修复单独编译内核报错的问题 close #I4O204 Signed-off-by: kenneth <zhushangyuan@huawei.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .gitee | ||
| arch | ||
| components | ||
| drivers | ||
| figures | ||
| kal | ||
| kernel | ||
| targets | ||
| testsuites | ||
| tools | ||
| utils | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| BUILD.gn | ||
| Kconfig | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| NOTICE | ||
| OAT.xml | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_zh.md | ||
| arch_spec.md | ||
| arch_spec_zh.md | ||
| liteos.gni | ||
README.md
LiteOS-M Kernel
Introduction
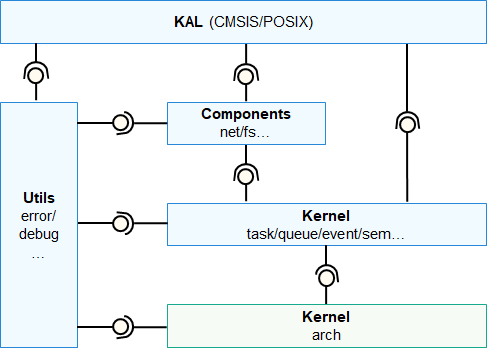
OpenHarmony LiteOS-M is a lightweight operating system kernel designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) field. It features small footprint, low power consumption, and high performance. It has a simple code structure, including the minimum kernel function set, kernel abstraction layer, optional components, and project directory. The LiteOS-M kernel is divided into the hardware layer and hardware-irrelevant layers. The hardware layer provides a unified hardware abstraction layer (HAL) interface for easier hardware adaptation. A range of compilation toolchains can be used with different chip architectures to meet the expansion of diversified hardware and compilation toolchains in the Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) field. Figure1 shows the architecture of the LiteOS-M kernel.
Figure 1 Architecture of the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel
Directory Structure
The directory structure is as follows. For more details, see arch_spec.md.
/kernel/liteos_m
├── components # Optional components
│ ├── backtrace # Backtrace support
│ ├── cppsupport # C++ support
│ └── cpup # CPU percent (CPUP)
│ ├── dynlink # Dynamic loading and linking
│ ├── exchook # Exception hooks
│ ├── fs # File systems
│ └── net # Networking functions
├── kal # Kernel abstraction layer
│ ├── cmsis # CMSIS API support
│ └── posix # POSIX API support
├── kernel # Minimum kernel function set
│ ├── arch # Code of the kernel instruction architecture layer
│ │ ├── arm # Code of the Arm32 architecture
│ │ └── include # APIs exposed externally
│ ├── include # APIs exposed externally
│ └── src # Source code of the minimum kernel function set
├── targets # Board-level projects
├── utils # Common directory
Constraints
OpenHarmony LiteOS-M supports only C and C++.
It applies only to Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, and RISC-V chip architectures.
As for dynamic loading module, the shared library to be loaded needs signature verification or source restriction to ensure security.
Usage
The OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel build system is a modular build system based on Generate Ninja (GN) and Ninja. It supports module-based configuration, tailoring, and assembling, and helps you build custom products. This document describes how to build a LiteOS-M project based on GN and Ninja. For details about the methods such as GCC+Makefile, IAR, and Keil MDK, visit the community websites.
Setting Up the Environment
Before setting up the environment for a development board, you must set up the basic system environment for OpenHarmony first. The basic system environment includes the OpenHarmony build environment and development environment. For details, see Setting Up Ubuntu Development Environment. You need to install Python3.7+, GN, Ninja, and hb. For the LiteOS-M kernel, you also need to install the Make build tool and GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain.
Obtaining the OpenHarmony Source Code
Obtain the latest OpenHarmony source code through Git clone on a Linux server. For details about how to obtain the source code, see Source Code Acquisition. This document assumes that the clone directory is ~/openHarmony after the complete OpenHarmony repository code is obtained.
Obtaining the Source Code of the Sample Project
The following uses the development board Nucleo-F767Zi as an example to describe how to build and run the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel project. In the local directory, run the following command to clone the sample code:
git clone https://gitee.com/harylee/nucleo_f767zi.git
The code is cloned to ~/nucleo_f767zi. Run the following commands to copy the device and vendor directories in the code directory to the corresponding directories of the openHarmony project:
mkdir ~/openHarmony/device/st
cp -r ~/nucleo_f767zi/device/st/nucleo_f767zi ~/openHarmony/device/st/nucleo_f767zi
chmod +x ~/openHarmony/device/st/nucleo_f767zi/build.sh
cp -r ~/nucleo_f767zi/vendor/st ~/openHarmony/vendor/st
For details about the directory of the sample code, see Board-Level Directory Specifications. If you need to port the development board, see Board-Level OS Porting.
Building and Running
Before the build, configure the bin directory of the cross compilation toolchain in the PATH environment variable or set board_toolchain_path in the device/st/nucleo_f767zi/liteos_m/config.gni file to the bin directory of the cross compilation toolchain. In the OpenHarmony root directory, run the hb set command to set the product path, select nucleo_f767zi, and run the hb build command to start the build.
Example:
user@dev:~/OpenHarmony$ hb set
[OHOS INFO] Input code path: # Press Enter and select nucleo_f767zi.
OHOS Which product do you need? nucleo_f767zi@st
user@dev:~/OpenHarmony$ hb build
The image is generated in the ~/openHarmony/out/nucleo_f767zi/ directory. You can download the image file to the board by using the STM32 ST-LINK Utility software and run the image.
Community Porting Project Links
The LiteOS-M kernel porting projects for specific development boards are provided by community developers. The following provides the links to these projects. If you have porting projects for more development boards, you can provide your links to share your projects.
-
Cortex-M3:
-
STM32F103 https://gitee.com/rtos_lover/stm32f103_simulator_keil
This repository provides the Keil project code for building the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel based on the STM32F103 chip architecture. This code supports build in Keil MDK mode.
-
-
Cortex-M4:
-
STM32F429IGTb https://gitee.com/harylee/stm32f429ig_firechallenger
This repository provides the project code for porting the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel to support the STM32F429IGTb development board. The code supports build in Ninja, GCC, and IAR modes.
-
-
Cortex-M7:
-
Nucleo-F767ZI https://gitee.com/harylee/nucleo_f767zi
This repository provides the project code for porting the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel to support the Nucleo-F767ZI development board. The code supports build in Ninja, GCC, and IAR modes.
-
Repositories Involved
kernel_liteos_m