对于单链表的这种场景,我们也可以使用双指针的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
第一个指针 `p1` 每次移动两个节点,第二个指针 `p2` 每次移动一个节点,如果该链表存在环的话,第一个指针一定会再次碰到第二个指针,反之,则不存在环。
|
||||
|
||||
比如:`head = [1,2,3,4,5]`,奇数
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
p1:1 3 5 2 4 1
|
||||
p2:1 2 3 4 5 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
比如:`head = [1,2,3,4]`,偶数
|
||||
```c
|
||||
p1:1 3 1 3 1
|
||||
p2:1 2 3 4 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 112 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 98.43% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24.9 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.13% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) {
|
||||
* val = x;
|
||||
* next = null;
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public bool HasCycle(ListNode head) {
|
||||
ListNode p1 = head;
|
||||
ListNode p2 = head;
|
||||
|
||||
while (p1 != null && p1.next != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
p1 = p1.next.next;
|
||||
p2 = p2.next;
|
||||
if (p1 == p2)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 题目04:反转链表
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:206
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
|
||||
|
||||
反转一个单链表。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
|
||||
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>进阶</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:利用双指针的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
`p1`作为前面的指针探路,`p2`作为后面的指针跟进,顺着链表跑一圈,搞定问题。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 116 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.50% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 23.3 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.26% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (head == null || head.next == null)
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode p1 = head;
|
||||
ListNode p2 = null;
|
||||
while (p1 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode temp = p1.next;
|
||||
p1.next = p2;
|
||||
p2 = p1;
|
||||
p1 = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目05:删除链表中的节点
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:237
|
||||
> - 难度:简单
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
|
||||
|
||||
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
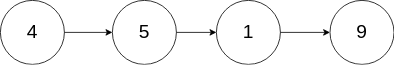
现有一个链表 -- head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
|
||||
输出: [4,1,9]
|
||||
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
|
||||
输出: [4,5,9]
|
||||
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>说明</b>:
|
||||
|
||||
- 链表至少包含两个节点。
|
||||
- 链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。
|
||||
- 给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。
|
||||
- 不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**思路:** 这道题没有给出链表的头节点,而是直接给出要删除的节点,让我们进行原地删除。我们对于该节点的前一个节点一无所知,所以无法直接执行删除操作。因此,我们将要删除节点的 next 节点的值赋值给要删除的节点,转而去删除 next 节点,从而达成目的。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 41 / 41 个通过测试用例
|
||||
- 执行用时: 120 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 99.55% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 24.4 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.88% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public void DeleteNode(ListNode node)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode temp = node.next;
|
||||
while (temp != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
node.val = temp.val;
|
||||
temp = temp.next;
|
||||
if (temp != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
node = node.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
node.next = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目06:两数相加
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:2
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
|
||||
|
||||
给出两个 <b>非空</b> 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 <b>逆序</b> 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 <b>一位</b> 数字。
|
||||
|
||||
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 1</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
|
||||
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
|
||||
原因:342 + 465 = 807
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例 2</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:(3 -> 7) + (9 -> 2)
|
||||
输出:2 -> 0 -> 1
|
||||
原因:73 + 29 = 102
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**思路**:模仿我们小学时代学的加法运算。个位相加超过十进一,十位相加有进位则加上进位,依次类推。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>参考代码:</b>
|
||||
|
||||
- 状态:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时: 144 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 97.98% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗: 26.7 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.07% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode AddTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode result = new ListNode(-1);
|
||||
ListNode l3 = result;
|
||||
int flag = 0;
|
||||
while (l1 != null && l2 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int a = l1.val;
|
||||
int b = l2.val;
|
||||
int c = a + b + flag;
|
||||
l3.next = new ListNode(c%10);
|
||||
|
||||
flag = c >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
l1 = l1.next;
|
||||
l2 = l2.next;
|
||||
l3 = l3.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (l1 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int a = l1.val + flag;
|
||||
|
||||
l3.next = new ListNode(a%10);
|
||||
|
||||
flag = a >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
l1 = l1.next;
|
||||
l3 = l3.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (l2 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int b = l2.val + flag;
|
||||
|
||||
l3.next = new ListNode(b%10);
|
||||
flag = b >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
|
||||
l2 = l2.next;
|
||||
l3 = l3.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (flag == 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
l3.next = new ListNode(flag);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目07:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:19
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第`n`个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例**:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
|
||||
|
||||
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**说明**:
|
||||
|
||||
给定的`n`保证是有效的。
|
||||
|
||||
**进阶**:
|
||||
|
||||
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
|
||||
|
||||
**思路:** 使用两个指针,前面的指针`p1`先走`n`步,接着让后面的指针`p2`与`p1`同步走,`p1`走到终点,`p2`即走到要移除的结点位置。
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码:**
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:104 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 86.93% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:24.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode RemoveNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode p1 = head;
|
||||
ListNode p2 = head;
|
||||
|
||||
while (n > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
p1 = p1.next;
|
||||
n--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (p1 == null) //移除头结点
|
||||
{
|
||||
return head.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
while (p1.next != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
p1 = p1.next;
|
||||
p2 = p2.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p2.next = p2.next.next;
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目08:两两交换链表中的节点
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:24
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
|
||||
|
||||
**你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值**,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例:**
|
||||
|
||||
> 给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:100 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 93.18% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:23.4 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 87.72% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode SwapPairs(ListNode head)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (head == null || head.next == null)
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
|
||||
head = Swap(head);
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode temp = head.next;
|
||||
|
||||
while (temp != null && temp.next != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp.next = Swap(temp.next);
|
||||
if (temp.next != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp = temp.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public ListNode Swap(ListNode node)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (node == null || node.next == null)
|
||||
return node;
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode t = node.next;
|
||||
node.next = t.next;
|
||||
t.next = node;
|
||||
return t;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目09:旋转链表
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:61
|
||||
> - 难度:中等
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
|
||||
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
|
||||
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
|
||||
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
|
||||
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
|
||||
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
|
||||
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
|
||||
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
|
||||
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:100 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 98.13% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:25.1 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode RotateRight(ListNode head, int k)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (head == null || k == 0)
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
|
||||
int len = GetLength(head);
|
||||
int index = len - k%len;
|
||||
|
||||
if (index == len)
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode temp1 = head;
|
||||
ListNode temp2 = head;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp1 = temp1.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
head = temp1.next;
|
||||
temp1.next = null;
|
||||
|
||||
temp1 = head;
|
||||
while (temp1.next != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp1 = temp1.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
temp1.next = temp2;
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public int GetLength(ListNode head)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode temp = head;
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
while (temp != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
temp = temp.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 题目10:合并K个排序链表
|
||||
|
||||
> - 题号:23
|
||||
> - 难度:困难
|
||||
> - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。
|
||||
|
||||
<b>示例</b>:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
输入:
|
||||
[
|
||||
1->4->5,
|
||||
1->3->4,
|
||||
2->6
|
||||
]
|
||||
输出: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<b>思路:</b>两两合并的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
构造合并两个有序链表得到一个新的有序链表的方法:`ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)`。可以使用该方法合并前两个有序链表得到一个新的有序链表,之后把这个新链表与第三个有序链表合并,依次类推,最后得到合并`K`个有序列表的新列表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**参考代码**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 执行结果:通过
|
||||
- 执行用时:256 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 36.69% 的用户
|
||||
- 内存消耗:29.3 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 18.37% 的用户
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
* public class ListNode {
|
||||
* public int val;
|
||||
* public ListNode next;
|
||||
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public class Solution
|
||||
{
|
||||
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ListNode pHead = new ListNode(int.MaxValue);
|
||||
ListNode temp = pHead;
|
||||
|
||||
while (l1 != null && l2 != null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (l1.val < l2.val)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp.next = l1;
|
||||
l1 = l1.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp.next = l2;
|
||||
l2 = l2.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
temp = temp.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (l1 != null)
|
||||
temp.next = l1;
|
||||
|
||||
if (l2 != null)
|
||||
temp.next = l2;
|
||||
|
||||
return pHead.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public ListNode MergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
|
||||
if (lists.Length == 0)
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
|
||||
ListNode result = lists[0];
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < lists.Length; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
result = MergeTwoLists(result, lists[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# 17 ͼ
|
||||
# 08 ͼ
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,679 @@
|
|||
# 09 排序
|
||||
|
||||
**知识结构:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. 排序的基本概念与术语
|
||||
|
||||
假设含有$n$个记录的序列为$\lbrace r_1,r_2,\cdots,r_n \rbrace$,其相应的关键字分别为$\lbrace k_1,k_2,\cdots,k_n \rbrace$,需确定 的一种排列$1,2,\cdots,n$,使其相应的关键字满足$k_{p_1}\leq k_{p_2}\leq\cdots\leq k_{p_n}$的关系,即使得序列成为一个按关键字有序的序列 ,这个样的操作就称为 **排列**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
能唯一标识某一记录的关键字称为 **主关键字**。
|
||||
|
||||
假设$k_i = k_j(1\leq i \leq n, 1\leq j\leq n,i\neq j)$,且在排序前的序列中$r_i$领先于$r_j$(即$i<j$ )。如果排序后$r_i$仍领先于$r_j$,则称所用的排序方法是**稳定的**;反之,若可能使得排序后的序列中$r_j$领先于$r_i$,则称所用的排序方法是**不稳定的**。
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- 待排序序列:$20,30,\overline{20}$
|
||||
- 稳定的排序结果:$20,\overline{20},30$
|
||||
- 不稳定的排序结果:$\overline{20},20,30$
|
||||
|
||||
**内部排序**:排序过程都在内存中进行的排序。
|
||||
|
||||
**外部排序**:排序过程需要在内存和外存之间不断交换数据的排序。
|
||||
|
||||
根据排序过程中借助的主要操作,我们把内排序分为:**插入排序**、**选择排序**、**交换排序**和**并归排序**。可以说,这些都是比较成熟的排序技术,已经被广泛地应用于许许多多的程序语言或数据库当中,甚至它们都已经封装了关于排序算法的实现代码。因此,我们学习这些排序算法的目的不是为了去现实排序算法,而是通过学习来提高我们编写算法的能力,以便于去解决更多复杂和灵活的应用性问题。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 插入排序
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1 直接插入排序
|
||||
|
||||
将一个记录插入到已经排好序的有序表中,从而得到一个新的记录增1的有序表。
|
||||
|
||||
即:先将序列的第1个记录看成是一个有序的子序列,然后从第2个记录逐个进行插入,直至整个序列有序为止。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
排序过程:
|
||||
|
||||
$init0\rightarrow [45],\overline{34},78,12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step1\rightarrow [\overline{34},45],78,12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step2\rightarrow [\overline{34},45,78],12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step3\rightarrow [12,\overline{34},45,78],34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step4\rightarrow [12,\overline{34},34,45,78],32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step5\rightarrow [12,32,\overline{34},34,45,78],29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step6\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34},34,45,78],64$
|
||||
|
||||
$result\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34},34,45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 直接插入排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void StraightInsertSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < array.Length; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int j = i - 1;
|
||||
T current = array[i];
|
||||
|
||||
while (j >= 0 && array[j].CompareTo(current) > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
array[j + 1] = array[j];
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[j + 1] = current;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果碰见一个和插入元素相等的,那么插入元素把想插入的元素放在相等元素的后面,所以,相等元素的前后顺序没有改变,从原无序序列出去的顺序就是排好序后的顺序,所以直接插入排序是稳定的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 希尔插入排序
|
||||
|
||||
希尔排序是1959年由D.L.Shell提出来的,相对直接插入排序有较大的改进。希尔插入排序又叫做**缩小增量排序**。
|
||||
|
||||
直接插入排序的效率在某些时候是很高的,比如我们的记录本身就是基本有序的,我们只需要少量的插入操作,就可以完成整个记录集的排序工作,此时直接插入排序很高效。还有就是记录数比较少时,直接插入的优势也比较明显。可问题在于,两个条件本身就过于苛刻,现实中记录少或者基本有序都属于特殊情况。
|
||||
|
||||
不过别着急,有条件当然是好,条件不存在,我们创造条件也是可以去做的。于是科学家希尔研究出了一种排序方法,对直接插入排序改进后可以增加效率。
|
||||
|
||||
思想:按待排序列下标的一定增量分组(如:增量序列$t_1,t_2,\cdots,t_k$,其中$t_i>t_j$,$t_k=1$),将整个待排序列分割成若干子序列,分别进行直接插入排序,随着增量逐渐减少,所分组包含的记录越来越多,到增量值减至1时,整个记录集被分成一组(这时待排序列“基本有序”),再对全体记录进行直接插入排序,算法终止(对待排序列进行了$k$趟直接插入排序)。
|
||||
|
||||
> 我所理解Shell Insertion Sort最牛的地方是,让排序算法能够并行化。
|
||||
|
||||
希尔插入排序增量的取法:
|
||||
|
||||
$delta1=\left[\frac{n}{2}\right] =\left[\frac{10}{2}\right]=5$
|
||||
|
||||
$delta2=\left[\frac{delta1}{2}\right]=\left[\frac{5}{2}\right]=2$
|
||||
|
||||
$delta3=\left[\frac{delta2}{2}\right]=\left[\frac{2}{2}\right]=1$
|
||||
|
||||
即:先将要排序的一组记录按某个增量$delta$($\left[\frac{n}{2}\right]$ ,$n$为要排序数的个数)分成若干组子序列,每组中记录的下标相差$delta$。对每组中全部元素进行直接插入排序,然后在用一个较小的增量($\left[\frac{delta}{2}\right]$ )对它进行分组,在每组中再进行直接插入排序。继续不断缩小增量直至为1,最后使用直接插入排序完成排序。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
排序过程:
|
||||
|
||||
$d=4\rightarrow 45,\overline{34},78,12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$d=2\rightarrow 34,32,29,12,45,\overline{34},78,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$d=1\rightarrow 29,12,34,32,45,\overline{34},78,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$result\rightarrow 12,29,32,34,\overline{34},45,64,78$
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
private static void Shell<T>(int delta, T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
//带增量的直接插入排序
|
||||
for (int i = delta; i < array.Length; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int j = i - delta;
|
||||
T current = array[i];
|
||||
while (j >= 0 && array[j].CompareTo(current) > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
array[j + delta] = array[j];
|
||||
j = j - delta;
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[j + delta] = current;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 希尔插入排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void ShellInsertSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int delta = array.Length/2; delta > 0; delta = delta/2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Shell(delta, array);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
希尔插入排序时效分析很难,关键码的比较次数与记录移动次数依赖于增量因子序列$delta$的选取。目前还没有人给出选取最好的增量因子序列的方法。希尔插入排序方法是一个不稳定的排序方法。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 选择排序
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 直接选择排序
|
||||
|
||||
思想:每一趟在$n-i(i=0,1,\cdots,n-1)$个记录中选取关键字最小的记录作为有序序列中第$i$个记录。(在要排列的一组数中,选出最小的一个数与第1个位置的数交换;然后在剩下的数当中再找最小的与第2个位置的数交换,依次类推,直到第$n-1$个元素和第$n$个元素比较为止。)
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
排序过程:
|
||||
|
||||
$i=0\rightarrow 12,\overline{34},78,45,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=1\rightarrow 12,29,78,45,34,32,\overline{34},64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=2\rightarrow 12,29,32,45,34,78,\overline{34},64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=3\rightarrow 12,29,32,34,45,78,\overline{34},64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=4\rightarrow 12,29,32,34,\overline{34},78,45,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=5\rightarrow 12,29,32,34,\overline{34},45,78,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=6\rightarrow 12,29,32,34,\overline{34},45,64,78$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 直接选择排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void StraightSelectSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int minIndex = i;
|
||||
T min = array[i];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int j = i + 1; j < array.Length; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (array[j].CompareTo(min) < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
min = array[j];
|
||||
minIndex = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (minIndex != i)
|
||||
{
|
||||
array[minIndex] = array[i];
|
||||
array[i] = min;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
直接选择排序是不稳定的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 堆选择排序
|
||||
|
||||
直接选择排序并没有把每一趟的比较结果保存下来,在后一趟的比较中,许多比较在前一趟已经做过了,但由于前一趟排序时未保存这些比较结果,所以后一趟排序时又重复执行了这些比较操作,因而执行的比较次数较多。
|
||||
|
||||
如果可以做到每次在选择到最小记录的同时,并根据比较结果对其他记录做出相应的调整,那样排序的总体效率就会非常高了。而堆选择排序是一种树形选择排序,是对直接选择排序的有效改进。堆选择排序算法是Floyd和Williams在1964年共同发明的,同时,他们也发明了“堆”这样的数据结构。
|
||||
|
||||
堆的概念:具有$n$个元素的序列$K=\lbrace k_1,k_2,⋯,k_n \rbrace$当且仅当满足
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\begin{cases}
|
||||
k_i\leq k_{2i}\\
|
||||
k_i\leq k_{2i+1}
|
||||
\end{cases},
|
||||
\begin{cases}
|
||||
k_i\geq k_{2i}\\
|
||||
k_i\geq k_{2i+1}
|
||||
\end{cases},
|
||||
i=1,2,\cdots,\left[\frac{n}{2}\right]
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
时称之为堆。
|
||||
|
||||
若关键码的集合$K=\lbrace k_1,k_2,⋯,k_n \rbrace$,把它们按照完全二叉树的顺序存放在一维数组中。
|
||||
- 若满足$k_i\leq k_{2i}$且$k_i\leq k_{2i+1}$则称作小根堆。
|
||||
- 若满足$k_i\geq k_{2i}$且$k_i \geq k_{2i+1}$则称作大根堆。
|
||||
|
||||
小根堆:`int[] Key = new int[]{9,17,65,23,45,78,87,53,31,58,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
大根堆:`int[] Key = new int[]{94,93,75,91,85,44,51,18,48,58,10,34};`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
思想(以大根堆为例):
|
||||
构建大根堆之后,输出堆顶记录,对剩余的$n-1$个记录接着构建大根堆,便可得到$n$个记录的次大值,如此反复执行,就能得到一个有序序列,这个过程称为堆选择排序。
|
||||
|
||||
堆选择排序需解决的两个问题:
|
||||
|
||||
问题1:如何建堆,对初始序列建堆的过程,就是一个反复进行筛选的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
- (1)对一棵具有$n$个结点的完全二叉树来说最后一个结点是第$[\frac{n}{2}]$个结点的子树。
|
||||
- (2)筛选从第$[\frac{n}{2}]$个结点为根的子树开始,该子树成为堆。
|
||||
- (3)之后向前依次对各结点为根的子树进行筛选,使之成为堆,直到根结点。
|
||||
|
||||
即把序号为$[\frac{n}{2}],[\frac{n}{2}]-1,\cdots,1$,的记录作为根的子树都调整为堆。
|
||||
|
||||
问题2:输出堆顶元素后,如何调整新堆。
|
||||
|
||||
- (1)设有$n$个元素的堆,输出堆顶元素后,剩下$n-1$个元素。将堆底元素送入堆顶(最后一个元素与堆顶进行交换),堆被破坏,其原因仅是根结点不满足堆的性质。
|
||||
- (2)将根结点与左,右子树中较大元素进行交换。
|
||||
- (3)若与左子树交换:如果左子树堆被破坏,即左子树的根结点不满足堆的性质,则重复第二步。
|
||||
- (4)若与右子树交换:如果右子树堆被破坏,即右子树的根结点不满足堆的性质,则重复第二步。
|
||||
- (5)继续对不满足堆性质的子树进行上述操作,直到叶子结点,堆被重建成。
|
||||
|
||||
即:输出堆顶元素,将最后一个叶子结点放在堆顶,重新构建大根堆。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
排序过程:
|
||||
|
||||
初始时:$Key1 \rightarrow -1,45,\overline{34},78,12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
建堆后:$Key1 \rightarrow -1,78,64,45,\overline{34},34,32,29,12$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
堆重建后:
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,64,\overline{34},45,12,34,32,29,[78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,45,\overline{34},32,12,34,29,[64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,\overline{34},34,32,12,29,[45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,34,29,32,12,[\overline{34},45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,32,29,12,[34,\overline{34},45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,29,12,[32,34,\overline{34},45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
$Key1 \rightarrow -1,12,[29,32,34,\overline{34},45,64,78]$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
private static void Restore<T>(T[] array, int j, int vCount) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
//构建以结点j为根,一共有vCount个结点的大根堆
|
||||
while (j <= vCount / 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int m = (2 * j + 1 <= vCount && array[2 * j + 1].CompareTo(array[2 * j]) > 0)
|
||||
? 2 * j + 1
|
||||
: 2 * j;
|
||||
if (array[m].CompareTo(array[j]) > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T temp = array[m];
|
||||
array[m] = array[j];
|
||||
array[j] = temp;
|
||||
j = m;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 堆选择排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void HeapSelectSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
int vCount = array.Length;
|
||||
T[] tempArray = new T[vCount + 1];
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < vCount; i++)
|
||||
tempArray[i + 1] = array[i];
|
||||
|
||||
//初建大根堆
|
||||
for (int i = vCount / 2; i >= 1; i--)
|
||||
Restore(tempArray, i, vCount);
|
||||
|
||||
//大根堆的重构与排序
|
||||
for (int i = vCount; i > 1; i--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T temp = tempArray[i];
|
||||
tempArray[i] = tempArray[1];
|
||||
tempArray[1] = temp;
|
||||
Restore(tempArray, 1, i - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < vCount; i++)
|
||||
array[i] = tempArray[i + 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. 交换排序
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1 冒泡交换排序
|
||||
|
||||
思想:通过相邻记录之间的比较和交换,使关键字较小的记录如气泡一般逐渐向上漂移直至水面。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
$i=0\rightarrow [12],45,\overline{34},78,29,34,32,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=1\rightarrow [12,29],45,\overline{34},78,32,34,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=2\rightarrow [12,29,32],45,\overline{34},78,34,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=3\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34}],45,34,78,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=4\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34},34],45,64,78$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=5\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34},34,45],64,78$
|
||||
|
||||
$i=6\rightarrow [12,29,32,\overline{34},34,45,64],78$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 冒泡交换排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void BubbleExchangeSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int j = array.Length - 1; j > i; j--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (array[j].CompareTo(array[j - 1]) < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T temp = array[j - 1];
|
||||
array[j - 1] = array[j];
|
||||
array[j] = temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对冒泡排序常见的改进方法是加入一个标志性变量`flag`,用于标志某一趟排序过程是否有数据交换,如果进行某一趟排序时并没有进行数据交换,则说明数据已经按要求排列好,可立即结束排序,避免不必要的比较过程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 改进的冒泡交换排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void BubbleExchangeSortImproved<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length - 1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
bool flag = false;
|
||||
for (int j = array.Length - 1; j > i; j--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (array[j].CompareTo(array[j - 1]) < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T temp = array[j - 1];
|
||||
array[j - 1] = array[j];
|
||||
array[j] = temp;
|
||||
flag = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (flag == false)
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2 快速交换排序
|
||||
|
||||
快速交换排序是由图灵奖获得者Tony Hoare(东尼.霍尔)所发展的一种排序算法,是采用分治策略的一个非常典型的应用。快速交换排序虽然高端,但其思想是来自冒泡交换排序的,冒泡交换排序是通过相邻元素的比较和交换把最小的冒泡到最顶端,而快速交换排序是比较和交换小数和大数,这样一来不仅小数冒泡到上面的同时也把大数沉到下面。
|
||||
|
||||
其基本思想如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- (1)选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素。
|
||||
- (2)通过一趟排序将待排序的记录分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的元素值均比基准元素值小,另一部分记录的元素值比基准值大。
|
||||
- (3)此时基准元素在其排好序的正确位置。
|
||||
- (4)然后分别对这两部分记录用同样的方法继续进行排序,直到整个序列有序。
|
||||
|
||||
即:从待排记录中选一记录,将其放入正确的位置,然后以该位置为界,对左右两部分再做快速排序,直到划分的长度为1。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$init\rightarrow 45,\overline{34},78,12,34,32,29,64$
|
||||
|
||||
$step1\rightarrow [32,\overline{34},29,12,34],45,[78,64]$
|
||||
|
||||
$step2\rightarrow [[29,12],32,[\overline{34},34]],45,[78,64]$
|
||||
|
||||
$step3\rightarrow [[[12],29],32,[\overline{34},34]],45,[78,64]$
|
||||
|
||||
$step4\rightarrow [[[12],29],32,[[34],\overline{34}]],45,[78,64]$
|
||||
|
||||
$step5\rightarrow [[[12],29],32,[[34],\overline{34}]],45,[[64],78]$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
private static void QuickSort<T>(T[] array, int left, int right) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
//快速排序递归函数
|
||||
if (left < right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T current = array[left];
|
||||
int i = left;
|
||||
int j = right;
|
||||
while (i < j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
while (array[j].CompareTo(current) > 0 && i < j)
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
while (array[i].CompareTo(current) <= 0 && i < j)
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
if (i < j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T temp = array[i];
|
||||
array[i] = array[j];
|
||||
array[j] = temp;
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[left] = array[j];
|
||||
array[j] = current;
|
||||
if (left < j - 1) QuickSort(array, left, j - 1);
|
||||
if (right > j + 1) QuickSort(array, j + 1, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 快速交换排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void QuickExchangeSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
QuickSort(array, 0, array.Length - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其实上面的代码还可以再优化,上面代码中基准元素已经在`current`中保存了,所以不需要每次交换都设置一个`temp`变量,在交换的时候只需要先后覆盖就可以了。这样既能较少空间的使用还能降低赋值运算的次数。
|
||||
|
||||
优化代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
private static void QuickSortImproved<T>(T[] array, int left, int right) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
//快速排序递归函数
|
||||
if (left < right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
T current = array[left];
|
||||
int i = left;
|
||||
int j = right;
|
||||
while (i < j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
while (array[j].CompareTo(current) > 0 && i < j)
|
||||
j--;
|
||||
array[i] = array[j];
|
||||
|
||||
while (array[i].CompareTo(current) <= 0 && i < j)
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
array[j] = array[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[j] = current;
|
||||
if (left < j - 1) QuickSortImproved(array, left, j - 1);
|
||||
if (right > j + 1) QuickSortImproved(array, j + 1, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 快速交换排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void QuickExchangeSortImproved<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
QuickSortImproved(array, 0, array.Length - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 5. 并归排序
|
||||
|
||||
我们首先先看两个有序序列合并的例子,如:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int[] Key1 = new int[]{1,3,5,7,9};
|
||||
int[] Key2 = new int[]{2,4,6,8,10,12,14}
|
||||
|
||||
int[] temp = new int[Key1.Length + Key2.Length];
|
||||
```
|
||||
$temp \rightarrow 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0$
|
||||
|
||||
$temp \rightarrow 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0,0,0$
|
||||
|
||||
$temp \rightarrow 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,14$
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 合并排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array1">有序记录集合1</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="array2">有序记录集合2</param>
|
||||
/// <returns>合并后的有序记录集合</returns>
|
||||
public static T[] MergeSort<T>(T[] array1,T[] array2) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
T[] temp = new T[array1.Length + array2.Length];
|
||||
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
|
||||
while (i < array1.Length && j < array2.Length)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (array1[i].CompareTo(array2[i]) < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array1[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array2[j++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (i < array1.Length)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array1[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (j < array2.Length)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array2[j++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return temp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们接着看一个序列的并归排序。
|
||||
|
||||
首先递归划分子问题,然后合并结果。把待排序列看成由两个有序的子序列构成,然后合并两个子序列,接着把子序列看成由两个有序序列组成……。倒过来看,其实就是先两两合并,然后四四合并……最终形成有序序列。该算法是采用分治策略的一个非常典型的应用,俗称 **2-路并归**。
|
||||
|
||||
如:`int[] Key = new int[]{45,34,78,12,34,32,29,64};`
|
||||
|
||||
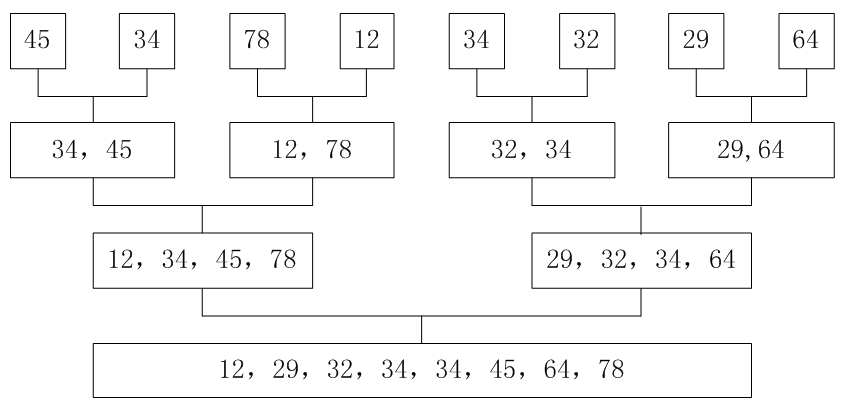
|
||||
|
||||
程序代码:
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 合并排序的递归合并函数
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="left">起点位置</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="mid">中间位置</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="right">终点位置</param>
|
||||
private static void Merge<T>(T[] array, int left, int mid, int right) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
T[] temp = new T[right - left + 1];
|
||||
int i = left;
|
||||
int j = mid + 1;
|
||||
int k = 0;
|
||||
while (i <= mid && j <= right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (array[i].CompareTo(array[j]) < 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array[j++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (i <= mid)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array[i++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (j <= right)
|
||||
{
|
||||
temp[k++] = array[j++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int n = 0; n < temp.Length; n++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
array[left + n] = temp[n];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 合并排序的递归分治函数
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="left">起点位置</param>
|
||||
/// <param name="right">终点位置</param>
|
||||
private static void MergeSort<T>(T[] array, int left, int right) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (left >= right)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
|
||||
MergeSort(array, left, mid); //递归排序左边
|
||||
MergeSort(array, mid + 1, right); //递归排序右边
|
||||
Merge(array, left, mid, right); //合并
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/// <summary>
|
||||
/// 合并排序
|
||||
/// </summary>
|
||||
/// <typeparam name="T">需要排序记录的类型</typeparam>
|
||||
/// <param name="array">需要排序的记录集合</param>
|
||||
public static void MergeSort<T>(T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
|
||||
{
|
||||
MergeSort(array, 0, array.Length - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,398 @@
|
|||
# 精选练习50
|
||||
|
||||
**01、数据在计算机中的表示称为数据的______。**
|
||||
- (A)存储结构
|
||||
- (B)抽象结构
|
||||
- (C)顺序结构
|
||||
- (D)逻辑结构
|
||||
|
||||
**02、哪一个不是算法的特性______。**
|
||||
- (A)有穷性
|
||||
- (B)确定性
|
||||
- (C)必须有输入
|
||||
- (D)必须有输出
|
||||
|
||||
**03、以下对于链式存储结构的叙述中错误的是______。**
|
||||
- (A)逻辑上相邻的结点,物理上不必相邻
|
||||
- (B)可以通过计算,直接确定第i个结点的存储地址
|
||||
- (C)插入、删除运算操作方便,不必大量移动结点
|
||||
- (D)结点包括指针域,存储密度小于顺序存储结构
|
||||
|
||||
**04、下面对于线性表的叙述中,不正确的是______。**
|
||||
- (A)线性表采用顺序存储时,必须占用一片连续的存储单元
|
||||
- (B)线性表采用链式存储时,不需要占用一片连续的存储单元
|
||||
- (C)线性表采用顺序存储时,便于进行插入和删除操作
|
||||
- (D)线性表采用链式存储时,便于进行插入和删除操作
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**05、在一个单链表中,若P所指结点不是最后结点,在P之后插入S所指结点,则执行______。**
|
||||
- (A)S.Next=P; P.Next=S;
|
||||
- (B)S.Next=P.Next; P.Next=S;
|
||||
- (C)S.Next=P.Next; P =S;
|
||||
- (D)P.Next=S; S.Next=P;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**06、在双向链表中,删除P所指的结点,则执行______。**
|
||||
- (A)P.Next.Prior=P.Prior; P.Prior.Next=P.Next;
|
||||
- (B)P.Next.Prior=P.Prior; P.Prior=P.Next;
|
||||
- (C)P.Prior.Next=P; P.Prior =P.Prior.Prior;
|
||||
- (D)P.Prior=P.Next.Next; P.Next=P.Prior.Prior;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**07、在一个长度为n的顺序表中,在第i个元素(1≤i≤n+1)之前插入一个新元素时须向后移动______个元素。**
|
||||
- (A)n-i
|
||||
- (B)n-i+1
|
||||
- (C)n-i-1
|
||||
- (D)i
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**08、栈的特点是______。**
|
||||
- (A)先进先出
|
||||
- (B)后进先出
|
||||
- (C)进优于出
|
||||
- (D)出优于进
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**09、队的特点是______。**
|
||||
- (A)先进先出
|
||||
- (B)后进先出
|
||||
- (C)进优于出
|
||||
- (D)出优于进
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**10、栈和队列的共同点是______。**
|
||||
- (A)都是先进后出
|
||||
- (B)都是先进先出
|
||||
- (C)只允许在端点处插入和删除元素
|
||||
- (D)没有共同点
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**11、以下______不是栈的基本运算。**
|
||||
- (A)删除栈顶元素
|
||||
- (B)删除栈底元素
|
||||
- (C)判断栈是否为空
|
||||
- (D)将栈置为空栈
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**12、设栈S和队列Q的初始状态为空,元素a,b,c,d,e,f依次通过栈S,一个元素出栈后即进入队列Q。假设6个元素出队的顺序是b,d,c,f,e,a则栈S的容量至少应是______。**
|
||||
- (A)2
|
||||
- (B)3
|
||||
- (C)4
|
||||
- (D)5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**13、1,2,3,4四个元素按顺序进栈,不可能的出栈顺序为______。**
|
||||
- (A)1,2,3,4
|
||||
- (B)2,3,4,1
|
||||
- (C)1,4,3,2
|
||||
- (D)3,1,4,2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**14、在解决计算机主机与打印机之间速度不匹配问题时通常设置一个打印数据缓冲区,主机将要输出的数据依次写入该缓冲区,而打印机则从该缓冲区中取出数据打印。该缓冲区应该是一个______结构。**
|
||||
- (A)堆栈
|
||||
- (B)队列
|
||||
- (C)数组
|
||||
- (D)线性表
|
||||
|
||||
**15、用链表表示线性表的优点是______。**
|
||||
- (A)便于随机存取
|
||||
- (B)花费的存储空间较顺序存储少
|
||||
- (C)便于插入和删除
|
||||
- (D)数据元素的物理顺序与逻辑顺序相同
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**16、对顺序存储的线性表,设其长度为n,在任何位置上插入或删除操作都是等概率的。插入一个元素时平均要移动表中的______个元素。**
|
||||
- (A)n/2
|
||||
- (B)(n+1)/2
|
||||
- (C)(n-1)/2
|
||||
- (D)n
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**17、对顺序存储的线性表,设其长度为n,在任何位置上插入或删除操作都是等概率的。删除一个元素时平均要移动表中的______个元素。**
|
||||
- (A)n/2
|
||||
- (B)(n+1)/2
|
||||
- (C)(n-1)/2
|
||||
- (D)n
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**18、循环链表的主要优点是______。**
|
||||
- (A)不再需要头指针了。
|
||||
- (B)已知某个结点的位置后,能够容易找到它的直接前趋。
|
||||
- (C)在进行插入、删除运算时,能更好的保证链表不断开。
|
||||
- (D)从表中的任意结点出发都能扫描到整个链表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**19、设有两个字符串P和Q,其中Q是P的子串,把Q在P中首次出现的位置作为子串Q在P中位置的算法称为______。**
|
||||
- (A)连接
|
||||
- (B)匹配
|
||||
- (C)求子串
|
||||
- (D)求串长
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**20、某二维数组A的行下标的范围是0到8,列下标的范围是0到4,数组中的元素用相邻的4个字节存储,存储器按字节编码。假设存储数组元素A[0,0]的第一个字节的地址是0。则存储数组A的最后一个元素第一个字节的地址是______。**
|
||||
- (A)175
|
||||
- (B)86
|
||||
- (C)68
|
||||
- (D)176
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**21、______是“abcd321ABCD”的子串。**
|
||||
- (A)abcd
|
||||
- (B)321AB
|
||||
- (C)“abcABC”
|
||||
- (D)“21AB”
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**22、已知一棵二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历序列分别为ABDEGCFH和DBGEACHF,则该二叉树的后序序列为______。**
|
||||
- (A)GEDHFBCA
|
||||
- (B)ACBFEDHG
|
||||
- (C)ABCDEFGH
|
||||
- (D)DGEBHFCA
|
||||
|
||||
**23、已知某二叉树前序遍历序列为ABDCE,则下面序列中有可能是对该二叉树进行中序遍历来得到的序列是______。**
|
||||
- (A)BCADE
|
||||
- (B)CBADE
|
||||
- (C)BDAEC
|
||||
- (D)BEACD
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**24、二叉树的后序遍历序列是DABEC,中序遍历序列是DEBAC,则此二叉树的前序遍历序列是______。**
|
||||
- (A)ACBED
|
||||
- (B)DECAB
|
||||
- (C)DEABC
|
||||
- (D)CEDBA
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**25、若树的度为4,其中度为1,2,3和4的结点个数分别为5,3,2和1。那么树中叶子结点的个数是______。**
|
||||
- (A)8
|
||||
- (B)10
|
||||
- (C)11
|
||||
- (D)12
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**26、下面几个符号串编码集合中,不是前缀编码的是______。**
|
||||
- (A){0,10,110,1111}
|
||||
- (B){11,10,001,101,0001}
|
||||
- (C){00,010,0110,1000}
|
||||
- (D){B,C,AA,AC,ABA,ABB,ABC}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**27、树的基本遍历策略可以分为前序遍历和后序遍历,二叉树的基本遍历策略可分为前序、中序、后序三种遍历。我们把由树转化得到的二叉树称为该树对应的二叉树,则下面正确的是______。**
|
||||
- (A)树的前序遍历序列与其对应的二叉树前序遍历序列相同
|
||||
- (B)树的后序遍历序列与其对应的二叉树后序遍历序列相同
|
||||
- (C)树的前序遍历序列与其对应的二叉树中序遍历序列相同
|
||||
- (D)以上都不对
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**28、n个结点的线索二叉树上含有的线索数为______。**
|
||||
- (A)2n
|
||||
- (B)n-1
|
||||
- (C)n+1
|
||||
- (D)n
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**29、具有6个结点的有向图至少应有______条边才能确保是一个强连通图。**
|
||||
- (A)5
|
||||
- (B)6
|
||||
- (C)7
|
||||
- (D)8
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**30、一个具有n个结点的连通无向图的生成树中有______条边。**
|
||||
- (A)n-1
|
||||
- (B)n
|
||||
- (C)n/2
|
||||
- (D)n+1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**31、设无向图的结点数为n,则该无向图最多有______条边。**
|
||||
- (A)n-1
|
||||
- (B)n(n-1)/2
|
||||
- (C)n(n+1)/2
|
||||
- (D)n*n
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**32、设有向图的结点数为n,则该有向图最多有______条边。**
|
||||
- (A)n-1
|
||||
- (B)n(n-1)
|
||||
- (C)n(n-1)/2
|
||||
- (D)n*n
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**33、一个有n个顶点的无向连通图,它所包含的连通分量个数为______。**
|
||||
- (A)0
|
||||
- (B)1
|
||||
- (C)n
|
||||
- (D)n+1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**34、一个图中包含k个连通分量,若按深度优先搜索方法访问所有结点,则必须调用______次深度优先搜索算法。**
|
||||
- (A)k
|
||||
- (B)1
|
||||
- (C)k-1
|
||||
- (D)k+1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**35、在有向图G的拓扑序列中,若顶点$v_i$在$v_j$之前,则下列情况不可能出现的是______。**
|
||||
- (A)G中有弧 $< v_i,v_j>$
|
||||
- (B)G中有一条$v_i$到$v_j$的路径
|
||||
- (C)G中没有弧$< v_i,v_j>$
|
||||
- (D)G中有一条$v_j$到$v_i$的路径
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**36、堆是一种有用的数据结构。例如关键码序列______是一个堆。**
|
||||
- (A)16,72,31,23,94,53
|
||||
- (B)94,53,31,72,16,53
|
||||
- (C)16,53,23,94,31,72
|
||||
- (D)16,31,23,94,53,72
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**37、以下序列不是堆的是______。**
|
||||
- (A)100,85,98,77,80,60,82,40,20,10,66
|
||||
- (B)100,98,85,82,80,77,66,60,40,20,10
|
||||
- (C)10,20,40,60,66,77,80,82,85,98,100
|
||||
- (D)100,85,40,77,80,60,66,98,82,10,20
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**38、对关键字序列{72,73,71,23,94,16,5,68,76,103}构建大根堆,必须从键值为______的结点开始。**
|
||||
- (A)103
|
||||
- (B)72
|
||||
- (C)94
|
||||
- (D)23
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**39、在排序算法中两两比较排序记录项,将那些与排序要求不符的记录交换位置,直到排好序为止的排序方法是______。**
|
||||
- (A)插入排序
|
||||
- (B)交换排序
|
||||
- (C)选择排序
|
||||
- (D)堆排序
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**40、在排序算法中把第i个记录插入到前面已排好的记录中,使插入后的前i个记录符合排序要求的排序方法是______。**
|
||||
- (A)插入排序
|
||||
- (B)交换排序
|
||||
- (C)选择排序
|
||||
- (D)堆排序
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**41、在排序算法中每次从全部还未排序的记录项中选择最小或最大的记录项,并把它接在已排好的记录项末尾的排序方法是______。**
|
||||
- (A)插入排序
|
||||
- (B)交换排序
|
||||
- (C)选择排序
|
||||
- (D)堆排序
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**42、在下列序列中,______才可能是执行第一趟快速排序后得到的序列。**
|
||||
- (A){8,6,18} 19 {16,10,50}
|
||||
- (B){6,4,8} 18 {81,19,36,18}
|
||||
- (C){81,1,2} 36 {99,81,69}
|
||||
- (D){2,3,4} 89 {78,98,68}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**43、对有8个元素的序列{49,38,65,97,76,13,27,50}按从小到大顺序进行排序,直接选择排序第一趟的排序结果是______。**
|
||||
- (A)13,38,65,97,76,49,27,50
|
||||
- (B)13,27,38,49,50,65,76,97
|
||||
- (C)97,76,65,50,49,38,27,13
|
||||
- (D)13,38,65,50,76,49,27,97
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**44、对序列{72,73,71,23,94,16,5,68,76,103}按照构建大根堆的方式从小到大进行排序,堆排序第一趟的排序结果是______。**
|
||||
|
||||
- (A)103,94,71,76,73,16,5,68,23,72
|
||||
- (B)72,94,71,76,73,16,5,68,23,103
|
||||
- (C)94,76,71,72,73,16,5,68,23,103
|
||||
- (D)23,76,71,72,73,16,5,68,94,103
|
||||
|
||||
**45、对序列{72,73,71,23,94,16,5,68,76,103}按照delta=5从小到大进行排序,希尔排序第一趟的排序结果是______。**
|
||||
|
||||
- (A)103,94,71,76,73,16,5,68,23,72
|
||||
- (B)16,5,68,23,73,71,76,72,94,103
|
||||
- (C)16,71,68,23,94,72,73,5,76,103
|
||||
- (D)16,5,68,23,94,72,73,71,76,103
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**46、对线性表进行二分查找时,要求线性表必须______。**
|
||||
- (A)以顺序方式存储
|
||||
- (B)以链式方式存储
|
||||
- (C)以顺序方式存储且结点按关键字有序排序
|
||||
- (D)以链式方式存储且结点按关键字有序排序
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**47、在顺序表{3,6,8,10,12,15,16,18,21,25,30}中,用二分法查找关键码11,所需的关键码比较次数为______。**
|
||||
- (A)2
|
||||
- (B)3
|
||||
- (C)4
|
||||
- (D)5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**48、在顺序表{2,5,7,10,14,15,18,23,35,41,52}中,用二分法查找关键码18,所需的关键码比较次数为______。**
|
||||
- (A)2
|
||||
- (B)3
|
||||
- (C)4
|
||||
- (D)5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**49、对于19个元素的有序记录集合Record采用二分查找,则查找Key=Record[3]的比较序列的下标(下标从0开始)为______。**
|
||||
- (A)9、5、3
|
||||
- (B)9、5、2、3
|
||||
- (C)9、4、2、3
|
||||
- (D)9、4、1、2、3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**50、对搜索二叉树进行______遍历可以得到结点的排序序列。**
|
||||
- (A)前序遍历
|
||||
- (B)中序遍历
|
||||
- (C)后序遍历
|
||||
- (D)层次遍历
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,396 @@
|
|||
# 输入和输出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. numpy 二进制文件
|
||||
|
||||
`save()`、`savez()`和`load()`函数以 numpy 专用的二进制类型(`.npy`、`.npz`)保存和读取数据,这三个函数会自动处理ndim、dtype、shape等信息,使用它们读写数组非常方便,但是`save()`和`savez()`输出的文件很难与其它语言编写的程序兼容。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def save(file, arr, allow_pickle=True, fix_imports=True):
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `save()`函数:以`.npy`格式将数组保存到二进制文件中。
|
||||
- `.npy`格式:以二进制的方式存储文件,在二进制文件第一行以文本形式保存了数据的元信息(ndim,dtype,shape等),可以用二进制工具查看内容。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def load(file, mmap_mode=None, allow_pickle=False, fix_imports=True, encoding='ASCII'):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `load()`函数:从`.npy`、`.npz`或 pickled文件加载数组或pickled对象。
|
||||
- `mmap_mode: {None, ‘r+’, ‘r’, ‘w+’, ‘c’};`:读取文件的方式。
|
||||
- `allow_pickle=False`:允许加载存储在`.npy`文件中的pickled对象数组。
|
||||
- `fix_imports=True`:若为True,pickle将尝试将旧的python2名称映射到python3中使用的新名称。
|
||||
- `encoding='ASCII'`:制定编码格式,默认为“ASCII”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】将一个数组保存到一个文件中。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\test.npy'
|
||||
np.random.seed(20200619)
|
||||
x = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1,size = [3, 5])
|
||||
np.save(outfile, x)
|
||||
y = np.load(outfile)
|
||||
print(y)
|
||||
# [[0.01123594 0.66790705 0.50212171 0.7230908 0.61668256]
|
||||
# [0.00668332 0.1234096 0.96092409 0.67925305 0.38596837]
|
||||
# [0.72342998 0.26258324 0.24318845 0.98795012 0.77370715]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def savez(file, *args, **kwds):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `savez()`函数:以未压缩的`.npz`格式将多个数组保存到单个文件中。
|
||||
- `.npz`格式:以压缩打包的方式存储文件,可以用压缩软件解压。
|
||||
- `savez()`函数:第一个参数是文件名,其后的参数都是需要保存的数组,也可以使用关键字参数为数组起一个名字,非关键字参数传递的数组会自动起名为`arr_0, arr_1, …`。
|
||||
- `savez()`函数:输出的是一个压缩文件(扩展名为`.npz`),其中每个文件都是一个`save()`保存的`.npy`文件,文件名对应于数组名。`load()`自动识别`.npz`文件,并且返回一个类似于字典的对象,可以通过数组名作为关键字获取数组的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】将多个数组保存到一个文件。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\test.npz'
|
||||
x = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 5)
|
||||
y = np.sin(x)
|
||||
z = np.cos(x)
|
||||
np.savez(outfile, x, y, z_d=z)
|
||||
data = np.load(outfile)
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
|
||||
print(data.files)
|
||||
# ['z_d', 'arr_0', 'arr_1']
|
||||
|
||||
print(data['arr_0'])
|
||||
# [0. 0.78539816 1.57079633 2.35619449 3.14159265]
|
||||
|
||||
print(data['arr_1'])
|
||||
# [0. 0.70710678 1. 0.70710678 0. ]
|
||||
|
||||
print(data['z_d'])
|
||||
# [ 1. 0.70710678 0. -0.70710678 -1. ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
用解压软件打开 test.npz 文件,会发现其中有三个文件:`arr_0.npy,arr_1.npy,z_d.npy`,其中分别保存着数组`x,y,z`的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 2. 文本文件
|
||||
`savetxt()`,`loadtxt()`和`genfromtxt()`函数用来存储和读取文本文件(如`.TXT`,`.CSV`等)。`genfromtxt()`比`loadtxt()`更加强大,可对缺失数据进行处理。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def savetxt(fname, X, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=' ', newline='\n',header='', footer='', comments='# ', encoding=None):
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `fname`:文件路径
|
||||
- `X`:存入文件的数组。
|
||||
- `fmt='%.18e'`:写入文件中每个元素的字符串格式,默认'%.18e'(保留18位小数的浮点数形式)。
|
||||
- `delimiter=' '`:分割字符串,默认以空格分隔。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def loadtxt(fname, dtype=float, comments='#', delimiter=None,
|
||||
converters=None, skiprows=0, usecols=None, unpack=False,
|
||||
ndmin=0, encoding='bytes', max_rows=None):
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `fname`:文件路径。
|
||||
- `dtype=float`:数据类型,默认为float。
|
||||
- `comments='#'`: 字符串或字符串组成的列表,默认为'#',表示注释字符集开始的标志。
|
||||
- `skiprows=0`:跳过多少行,一般跳过第一行表头。
|
||||
- `usecols=None`:元组(元组内数据为列的数值索引), 用来指定要读取数据的列(第一列为0)。
|
||||
- `unpack=False`:当加载多列数据时是否需要将数据列进行解耦赋值给不同的变量。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【例】写入和读出TXT文件。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\test.txt'
|
||||
x = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(2, -1)
|
||||
np.savetxt(outfile, x)
|
||||
y = np.loadtxt(outfile)
|
||||
print(y)
|
||||
# [[0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]
|
||||
# [5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
test.txt文件如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
0.000000000000000000e+00 1.000000000000000000e+00 2.000000000000000000e+00 3.000000000000000000e+00 4.000000000000000000e+00
|
||||
5.000000000000000000e+00 6.000000000000000000e+00 7.000000000000000000e+00 8.000000000000000000e+00 9.000000000000000000e+00
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】写入和读出CSV文件。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\test.csv'
|
||||
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.5).reshape(4, -1)
|
||||
np.savetxt(outfile, x, fmt='%.3f', delimiter=',')
|
||||
y = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',')
|
||||
print(y)
|
||||
# [[0. 0.5 1. 1.5 2. ]
|
||||
# [2.5 3. 3.5 4. 4.5]
|
||||
# [5. 5.5 6. 6.5 7. ]
|
||||
# [7.5 8. 8.5 9. 9.5]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
test.csv文件如下:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
0.000,0.500,1.000,1.500,2.000
|
||||
2.500,3.000,3.500,4.000,4.500
|
||||
5.000,5.500,6.000,6.500,7.000
|
||||
7.500,8.000,8.500,9.000,9.500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def genfromtxt(fname, dtype=float, comments='#', delimiter=None,
|
||||
skip_header=0, skip_footer=0, converters=None,
|
||||
missing_values=None, filling_values=None, usecols=None,
|
||||
names=None, excludelist=None,
|
||||
deletechars=''.join(sorted(NameValidator.defaultdeletechars)),
|
||||
replace_space='_', autostrip=False, case_sensitive=True,
|
||||
defaultfmt="f%i", unpack=None, usemask=False, loose=True,
|
||||
invalid_raise=True, max_rows=None, encoding='bytes'):
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `genfromtxt()`函数:从文本文件加载数据,并按指定方式处理缺少的值(是面向结构数组和缺失数据处理的。)。
|
||||
- `names=None`:设置为True时,程序将把第一行作为列名称。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
data.csv文件(不带缺失值)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
id,value1,value2,value3
|
||||
1,123,1.4,23
|
||||
2,110,0.5,18
|
||||
3,164,2.1,19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\data.csv'
|
||||
x = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [[ 1. 123. 1.4 23. ]
|
||||
# [ 2. 110. 0.5 18. ]
|
||||
# [ 3. 164. 2.1 19. ]]
|
||||
|
||||
x = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=(1, 2))
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [[123. 1.4]
|
||||
# [110. 0.5]
|
||||
# [164. 2.1]]
|
||||
|
||||
val1, val2 = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=(1, 2), unpack=True)
|
||||
print(val1) # [123. 110. 164.]
|
||||
print(val2) # [1.4 0.5 2.1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\data.csv'
|
||||
x = np.genfromtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', names=True)
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [(1., 123., 1.4, 23.) (2., 110., 0.5, 18.) (3., 164., 2.1, 19.)]
|
||||
|
||||
print(type(x))
|
||||
# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
|
||||
|
||||
print(x.dtype)
|
||||
# [('id', '<f8'), ('value1', '<f8'), ('value2', '<f8'), ('value3', '<f8')]
|
||||
|
||||
print(x['id']) # [1. 2. 3.]
|
||||
print(x['value1']) # [123. 110. 164.]
|
||||
print(x['value2']) # [1.4 0.5 2.1]
|
||||
print(x['value3']) # [23. 18. 19.]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
data1.csv文件(带有缺失值)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
id,value1,value2,value3
|
||||
1,123,1.4,23
|
||||
2,110,,18
|
||||
3,,2.1,19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
outfile = r'.\data1.csv'
|
||||
x = np.genfromtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', names=True)
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [(1., 123., 1.4, 23.) (2., 110., nan, 18.) (3., nan, 2.1, 19.)]
|
||||
|
||||
print(type(x))
|
||||
# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
|
||||
|
||||
print(x.dtype)
|
||||
# [('id', '<f8'), ('value1', '<f8'), ('value2', '<f8'), ('value3', '<f8')]
|
||||
|
||||
print(x['id']) # [1. 2. 3.]
|
||||
print(x['value1']) # [123. 110. nan]
|
||||
print(x['value2']) # [1.4 nan 2.1]
|
||||
print(x['value3']) # [23. 18. 19.]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 3. 文本格式选项
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def set_printoptions(precision=None, threshold=None, edgeitems=None,
|
||||
linewidth=None, suppress=None, nanstr=None, infstr=None,
|
||||
formatter=None, sign=None, floatmode=None, **kwarg):
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `set_printoptions()`函数:设置打印选项。这些选项决定浮点数、数组和其它NumPy对象的显示方式。
|
||||
- `precision=8`:设置浮点精度,控制输出的小数点个数,默认是8。
|
||||
- `threshold=1000`:概略显示,超过该值则以“…”的形式来表示,默认是1000。
|
||||
- `linewidth=75`:用于确定每行多少字符数后插入换行符,默认为75。
|
||||
- `suppress=False`:当`suppress=True`,表示小数不需要以科学计数法的形式输出,默认是False。
|
||||
- `nanstr=nan`:浮点非数字的字符串表示形式,默认`nan`。
|
||||
- `infstr=inf`:浮点无穷大的字符串表示形式,默认`inf`。
|
||||
- `formatter`:一个字典,自定义格式化用于显示的数组元素。键为需要格式化的类型,值为格式化的字符串。
|
||||
- 'bool'
|
||||
- 'int'
|
||||
- 'float'
|
||||
- 'str' : all other strings
|
||||
- 'all' : sets all types
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(precision=4)
|
||||
x = np.array([1.123456789])
|
||||
print(x) # [1.1235]
|
||||
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(threshold=20)
|
||||
x = np.arange(50)
|
||||
print(x) # [ 0 1 2 ... 47 48 49]
|
||||
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.iinfo(np.int).max)
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
|
||||
# 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
|
||||
# 48 49]
|
||||
|
||||
eps = np.finfo(float).eps
|
||||
x = np.arange(4.)
|
||||
x = x ** 2 - (x + eps) ** 2
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [-4.9304e-32 -4.4409e-16 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00]
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
|
||||
print(x) # [-0. -0. 0. 0.]
|
||||
|
||||
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 10)
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# [ 0. 1.1111 2.2222 3.3333 4.4444 5.5556 6.6667 7.7778 8.8889
|
||||
# 10. ]
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(precision=2, suppress=True, threshold=5)
|
||||
print(x) # [ 0. 1.11 2.22 ... 7.78 8.89 10. ]
|
||||
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(formatter={'all': lambda x: 'int: ' + str(-x)})
|
||||
x = np.arange(3)
|
||||
print(x) # [int: 0 int: -1 int: -2]
|
||||
|
||||
np.set_printoptions() # formatter gets reset
|
||||
print(x) # [0 1 2]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】恢复默认选项
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(edgeitems=3, infstr='inf', linewidth=75,
|
||||
nanstr='nan', precision=8, suppress=False,
|
||||
threshold=1000, formatter=None)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
【函数】
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def get_printoptions():
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `get_printoptions()`函数:获取当前打印选项。
|
||||
|
||||
【例子】
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
x = np.get_printoptions()
|
||||
print(x)
|
||||
# {
|
||||
# 'edgeitems': 3,
|
||||
# 'threshold': 1000,
|
||||
# 'floatmode': 'maxprec',
|
||||
# 'precision': 8,
|
||||
# 'suppress': False,
|
||||
# 'linewidth': 75,
|
||||
# 'nanstr': 'nan',
|
||||
# 'infstr': 'inf',
|
||||
# 'sign': '-',
|
||||
# 'formatter': None,
|
||||
# 'legacy': False
|
||||
# }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 4. 练习
|
||||
|
||||
**(1)只打印或显示numpy数组rand_arr的小数点后3位。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:输入和输出】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy数组中只打印小数点后三位?
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
np.random.seed(2002)
|
||||
rand_arr = np.random.random([5,3])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**(2)将numpy数组a中打印的项数限制为最多6个元素。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:输入和输出】
|
||||
- 如何限制numpy数组输出中打印的项目数?
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
a = np.arange(15)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**(3)打印完整的numpy数组a而不中断。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:输入和输出】
|
||||
|
||||
- 如何打印完整的numpy数组而不中断?
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
a = np.arange(15)
|
||||
np.set_printoptions(threshold=6)
|
||||
print(a)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
|||
# 大作业
|
||||
|
||||
本次练习使用 鸢尾属植物数据集`.\iris.data`,在这个数据集中,包括了三类不同的鸢尾属植物:Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica。每类收集了50个样本,因此这个数据集一共包含了150个样本。
|
||||
|
||||
- sepallength:萼片长度
|
||||
- sepalwidth:萼片宽度
|
||||
- petallength:花瓣长度
|
||||
- petalwidth:花瓣宽度
|
||||
|
||||
以上四个特征的单位都是厘米(cm)。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth species
|
||||
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
|
||||
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
|
||||
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa
|
||||
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
|
||||
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
|
||||
.. ... ... ... ... ...
|
||||
145 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3 Iris-virginica
|
||||
146 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9 Iris-virginica
|
||||
147 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 Iris-virginica
|
||||
148 6.2 3.4 5.4 2.3 Iris-virginica
|
||||
149 5.9 3.0 5.1 1.8 Iris-virginica
|
||||
|
||||
[150 rows x 5 columns]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 导入鸢尾属植物数据集,保持文本不变。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:输入和输出】
|
||||
- 如何导入存在数字和文本的数据集?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 求出鸢尾属植物萼片长度的平均值、中位数和标准差(第1列,sepallength)**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:统计相关】
|
||||
- 如何计算numpy数组的均值,中位数,标准差?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 创建一种标准化形式的鸢尾属植物萼片长度,其值正好介于0和1之间,这样最小值为0,最大值为1(第1列,sepallength)。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:统计相关】
|
||||
- 如何标准化数组?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 找到鸢尾属植物萼片长度的第5和第95百分位数(第1列,sepallength)。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:统计相关】
|
||||
- 如何找到numpy数组的百分位数?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 把iris_data数据集中的20个随机位置修改为np.nan值。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:随机抽样】
|
||||
- 如何在数组中的随机位置修改值?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**6. 在iris_data的sepallength中查找缺失值的个数和位置(第1列)。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:逻辑函数、搜索】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy数组中找到缺失值的位置?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**7. 筛选具有 sepallength(第1列)< 5.0 并且 petallength(第3列)> 1.5 的 iris_data行。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:搜索】
|
||||
- 如何根据两个或多个条件筛选numpy数组?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**8. 选择没有任何 nan 值的 iris_data行。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:逻辑函数、搜索】
|
||||
- 如何从numpy数组中删除包含缺失值的行?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**9. 计算 iris_data 中sepalLength(第1列)和petalLength(第3列)之间的相关系数。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:统计相关】
|
||||
- 如何计算numpy数组两列之间的相关系数?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**10. 找出iris_data是否有任何缺失值。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:逻辑函数】
|
||||
- 如何查找给定数组是否具有空值?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**11. 在numpy数组中将所有出现的nan替换为0。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:逻辑函数】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy数组中用0替换所有缺失值?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**12. 找出鸢尾属植物物种中的唯一值和唯一值出现的数量。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:数组操作】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy数组中查找唯一值的计数?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**13. 将 iris_data 的花瓣长度(第3列)以形成分类变量的形式显示。定义:Less than 3 --> 'small';3-5 --> 'medium';'>=5 --> 'large'。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:统计相关】
|
||||
- 如何将数字转换为分类(文本)数组?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**14. 在 iris_data 中创建一个新列,其中 volume 是 `(pi x petallength x sepallength ^ 2)/ 3`。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:数组操作】
|
||||
- 如何从numpy数组的现有列创建新列?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**15. 随机抽鸢尾属植物的种类,使得Iris-setosa的数量是Iris-versicolor和Iris-virginica数量的两倍。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:随机抽样】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy中进行概率抽样?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**16. 根据 sepallength 列对数据集进行排序。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:排序】
|
||||
- 如何按列对2D数组进行排序?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**17. 在鸢尾属植物数据集中找到最常见的花瓣长度值(第3列)。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:数组操作】
|
||||
- 如何在numpy数组中找出出现次数最多的值?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**18. 在鸢尾花数据集的 petalwidth(第4列)中查找第一次出现的值大于1.0的位置。**
|
||||
|
||||
【知识点:搜索】
|
||||
- 如何找到第一次出现大于给定值的位置?
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
|||
sepallength,sepalwidth,petallength,petalwidth,species
|
||||
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.9,3.0,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.7,3.2,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.6,3.1,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.6,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.4,3.9,1.7,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.6,3.4,1.4,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.4,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.4,2.9,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.4,3.7,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.8,3.4,1.6,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.8,3.0,1.4,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.3,3.0,1.1,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.8,4.0,1.2,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.7,4.4,1.5,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.4,3.9,1.3,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.7,3.8,1.7,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.8,1.5,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.4,3.4,1.7,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.7,1.5,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.6,3.6,1.0,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.3,1.7,0.5,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.8,3.4,1.9,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.0,1.6,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.4,1.6,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.2,3.5,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.2,3.4,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.7,3.2,1.6,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.8,3.1,1.6,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.4,3.4,1.5,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.2,4.1,1.5,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.5,4.2,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.2,1.2,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.5,3.5,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.4,3.0,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.4,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.5,1.3,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.5,2.3,1.3,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.4,3.2,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.5,1.6,0.6,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.8,1.9,0.4,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.8,3.0,1.4,0.3,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.1,3.8,1.6,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
4.6,3.2,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.3,3.7,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
5.0,3.3,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa
|
||||
7.0,3.2,4.7,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.9,3.1,4.9,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.5,2.3,4.0,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.5,2.8,4.6,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.7,2.8,4.5,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.3,3.3,4.7,1.6,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
4.9,2.4,3.3,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.6,2.9,4.6,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.2,2.7,3.9,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.0,2.0,3.5,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.9,3.0,4.2,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.0,2.2,4.0,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.1,2.9,4.7,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.6,2.9,3.6,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.7,3.1,4.4,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.6,3.0,4.5,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.8,2.7,4.1,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.2,2.2,4.5,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.6,2.5,3.9,1.1,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.9,3.2,4.8,1.8,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.1,2.8,4.0,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.3,2.5,4.9,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.1,2.8,4.7,1.2,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.4,2.9,4.3,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.6,3.0,4.4,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.8,2.8,4.8,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.7,3.0,5.0,1.7,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.0,2.9,4.5,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.7,2.6,3.5,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.5,2.4,3.8,1.1,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.5,2.4,3.7,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.8,2.7,3.9,1.2,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.0,2.7,5.1,1.6,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.4,3.0,4.5,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.0,3.4,4.5,1.6,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.7,3.1,4.7,1.5,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.3,2.3,4.4,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.6,3.0,4.1,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.5,2.5,4.0,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.5,2.6,4.4,1.2,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.1,3.0,4.6,1.4,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.8,2.6,4.0,1.2,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.0,2.3,3.3,1.0,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.6,2.7,4.2,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.7,3.0,4.2,1.2,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.7,2.9,4.2,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.2,2.9,4.3,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.1,2.5,3.0,1.1,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
5.7,2.8,4.1,1.3,Iris-versicolor
|
||||
6.3,3.3,6.0,2.5,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.1,3.0,5.9,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.3,2.9,5.6,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.5,3.0,5.8,2.2,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.6,3.0,6.6,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
4.9,2.5,4.5,1.7,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.3,2.9,6.3,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.7,2.5,5.8,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.2,3.6,6.1,2.5,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.5,3.2,5.1,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.4,2.7,5.3,1.9,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.8,3.0,5.5,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.7,2.5,5.0,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.8,2.8,5.1,2.4,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.4,3.2,5.3,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.5,3.0,5.5,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.7,3.8,6.7,2.2,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.7,2.6,6.9,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.0,2.2,5.0,1.5,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.9,3.2,5.7,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.6,2.8,4.9,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.7,2.8,6.7,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.3,2.7,4.9,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.2,3.2,6.0,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.2,2.8,4.8,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.1,3.0,4.9,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.2,3.0,5.8,1.6,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.4,2.8,6.1,1.9,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.9,3.8,6.4,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.2,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.3,2.8,5.1,1.5,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.1,2.6,5.6,1.4,Iris-virginica
|
||||
7.7,3.0,6.1,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.3,3.4,5.6,2.4,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.4,3.1,5.5,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.0,3.0,4.8,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.9,3.1,5.4,2.1,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.7,3.1,5.6,2.4,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.9,3.1,5.1,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.8,2.7,5.1,1.9,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.8,3.2,5.9,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.7,3.3,5.7,2.5,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.7,3.0,5.2,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.3,2.5,5.0,1.9,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.5,3.0,5.2,2.0,Iris-virginica
|
||||
6.2,3.4,5.4,2.3,Iris-virginica
|
||||
5.9,3.0,5.1,1.8,Iris-virginica
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
## 基本信息
|
||||
|
||||
- 学习周期:11天,每天平均花费时间3小时-5小时不等,根据个人学习接受能力强弱有所浮动。
|
||||
- 学习周期:10天,每天平均花费时间3小时-5小时不等,根据个人学习接受能力强弱有所浮动。
|
||||
- 学习形式:理论学习 + 练习
|
||||
- 人群定位:有一定python编程的基础。
|
||||
- 先修内容:[Python编程语言](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/PythonLanguage)
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,7 +71,7 @@
|
|||
- 熟悉打开规则
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Task01:输入输出(2天)
|
||||
### Task01:输入输出(1天)
|
||||
- 熟悉 Numpy 如何处理二进制文件和文本文件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,229 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:05:42.613206Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:05:42.609217Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**只打印或显示numpy数组rand_arr的小数点后3位。**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `rand_arr = np.random.random([5, 3])`\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【知识点:输入和输出】\n",
|
||||
"- 如何在numpy数组中只打印小数点后三位?"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:03.840763Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:03.834778Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"[[0.25106063 0.32735642 0.17623774]\n",
|
||||
" [0.85566173 0.11420437 0.53735783]\n",
|
||||
" [0.82253612 0.07625331 0.9358199 ]\n",
|
||||
" [0.97268875 0.91794448 0.61845404]\n",
|
||||
" [0.58615827 0.28096349 0.88048956]]\n",
|
||||
"[[0.251 0.327 0.176]\n",
|
||||
" [0.856 0.114 0.537]\n",
|
||||
" [0.823 0.076 0.936]\n",
|
||||
" [0.973 0.918 0.618]\n",
|
||||
" [0.586 0.281 0.88 ]]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"rand_arr = np.random.random([5, 3])\n",
|
||||
"print(rand_arr)\n",
|
||||
"# [[0.33033427 0.05538836 0.05947305]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.36199439 0.48844555 0.26309599]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.05361816 0.71539075 0.60645637]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.95000384 0.31424729 0.41032467]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.36082793 0.50101268 0.6306832 ]]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(precision=3)\n",
|
||||
"print(rand_arr)\n",
|
||||
"# [[0.33 0.055 0.059]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.362 0.488 0.263]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.054 0.715 0.606]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.95 0.314 0.41 ]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.361 0.501 0.631]]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:22.855956Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:22.850970Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**将numpy数组a中打印的项数限制为最多6个元素。**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【知识点:输入和输出】\n",
|
||||
"- 如何限制numpy数组输出中打印的项目数?"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:51.128200Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:06:51.123215Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]\n",
|
||||
"[ 0 1 2 ... 12 13 14]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"a = np.arange(15)\n",
|
||||
"print(a)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(threshold=6)\n",
|
||||
"print(a)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0 1 2 ... 12 13 14]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:07:14.131621Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:07:14.126608Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"**打印完整的numpy数组a而不中断。**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【知识点:输入和输出】\n",
|
||||
"- 如何打印完整的numpy数组而不中断?"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 6,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2020-09-06T03:07:47.868079Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2020-09-06T03:07:47.863126Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"[ 0 1 2 ... 12 13 14]\n",
|
||||
"[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"a = np.arange(15)\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(threshold=6)\n",
|
||||
"print(a)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0 1 2 ... 12 13 14]\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.iinfo(np.int).max)\n",
|
||||
"print(a)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python35",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python35"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.10"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"toc": {
|
||||
"base_numbering": 1,
|
||||
"nav_menu": {},
|
||||
"number_sections": true,
|
||||
"sideBar": true,
|
||||
"skip_h1_title": false,
|
||||
"title_cell": "Table of Contents",
|
||||
"title_sidebar": "Contents",
|
||||
"toc_cell": false,
|
||||
"toc_position": {},
|
||||
"toc_section_display": true,
|
||||
"toc_window_display": false
|
||||
},
|
||||
"varInspector": {
|
||||
"cols": {
|
||||
"lenName": 16,
|
||||
"lenType": 16,
|
||||
"lenVar": 40
|
||||
},
|
||||
"kernels_config": {
|
||||
"python": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": "",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.py",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"r": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.r",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"types_to_exclude": [
|
||||
"module",
|
||||
"function",
|
||||
"builtin_function_or_method",
|
||||
"instance",
|
||||
"_Feature"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"window_display": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,372 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# 输入和输出\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"## numpy 二进制文件\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`save()`、`savez()`和`load()`函数以 numpy 专用的二进制类型(npy、npz)保存和读取数据,这三个函数会自动处理ndim、dtype、shape等信息,使用它们读写数组非常方便,但是`save()`输出的文件很难与其它语言编写的程序兼容。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"npy格式:以二进制的方式存储文件,在二进制文件第一行以文本形式保存了数据的元信息(ndim,dtype,shape等),可以用二进制工具查看内容。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"npz格式:以压缩打包的方式存储文件,可以用压缩软件解压。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.save(file, arr, allow_pickle=True, fix_imports=True)` Save an array to a binary file in NumPy `.npy` format.\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.load(file, mmap_mode=None, allow_pickle=False, fix_imports=True, encoding='ASCII')` Load arrays or pickled objects from ``.npy``, ``.npz`` or pickled files.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\test.npy'\n",
|
||||
"np.random.seed(20200619)\n",
|
||||
"x = np.random.uniform(0, 1, [3, 5])\n",
|
||||
"np.save(outfile, x)\n",
|
||||
"y = np.load(outfile)\n",
|
||||
"print(y)\n",
|
||||
"# [[0.01123594 0.66790705 0.50212171 0.7230908 0.61668256]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.00668332 0.1234096 0.96092409 0.67925305 0.38596837]\n",
|
||||
"# [0.72342998 0.26258324 0.24318845 0.98795012 0.77370715]]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.savez(file, *args, **kwds)` Save several arrays into a single file in uncompressed `.npz` format.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`savez()`第一个参数是文件名,其后的参数都是需要保存的数组,也可以使用关键字参数为数组起一个名字,非关键字参数传递的数组会自动起名为`arr_0, arr_1, …`。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`savez()`输出的是一个压缩文件(扩展名为npz),其中每个文件都是一个`save()`保存的npy文件,文件名对应于数组名。`load()`自动识别npz文件,并且返回一个类似于字典的对象,可以通过数组名作为关键字获取数组的内容。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】将多个数组保存到一个文件,可以使用`numpy.savez()`函数。\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\test.npz'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 5)\n",
|
||||
"y = np.sin(x)\n",
|
||||
"z = np.cos(x)\n",
|
||||
"np.savez(outfile, x, y, z_d=z)\n",
|
||||
"data = np.load(outfile)\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(data.files) \n",
|
||||
"# ['z_d', 'arr_0', 'arr_1']\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(data['arr_0'])\n",
|
||||
"# [0. 0.78539816 1.57079633 2.35619449 3.14159265]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(data['arr_1'])\n",
|
||||
"# [0. 0.70710678 1. 0.70710678 0. ]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(data['z_d'])\n",
|
||||
"# [ 1. 0.70710678 0. -0.70710678 -1. ]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"用解压软件打开 test.npz 文件,会发现其中有三个文件:`arr_0.npy,arr_1.npy,z_d.npy`,其中分别保存着数组`x,y,z`的内容。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"---\n",
|
||||
"## 文本文件\n",
|
||||
"`savetxt()`,`loadtxt()`和`genfromtxt()`函数用来存储和读取文本文件(如TXT,CSV等)。`genfromtxt()`比`loadtxt()`更加强大,可对缺失数据进行处理。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.savetxt(fname, X, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=' ', newline='\\n', header='', footer='', comments='# ', encoding=None)` Save an array to a text file.\n",
|
||||
" - fname:文件路径\n",
|
||||
" - X:存入文件的数组。\n",
|
||||
" - fmt:写入文件中每个元素的字符串格式,默认'%.18e'(保留18位小数的浮点数形式)。\n",
|
||||
" - delimiter:分割字符串,默认以空格分隔。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.loadtxt(fname, dtype=float, comments='#', delimiter=None, converters=None, skiprows=0, usecols=None, unpack=False, ndmin=0, encoding='bytes', max_rows=None)` Load data from a text file. \n",
|
||||
" - fname:文件路径。\n",
|
||||
" - dtype:数据类型,默认为float。\n",
|
||||
" - comments: 字符串或字符串组成的列表,默认为# , 表示注释字符集开始的标志。\n",
|
||||
" - skiprows:跳过多少行,一般跳过第一行表头。\n",
|
||||
" - usecols:元组(元组内数据为列的数值索引), 用来指定要读取数据的列(第一列为0)。\n",
|
||||
" - unpack:当加载多列数据时是否需要将数据列进行解耦赋值给不同的变量。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】写入和读出TXT文件。\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\test.txt'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(2, -1)\n",
|
||||
"np.savetxt(outfile, x)\n",
|
||||
"y = np.loadtxt(outfile)\n",
|
||||
"print(y)\n",
|
||||
"# [[0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]\n",
|
||||
"# [5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test.txt文件如下:\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"0.000000000000000000e+00 1.000000000000000000e+00 2.000000000000000000e+00 3.000000000000000000e+00 4.000000000000000000e+00\n",
|
||||
"5.000000000000000000e+00 6.000000000000000000e+00 7.000000000000000000e+00 8.000000000000000000e+00 9.000000000000000000e+00\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】写入和读出CSV文件。\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\test.csv'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.5).reshape(4, -1)\n",
|
||||
"np.savetxt(outfile, x, fmt='%.3f', delimiter=',')\n",
|
||||
"y = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',')\n",
|
||||
"print(y)\n",
|
||||
"# [[0. 0.5 1. 1.5 2. ]\n",
|
||||
"# [2.5 3. 3.5 4. 4.5]\n",
|
||||
"# [5. 5.5 6. 6.5 7. ]\n",
|
||||
"# [7.5 8. 8.5 9. 9.5]]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"test.csv文件如下:\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"0.000,0.500,1.000,1.500,2.000\n",
|
||||
"2.500,3.000,3.500,4.000,4.500\n",
|
||||
"5.000,5.500,6.000,6.500,7.000\n",
|
||||
"7.500,8.000,8.500,9.000,9.500\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"`genfromtxt()`是面向结构数组和缺失数据处理的。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.genfromtxt(fname, dtype=float, comments='#', delimiter=None, skip_header=0, skip_footer=0, converters=None, missing_values=None, filling_values=None, usecols=None, names=None, excludelist=None, deletechars=''.join(sorted(NameValidator.defaultdeletechars)), replace_space='_', autostrip=False, case_sensitive=True, defaultfmt=\"f%i\", unpack=None, usemask=False, loose=True, invalid_raise=True, max_rows=None, encoding='bytes')` Load data from a text file, with missing values handled as specified.\n",
|
||||
" - names:设置为True时,程序将把第一行作为列名称。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"data.csv文件如下:\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"id,value1,value2,value3\n",
|
||||
"1,123,1.4,23\n",
|
||||
"2,110,0.5,18\n",
|
||||
"3,164,2.1,19\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\data.csv'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [[ 1. 123. 1.4 23. ]\n",
|
||||
"# [ 2. 110. 0.5 18. ]\n",
|
||||
"# [ 3. 164. 2.1 19. ]]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"x = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=(1, 2))\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [[123. 1.4]\n",
|
||||
"# [110. 0.5]\n",
|
||||
"# [164. 2.1]]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"val1, val2 = np.loadtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=(1, 2), unpack=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(val1) # [123. 110. 164.]\n",
|
||||
"print(val2) # [1.4 0.5 2.1]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\data.csv'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.genfromtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', names=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [(1., 123., 1.4, 23.) (2., 110., 0.5, 18.) (3., 164., 2.1, 19.)]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(type(x)) \n",
|
||||
"# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(x.dtype)\n",
|
||||
"# [('id', '<f8'), ('value1', '<f8'), ('value2', '<f8'), ('value3', '<f8')]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(x['id']) # [1. 2. 3.]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value1']) # [123. 110. 164.]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value2']) # [1.4 0.5 2.1]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value3']) # [23. 18. 19.]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"data1.csv文件\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"id,value1,value2,value3\n",
|
||||
"1,123,1.4,23\n",
|
||||
"2,110,,18\n",
|
||||
"3,,2.1,19\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"outfile = r'.\\data1.csv'\n",
|
||||
"x = np.genfromtxt(outfile, delimiter=',', names=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [(1., 123., 1.4, 23.) (2., 110., nan, 18.) (3., nan, 2.1, 19.)]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(type(x)) \n",
|
||||
"# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(x.dtype)\n",
|
||||
"# [('id', '<f8'), ('value1', '<f8'), ('value2', '<f8'), ('value3', '<f8')]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"print(x['id']) # [1. 2. 3.]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value1']) # [123. 110. nan]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value2']) # [1.4 nan 2.1]\n",
|
||||
"print(x['value3']) # [23. 18. 19.]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"---\n",
|
||||
"## 文本格式选项\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.set_printoptions(precision=None,threshold=None, edgeitems=None,linewidth=None, suppress=None, nanstr=None, infstr=None,formatter=None, sign=None, floatmode=None, **kwarg)` Set printing options.\n",
|
||||
" - `precision`:设置浮点精度,控制输出的小数点个数,默认是8。\n",
|
||||
" - `threshold`:概略显示,超过该值则以“…”的形式来表示,默认是1000。\n",
|
||||
" - `linewidth`:用于确定每行多少字符数后插入换行符,默认为75。\n",
|
||||
" - `suppress`:当`suppress=True`,表示小数不需要以科学计数法的形式输出,默认是False。\n",
|
||||
" - `nanstr`:浮点非数字的字符串表示形式,默认`nan`。\n",
|
||||
" - `infstr`:浮点无穷大的字符串表示形式,默认`inf`。\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"These options determine the way floating point numbers, arrays and other NumPy objects are displayed.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(precision=4)\n",
|
||||
"x = np.array([1.123456789])\n",
|
||||
"print(x) # [1.1235]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(threshold=20)\n",
|
||||
"x = np.arange(50)\n",
|
||||
"print(x) # [ 0 1 2 ... 47 48 49]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.iinfo(np.int).max)\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23\n",
|
||||
"# 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47\n",
|
||||
"# 48 49]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"eps = np.finfo(float).eps\n",
|
||||
"x = np.arange(4.)\n",
|
||||
"x = x ** 2 - (x + eps) ** 2\n",
|
||||
"print(x) \n",
|
||||
"# [-4.9304e-32 -4.4409e-16 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00]\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)\n",
|
||||
"print(x) # [-0. -0. 0. 0.]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"x = np.linspace(0, 10, 10)\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# [ 0. 1.1111 2.2222 3.3333 4.4444 5.5556 6.6667 7.7778 8.8889\n",
|
||||
"# 10. ]\n",
|
||||
"np.set_printoptions(precision=2, suppress=True, threshold=5)\n",
|
||||
"print(x) # [ 0. 1.11 2.22 ... 7.78 8.89 10. ]\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- `numpy.get_printoptions()` Return the current print options.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"【例】\n",
|
||||
"```python\n",
|
||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"x = np.get_printoptions()\n",
|
||||
"print(x)\n",
|
||||
"# {\n",
|
||||
"# 'edgeitems': 3, \n",
|
||||
"# 'threshold': 1000, \n",
|
||||
"# 'floatmode': 'maxprec', \n",
|
||||
"# 'precision': 8, \n",
|
||||
"# 'suppress': False, \n",
|
||||
"# 'linewidth': 75, \n",
|
||||
"# 'nanstr': 'nan', \n",
|
||||
"# 'infstr': 'inf', \n",
|
||||
"# 'sign': '-', \n",
|
||||
"# 'formatter': None, \n",
|
||||
"# 'legacy': False\n",
|
||||
"# }\n",
|
||||
"```\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python35",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python35"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.6.10"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"toc": {
|
||||
"base_numbering": 1,
|
||||
"nav_menu": {},
|
||||
"number_sections": true,
|
||||
"sideBar": true,
|
||||
"skip_h1_title": false,
|
||||
"title_cell": "Table of Contents",
|
||||
"title_sidebar": "Contents",
|
||||
"toc_cell": false,
|
||||
"toc_position": {},
|
||||
"toc_section_display": true,
|
||||
"toc_window_display": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"varInspector": {
|
||||
"cols": {
|
||||
"lenName": 16,
|
||||
"lenType": 16,
|
||||
"lenVar": 40
|
||||
},
|
||||
"kernels_config": {
|
||||
"python": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": "",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.py",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"r": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.r",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"types_to_exclude": [
|
||||
"module",
|
||||
"function",
|
||||
"builtin_function_or_method",
|
||||
"instance",
|
||||
"_Feature"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"window_display": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
|||
|
||||
# 编程实践(LeetCode 腾讯精选练习50)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
开源内容:https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/LeetCodeTencent
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本信息
|
||||
|
||||
- 学习周期:17天,每天平均花费时间2小时-5小时不等,根据个人学习接受能力强弱有所浮动。
|
||||
- 学习形式:练习
|
||||
- 人群定位:有一定编程基础,对学习算法有需求的学员。
|
||||
- 先修内容:[Python编程语言](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/PythonLanguage)、[数据结构与算法](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/DataStructureAndAlgorithm)、[编程实践(LeetCode 分类练习)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/LeetCodeClassification)
|
||||
- 难度系数:中
|
||||
|
||||
## 学习目标
|
||||
|
||||
每天刷三道题,利用17天完成Leetcode腾讯精选练习50题。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 任务安排
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Task00:熟悉规则(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- 组队、修改群昵称
|
||||
- 熟悉打卡规则
|
||||
|
||||
### Task01:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [002 两数相加](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/)
|
||||
- [004 寻找两个正序数组的中位数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/)
|
||||
- [005 最长回文子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task02: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [007 整数反转](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-integer/)
|
||||
- [008 字符串转换整数 (atoi)](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/)
|
||||
- [009 回文数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-number/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task03: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [011 盛最多水的容器](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/container-with-most-water/)
|
||||
- [014 最长公共前缀](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-prefix/)
|
||||
- [015 三数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task04: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [016 最接近的三数之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum-closest/)
|
||||
- [020 有效的括号](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
|
||||
- [021 合并两个有序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task05: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [023 合并K个排序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/)
|
||||
- [026 删除排序数组中的重复项](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/)
|
||||
- [033 搜索旋转排序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task06:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [043 字符串相乘](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/multiply-strings/)
|
||||
- [046 全排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/)
|
||||
- [053 最大子序和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task07: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [054 螺旋矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/)
|
||||
- [059 螺旋矩阵 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/)
|
||||
- [061 旋转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task 08: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [062 不同路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/)
|
||||
- [070 爬楼梯](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
|
||||
- [078 子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task09: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [088 合并两个有序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/)
|
||||
- [089 格雷编码](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gray-code/)
|
||||
- [104 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task10: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [121 买卖股票的最佳时机](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/)
|
||||
- [122 买卖股票的最佳时机 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/)
|
||||
- [124 二叉树中的最大路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task11: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [136 只出现一次的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number/)
|
||||
- [141 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
|
||||
- [142 环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task12: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [146 LRU缓存机制](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/)
|
||||
- [148 排序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/)
|
||||
- [155 最小栈](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-stack/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task13: 完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [160 相交链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/)
|
||||
- [169 多数元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/majority-element/)
|
||||
- [206 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Task14:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [215 数组中的第K个最大元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/)
|
||||
- [217 存在重复元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate/)
|
||||
- [230 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task15:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [231 2的幂](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/power-of-two/)
|
||||
- [235 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
- [236 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task16:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [237 删除链表中的节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/)
|
||||
- [238 除自身以外数组的乘积](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/product-of-array-except-self/)
|
||||
- [292 Nim 游戏](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/nim-game/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Task17:完成以下三个题目并打卡(1天)
|
||||
|
||||
- [344 反转字符串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string/)
|
||||
- [557 反转字符串中的单词 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string-iii/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 贡献人员
|
||||
|
||||
姓名 | 博客|备注
|
||||
---|---|---
|
||||
马燕鹏|CSDN:https://lsgogroup.blog.csdn.net/<br>微信公众号:LSGO软件技术团队|华北电力大学
|
||||
韩绘锦|CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45569785|华北电力大学
|
||||
姚行志|CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/soulmate______|华北电力大学
|
||||
徐韬||华北电力大学
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
|||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -13,6 +13,9 @@
|
|||
- [编程实践(Python 爬虫)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/WebSpider)
|
||||
- [编程实践(Python综合)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/ProjectPractice)
|
||||
- [编程实践(设计模式)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/DesignPattern)
|
||||
- [编程实践(欢欢喜喜情人节)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/ValentineDay)
|
||||
- [编程实践(青少年编程Turtle)](https://github.com/datawhalechina/team-learning-program/tree/master/Turtle)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 备注
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue