Merge branch '3.0' of https://github.com/taosdata/TDengine into fix/TD-28032
This commit is contained in:
commit
411ea39649
|
|
@ -306,7 +306,7 @@ def pre_test_build_win() {
|
|||
cd %WIN_CONNECTOR_ROOT%
|
||||
python.exe -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
python -m pip uninstall taospy -y
|
||||
python -m pip install taospy==2.7.12
|
||||
python -m pip install taospy==2.7.13
|
||||
python -m pip uninstall taos-ws-py -y
|
||||
python -m pip install taos-ws-py==0.3.1
|
||||
xcopy /e/y/i/f %WIN_INTERNAL_ROOT%\\debug\\build\\lib\\taos.dll C:\\Windows\\System32
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/taosdata/TDengine)
|
||||
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/sangshuduo/tdengine-2n8ge/branch/master)
|
||||
[](https://coveralls.io/github/taosdata/TDengine?branch=develop)
|
||||
[](https://coveralls.io/github/taosdata/TDengine?branch=3.0)
|
||||
[](https://bestpractices.coreinfrastructure.org/projects/4201)
|
||||
|
||||
简体中文 | [English](README.md) | [TDengine 云服务](https://cloud.taosdata.com/?utm_medium=cn&utm_source=github) | 很多职位正在热招中,请看[这里](https://www.taosdata.com/cn/careers/)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
[](https://cloud.drone.io/taosdata/TDengine)
|
||||
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/sangshuduo/tdengine-2n8ge/branch/master)
|
||||
[](https://coveralls.io/github/taosdata/TDengine?branch=develop)
|
||||
[](https://coveralls.io/github/taosdata/TDengine?branch=3.0)
|
||||
[](https://bestpractices.coreinfrastructure.org/projects/4201)
|
||||
<br />
|
||||
[](https://twitter.com/tdenginedb)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
|||
IF (DEFINED VERNUMBER)
|
||||
SET(TD_VER_NUMBER ${VERNUMBER})
|
||||
ELSE ()
|
||||
SET(TD_VER_NUMBER "3.2.3.0.alpha")
|
||||
SET(TD_VER_NUMBER "3.2.4.0.alpha")
|
||||
ENDIF ()
|
||||
|
||||
IF (DEFINED VERCOMPATIBLE)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|||
# openssl
|
||||
ExternalProject_Add(openssl
|
||||
URL https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-3.1.3.tar.gz
|
||||
URL https://github.com/openssl/openssl/releases/download/openssl-3.1.3/openssl-3.1.3.tar.gz
|
||||
URL_HASH SHA256=f0316a2ebd89e7f2352976445458689f80302093788c466692fb2a188b2eacf6
|
||||
DOWNLOAD_NO_PROGRESS 1
|
||||
DOWNLOAD_DIR "${TD_CONTRIB_DIR}/deps-download"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
|
|
@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ Query OK, 2 row(s) in set (0.004076s)
|
|||
|
||||
## Query Examples
|
||||
|
||||
If you want query the data of "tags": {"location": "California.LosAngeles", "groupid": 1}, here is the query SQL:
|
||||
If you want query the data of "tags": {"location": "California.LosAngeles", "groupid": 1}, here is the query SQL:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT * FROM `meters_current` WHERE location = "California.LosAngeles" AND groupid = 3;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ import CAsync from "./_c_async.mdx";
|
|||
SQL is used by TDengine as its query language. Application programs can send SQL statements to TDengine through REST API or client libraries. TDengine's CLI `taos` can also be used to execute ad hoc SQL queries. Here is the list of major query functionalities supported by TDengine:
|
||||
|
||||
- Query on single column or multiple columns
|
||||
- Filter on tags or data columns: >, <, =, <\>, like
|
||||
- Filter on tags or data columns: >, <, =, <>, like
|
||||
- Grouping of results: `Group By` - Sorting of results: `Order By` - Limit the number of results: `Limit/Offset`
|
||||
- Windowed aggregate queries for time windows (interval), session windows (session), and state windows (state_window)
|
||||
- Arithmetic on columns of numeric types or aggregate results
|
||||
|
|
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ In the section describing [Insert](../insert-data/sql-writing), a database named
|
|||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
1. With either REST connection or native connection, the above sample code works well.
|
||||
2. Please note that `use db` can't be used in case of REST connection because it's stateless. You can specify the database name by either the REST endpoint's parameter or <db_name>.<table_name> in the SQL command.
|
||||
2. Please note that `use db` can't be used in case of REST connection because it's stateless. You can specify the database name by either the REST endpoint's parameter or <db_name>.<table_name> in the SQL command.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ Replace `aggfn` with the name of your function.
|
|||
|
||||
### UDF Interface Definition in C
|
||||
|
||||
There are strict naming conventions for interface functions. The names of the start, finish, init, and destroy interfaces must be <udf-name\>_start, <udf-name\>_finish, <udf-name\>_init, and <udf-name\>_destroy, respectively. Replace `scalarfn`, `aggfn`, and `udf` with the name of your user-defined function.
|
||||
There are strict naming conventions for interface functions. The names of the start, finish, init, and destroy interfaces must be <udf-name>_start, <udf-name>_finish, <udf-name>_init, and <udf-name>_destroy, respectively. Replace `scalarfn`, `aggfn`, and `udf` with the name of your user-defined function.
|
||||
|
||||
Interface functions return a value that indicates whether the operation was successful. If an operation fails, the interface function returns an error code. Otherwise, it returns TSDB_CODE_SUCCESS. The error codes are defined in `taoserror.h` and in the common API error codes in `taos.h`. For example, TSDB_CODE_UDF_INVALID_INPUT indicates invalid input. TSDB_CODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY indicates insufficient memory.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,7 +194,7 @@ typedef struct SUdfInterBuf {
|
|||
```
|
||||
The data structure is described as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- The SUdfDataBlock block includes the number of rows (numOfRows) and the number of columns (numCols). udfCols[i] (0 <= i <= numCols-1) indicates that each column is of type SUdfColumn.
|
||||
- The SUdfDataBlock block includes the number of rows (numOfRows) and the number of columns (numCols). udfCols[i] (0 <= i <= numCols-1) indicates that each column is of type SUdfColumn.
|
||||
- SUdfColumn includes the definition of the data type of the column (colMeta) and the data in the column (colData).
|
||||
- The member definitions of SUdfColumnMeta are the same as the data type definitions in `taos.h`.
|
||||
- The data in SUdfColumnData can become longer. varLenCol indicates variable-length data, and fixLenCol indicates fixed-length data.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -186,7 +186,7 @@ The base API is used to do things like create database connections and provide a
|
|||
|
||||
- The variables database and len are applied by the user outside and allocated space. The current database name and length will be assigned to database and len.
|
||||
- As long as the db name is not assigned to the database normally (including truncation), an error will be returned with the return value of -1, and then the user can use taos_errstr(NULL) to get error message.
|
||||
- If database==NULL or len<=0, returns an error, the space required to store the db (including the last '\0') in the variable required
|
||||
- If database==NULL or len<=0, returns an error, the space required to store the db (including the last '\0') in the variable required
|
||||
- If len is less than the space required to store the db (including the last '\0'), an error is returned. The truncated data assigned in the database ends with '\0'.
|
||||
- If len is greater than or equal to the space required to store the db (including the last '\0'), return normal 0, and assign the db name ending with '\0' in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ TDengine currently supports timestamp, number, character, Boolean type, and the
|
|||
| SMALLINT | i16 |
|
||||
| TINYINT | i8 |
|
||||
| BOOL | bool |
|
||||
| BINARY | Vec<u8\> |
|
||||
| BINARY | Vec<u8> |
|
||||
| NCHAR | String |
|
||||
| JSON | serde_json::Value |
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -315,7 +315,7 @@ The `connect()` function returns a `taos.TaosConnection` instance. In client-sid
|
|||
|
||||
All arguments to the `connect()` function are optional keyword arguments. The following are the connection parameters specified.
|
||||
|
||||
- `url`: The URL of taosAdapter REST service. The default is <http://localhost:6041>.
|
||||
- `url`: The URL of taosAdapter REST service. The default is `http://localhost:6041`.
|
||||
- `user`: TDengine user name. The default is `root`.
|
||||
- `password`: TDengine user password. The default is `taosdata`.
|
||||
- `timeout`: HTTP request timeout. Enter a value in seconds. The default is `socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT`. Usually, no configuration is needed.
|
||||
|
|
@ -842,12 +842,12 @@ consumer = Consumer({"group.id": "local", "td.connect.ip": "127.0.0.1"})
|
|||
|
||||
In addition to native connections, the client library also supports subscriptions via websockets.
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax for creating a consumer is "consumer = consumer = Consumer(conf=configs)". You need to specify that the `td.connect.websocket.scheme` parameter is set to "ws" in the configuration. For more subscription api parameters, please refer to [Data Subscription](../../develop/tmq/#create-a-consumer).
|
||||
The syntax for creating a consumer is "consumer = Consumer(conf=configs)". You need to specify that the `td.connect.websocket.scheme` parameter is set to "ws" in the configuration. For more subscription api parameters, please refer to [Data Subscription](../../develop/tmq/#create-a-consumer).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import taosws
|
||||
|
||||
consumer = taosws.(conf={"group.id": "local", "td.connect.websocket.scheme": "ws"})
|
||||
consumer = taosws.Consumer(conf={"group.id": "local", "td.connect.websocket.scheme": "ws"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
|
@ -887,13 +887,13 @@ The `poll` function is used to consume data in tmq. The parameter of the `poll`
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
res = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not res:
|
||||
message = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not message:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
err = res.error()
|
||||
err = message.error()
|
||||
if err is not None:
|
||||
raise err
|
||||
val = res.value()
|
||||
val = message.value()
|
||||
|
||||
for block in val:
|
||||
print(block.fetchall())
|
||||
|
|
@ -902,16 +902,14 @@ while True:
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="websocket" label="WebSocket connection">
|
||||
|
||||
The `poll` function is used to consume data in tmq. The parameter of the `poll` function is a value of type float representing the timeout in seconds. It returns a `Message` before timing out, or `None` on timing out. You have to handle error messages in response data.
|
||||
The `poll` function is used to consume data in tmq. The parameter of the `poll` function is a value of type float representing the timeout in seconds. It returns a `Message` before timing out, or `None` on timing out.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
res = consumer.poll(timeout=1.0)
|
||||
if not res:
|
||||
message = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not message:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
err = res.error()
|
||||
if err is not None:
|
||||
raise err
|
||||
|
||||
for block in message:
|
||||
for row in block:
|
||||
print(row)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ TDengine ODBC driver supports two kinds of connections to TDengine cluster, nati
|
|||
|
||||
4.2 [Connection Type]: required field, we choose "WebSocket"
|
||||
|
||||
4.3 [URL]: required field, the URL for the ODBC data source, for example, `http://localhost:6041` is the URL for a local TDengine cluster, `https://gw.cloud.taosdata.com?token=your_token` is the URL for a TDengine cloud service.
|
||||
4.3 [URL]: required field, the URL for the ODBC data source, for example, `http://localhost:6041` is the URL for a local TDengine cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
4.4 [Database]: optional field, the default database to access
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ description: This document describes the TDengine PHP client library.
|
|||
|
||||
PHP client library relies on TDengine client driver.
|
||||
|
||||
Project Repository: <https://github.com/Yurunsoft/php-tdengine>
|
||||
Project Repository: [https://github.com/Yurunsoft/php-tdengine](https://github.com/Yurunsoft/php-tdengine)
|
||||
|
||||
After TDengine client or server is installed, `taos.h` is located at:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ If you want to start your application in a container, you need to add the corres
|
|||
FROM ubuntu:20.04
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y wget
|
||||
ENV TDENGINE_VERSION=3.0.0.0
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://www.taosdata.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://tdengine.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& tar xvf TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& cd TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION} \
|
||||
&& ./install_client.sh \
|
||||
|
|
@ -229,7 +229,7 @@ Here is the full Dockerfile:
|
|||
```docker
|
||||
FROM golang:1.17.6-buster as builder
|
||||
ENV TDENGINE_VERSION=3.0.0.0
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://www.taosdata.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://tdengine.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& tar xvf TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& cd TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION} \
|
||||
&& ./install_client.sh \
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,7 +245,7 @@ RUN go build
|
|||
FROM ubuntu:20.04
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y wget
|
||||
ENV TDENGINE_VERSION=3.0.0.0
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://www.taosdata.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
RUN wget -c https://tdengine.com/assets-download/3.0/TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& tar xvf TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION}-Linux-x64.tar.gz \
|
||||
&& cd TDengine-client-${TDENGINE_VERSION} \
|
||||
&& ./install_client.sh \
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ description: This document describes how to deploy TDengine on Kubernetes.
|
|||
|
||||
As a time series database for Cloud Native architecture design, TDengine supports Kubernetes deployment. Firstly we introduce how to use YAML files to create a highly available TDengine cluster from scratch step by step for production usage, and highlight the common operations of TDengine in Kubernetes environment.
|
||||
|
||||
To meet [high availability ](https://docs.taosdata.com/tdinternal/high-availability/)requirements, clusters need to meet the following requirements:
|
||||
To meet [high availability](../../tdinternal/high-availability/) requirements, clusters need to meet the following requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- 3 or more dnodes: multiple vnodes in the same vgroup of TDengine are not allowed to be distributed in one dnode at the same time, so if you create a database with 3 replicas, the number of dnodes is greater than or equal to 3
|
||||
- 3 mnodes: mnode is responsible for the management of the entire TDengine cluster. The default number of mnode in TDengine cluster is only one. If the dnode where the mnode located is dropped, the entire cluster is unavailable.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -68,14 +68,14 @@ TDengine supports a variety of constants:
|
|||
|
||||
| # | **Syntax** | **Type** | **Description** |
|
||||
| --- | :-----------------------------------------------: | --------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 1 | [{+ \| -}]123 | BIGINT | Integer literals are of type BIGINT. Data that exceeds the length of the BIGINT type is truncated. |
|
||||
| 1 | [+ \| -]123 | BIGINT | Integer literals are of type BIGINT. Data that exceeds the length of the BIGINT type is truncated. |
|
||||
| 2 | 123.45 | DOUBLE | Floating-point literals are of type DOUBLE. Numeric values will be determined as integer or float type according to whether there is decimal point or whether scientific notation is used. |
|
||||
| 3 | 1.2E3 | DOUBLE | Literals in scientific notation are of type DOUBLE. |
|
||||
| 4 | 'abc' | BINARY | Content enclosed in single quotation marks is of type BINARY. The size of a BINARY is the size of the string in bytes. A literal single quote inside the string must be escaped with a backslash `\'`. |
|
||||
| 5 | 'abc' | BINARY | Content enclosed in double quotation marks is of type BINARY. The size of a BINARY is the size of the string in bytes. A literal double quote inside the string must be escaped with a backslash `\"`. |
|
||||
| 6 | TIMESTAMP {'literal' \| "literal"} | TIMESTAMP | The TIMESTAMP keyword indicates that the following string literal is interpreted as a timestamp. The string must be in YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.MS format. The precision is inherited from the database configuration. |
|
||||
| 7 | {TRUE \| FALSE} | BOOL | Boolean literals are of type BOOL. |
|
||||
| 8 | {'' \| "" \| '\t' \| "\t" \| ' ' \| " " \| NULL } | -- | The preceding characters indicate null literals. These can be used with any data type. |
|
||||
| 6 | TIMESTAMP ['literal' \| "literal"] | TIMESTAMP | The TIMESTAMP keyword indicates that the following string literal is interpreted as a timestamp. The string must be in YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.MS format. The precision is inherited from the database configuration. |
|
||||
| 7 | [TRUE \| FALSE] | BOOL | Boolean literals are of type BOOL. |
|
||||
| 8 | ['' \| "" \| '\t' \| "\t" \| ' ' \| " " \| NULL ] | -- | The preceding characters indicate null literals. These can be used with any data type. |
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Numeric values will be determined as integer or float type according to whether there is decimal point or whether scientific notation is used, so attention must be paid to avoid overflow. For example, 9999999999999999999 will be considered as overflow because it exceeds the upper limit of long integer, but 9999999999999999999.0 will be considered as a legal float number.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ database_option: {
|
|||
- WAL_FSYNC_PERIOD: specifies the interval (in milliseconds) at which data is written from the WAL to disk. This parameter takes effect only when the WAL parameter is set to 2. The default value is 3000. Enter a value between 0 and 180000. The value 0 indicates that incoming data is immediately written to disk.
|
||||
- MAXROWS: specifies the maximum number of rows recorded in a block. The default value is 4096.
|
||||
- MINROWS: specifies the minimum number of rows recorded in a block. The default value is 100.
|
||||
- KEEP: specifies the time for which data is retained. Enter a value between 1 and 365000. The default value is 3650. The value of the KEEP parameter must be greater than or equal to three times of the value of the DURATION parameter. TDengine automatically deletes data that is older than the value of the KEEP parameter. You can use m (minutes), h (hours), and d (days) as the unit, for example KEEP 100h or KEEP 10d. If you do not include a unit, d is used by default. TDengine Enterprise supports [Tiered Storage](https://docs.tdengine.com/tdinternal/arch/#tiered-storage) function, thus multiple KEEP values (comma separated and up to 3 values supported, and meet keep 0 <= keep 1 <= keep 2, e.g. KEEP 100h,100d,3650d) are supported; TDengine OSS does not support Tiered Storage function (although multiple keep values are configured, they do not take effect, only the maximum keep value is used as KEEP).
|
||||
- KEEP: specifies the time for which data is retained. Enter a value between 1 and 365000. The default value is 3650. The value of the KEEP parameter must be greater than or equal to three times of the value of the DURATION parameter. TDengine automatically deletes data that is older than the value of the KEEP parameter. You can use m (minutes), h (hours), and d (days) as the unit, for example KEEP 100h or KEEP 10d. If you do not include a unit, d is used by default. TDengine Enterprise supports [Tiered Storage](https://docs.tdengine.com/tdinternal/arch/#tiered-storage) function, thus multiple KEEP values (comma separated and up to 3 values supported, and meet keep 0 <= keep 1 <= keep 2, e.g. KEEP 100h,100d,3650d) are supported; TDengine OSS does not support Tiered Storage function (although multiple keep values are configured, they do not take effect, only the maximum keep value is used as KEEP).
|
||||
- PAGES: specifies the number of pages in the metadata storage engine cache on each vnode. Enter a value greater than or equal to 64. The default value is 256. The space occupied by metadata storage on each vnode is equal to the product of the values of the PAGESIZE and PAGES parameters. The space occupied by default is 1 MB.
|
||||
- PAGESIZE: specifies the size (in KB) of each page in the metadata storage engine cache on each vnode. The default value is 4. Enter a value between 1 and 16384.
|
||||
- PRECISION: specifies the precision at which a database records timestamps. Enter ms for milliseconds, us for microseconds, or ns for nanoseconds. The default value is ms.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ SELECT [hints] [DISTINCT] [TAGS] select_list
|
|||
hints: /*+ [hint([hint_param_list])] [hint([hint_param_list])] */
|
||||
|
||||
hint:
|
||||
BATCH_SCAN | NO_BATCH_SCAN | SORT_FOR_GROUP
|
||||
BATCH_SCAN | NO_BATCH_SCAN | SORT_FOR_GROUP | PARA_TABLES_SORT | PARTITION_FIRST | SMALLDATA_TS_SORT
|
||||
|
||||
select_list:
|
||||
select_expr [, select_expr] ...
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,12 +87,14 @@ Hints are a means of user control over query optimization for individual stateme
|
|||
|
||||
The list of currently supported Hints is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
| **Hint** | **Params** | **Comment** | **Scopt** |
|
||||
| **Hint** | **Params** | **Comment** | **Scope** |
|
||||
| :-----------: | -------------- | -------------------------- | -----------------------------------|
|
||||
| BATCH_SCAN | None | Batch table scan | JOIN statment for stable |
|
||||
| NO_BATCH_SCAN | None | Sequential table scan | JOIN statment for stable |
|
||||
| SORT_FOR_GROUP| None | Use sort for partition, conflict with PARTITION_FIRST | With normal column in partition by list |
|
||||
| PARTITION_FIRST| None | Use Partition before aggregate, conflict with SORT_FOR_GROUP | With normal column in partition by list |
|
||||
| PARA_TABLES_SORT| None | When sorting the supertable rows by timestamp, No temporary disk space is used. When there are numerous tables, each with long rows, the corresponding algorithm associated with this prompt may consume a substantial amount of memory, potentially leading to an Out Of Memory (OOM) situation. | Sorting the supertable rows by timestamp |
|
||||
| SMALLDATA_TS_SORT| None | When sorting the supertable rows by timestamp, if the length of query columns >= 256, and there are relatively few rows, this hint can improve performance. | Sorting the supertable rows by timestamp |
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,6 +102,8 @@ For example:
|
|||
SELECT /*+ BATCH_SCAN() */ a.ts FROM stable1 a, stable2 b where a.tag0 = b.tag0 and a.ts = b.ts;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ SORT_FOR_GROUP() */ count(*), c1 FROM stable1 PARTITION BY c1;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ PARTITION_FIRST() */ count(*), c1 FROM stable1 PARTITION BY c1;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ PARA_TABLES_SORT() */ * from stable1 order by ts;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ SMALLDATA_TS_SORT() */ * from stable1 order by ts;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Lists
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -491,6 +491,8 @@ TO_CHAR(ts, format_str_literal)
|
|||
|
||||
**Description**: Convert a ts column to string as the format specified
|
||||
|
||||
**Version**: Since ver-3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
**Return value type**: VARCHAR
|
||||
|
||||
**Applicable column types**: TIMESTAMP
|
||||
|
|
@ -550,6 +552,8 @@ TO_TIMESTAMP(ts_str_literal, format_str_literal)
|
|||
|
||||
**Description**: Convert a formated timestamp string to a timestamp
|
||||
|
||||
**Version**: Since ver-3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
**Return value type**: TIMESTAMP
|
||||
|
||||
**Applicable column types**: VARCHAR
|
||||
|
|
@ -877,11 +881,11 @@ HISTOGRAM(expr, bin_type, bin_description, normalized)
|
|||
- "user_input": "[1, 3, 5, 7]":
|
||||
User specified bin values.
|
||||
|
||||
- "linear_bin": "{"start": 0.0, "width": 5.0, "count": 5, "infinity": true}"
|
||||
- "linear_bin": "{"start": 0.0, "width": 5.0, "count": 5, "infinity": true}"
|
||||
"start" - bin starting point. "width" - bin offset. "count" - number of bins generated. "infinity" - whether to add (-inf, inf) as start/end point in generated set of bins.
|
||||
The above "linear_bin" descriptor generates a set of bins: [-inf, 0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, +inf].
|
||||
|
||||
- "log_bin": "{"start":1.0, "factor": 2.0, "count": 5, "infinity": true}"
|
||||
- "log_bin": "{"start":1.0, "factor": 2.0, "count": 5, "infinity": true}"
|
||||
"start" - bin starting point. "factor" - exponential factor of bin offset. "count" - number of bins generated. "infinity" - whether to add (-inf, inf) as start/end point in generated range of bins.
|
||||
The above "linear_bin" descriptor generates a set of bins: [-inf, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 8.0, 16.0, +inf].
|
||||
- normalized: setting to 1/0 to turn on/off result normalization. Valid values are 0 or 1.
|
||||
|
|
@ -977,7 +981,7 @@ ignore_null_values: {
|
|||
- `INTERP` is used to get the value that matches the specified time slice from a column. If no such value exists an interpolation value will be returned based on `FILL` parameter.
|
||||
- The input data of `INTERP` is the value of the specified column and a `where` clause can be used to filter the original data. If no `where` condition is specified then all original data is the input.
|
||||
- `INTERP` must be used along with `RANGE`, `EVERY`, `FILL` keywords.
|
||||
- The output time range of `INTERP` is specified by `RANGE(timestamp1,timestamp2)` parameter, with timestamp1 <= timestamp2. timestamp1 is the starting point of the output time range. timestamp2 is the ending point of the output time range.
|
||||
- The output time range of `INTERP` is specified by `RANGE(timestamp1,timestamp2)` parameter, with timestamp1 <= timestamp2. timestamp1 is the starting point of the output time range. timestamp2 is the ending point of the output time range.
|
||||
- The number of rows in the result set of `INTERP` is determined by the parameter `EVERY(time_unit)`. Starting from timestamp1, one interpolation is performed for every time interval specified `time_unit` parameter. The parameter `time_unit` must be an integer, with no quotes, with a time unit of: a(millisecond)), s(second), m(minute), h(hour), d(day), or w(week). For example, `EVERY(500a)` will interpolate every 500 milliseconds.
|
||||
- Interpolation is performed based on `FILL` parameter. For more information about FILL clause, see [FILL Clause](../distinguished/#fill-clause).
|
||||
- When only one timestamp value is specified in `RANGE` clause, `INTERP` is used to generate interpolation at this point in time. In this case, `EVERY` clause can be omitted. For example, SELECT INTERP(col) FROM tb RANGE('2023-01-01 00:00:00') FILL(linear).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -41,16 +41,28 @@ window_clause: {
|
|||
SESSION(ts_col, tol_val)
|
||||
| STATE_WINDOW(col)
|
||||
| INTERVAL(interval_val [, interval_offset]) [SLIDING (sliding_val)]
|
||||
| EVENT_WINDOW START WITH start_trigger_condition END WITH end_trigger_condition
|
||||
| COUNT_WINDOW(count_val[, sliding_val])
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`SESSION` indicates a session window, and `tol_val` indicates the maximum range of the time interval. If the time interval between two continuous rows are within the time interval specified by `tol_val` they belong to the same session window; otherwise a new session window is started automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
`EVENT_WINDOW` is determined according to the window start condition and the window close condition. The window is started when `start_trigger_condition` is evaluated to true, the window is closed when `end_trigger_condition` is evaluated to true. `start_trigger_condition` and `end_trigger_condition` can be any conditional expressions supported by TDengine and can include multiple columns.
|
||||
|
||||
`COUNT_WINDOW` is a counting window that is divided by a fixed number of data rows.`count_val`: A constant, which is a positive integer and must be greater than or equal to 2. The maximum value is 2147483648. `count_val` represents the maximum number of data rows contained in each `COUNT_WINDOW`. When the total number of data rows cannot be divided by `count_val`, the number of rows in the last window will be less than `count_val`. `sliding_val`: is a constant that represents the number of window slides, similar to `SLIDING` in `INTERVAL`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the following SQL statement creates a stream and automatically creates a supertable named `avg_vol`. The stream has a 1 minute time window that slides forward in 30 second intervals to calculate the average voltage of the meters supertable.
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE STREAM avg_vol_s INTO avg_vol AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) FROM meters PARTITION BY tbname INTERVAL(1m) SLIDING(30s);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE STREAM streams0 INTO streamt0 AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) from meters PARTITION BY tbname EVENT_WINDOW START WITH voltage < 0 END WITH voltage > 9;
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE STREAM streams1 IGNORE EXPIRED 1 WATERMARK 100s INTO streamt1 AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) from meters PARTITION BY tbname COUNT_WINDOW(10);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Partitions of Stream
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,7 +79,7 @@ If a stream is created with PARTITION BY clause and SUBTABLE clause, the name of
|
|||
CREATE STREAM avg_vol_s INTO avg_vol SUBTABLE(CONCAT('new-', tname)) AS SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) FROM meters PARTITION BY tbname tname INTERVAL(1m);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
IN PARTITION clause, 'tbname', representing each subtable name of source supertable, is given alias 'tname'. And 'tname' is used in SUBTABLE clause. In SUBTABLE clause, each auto created subtable will concat 'new-' and source subtable name as their name. Other expressions are also allowed in SUBTABLE clause, but the output type must be varchar.
|
||||
IN PARTITION clause, 'tbname', representing each subtable name of source supertable, is given alias 'tname'. And 'tname' is used in SUBTABLE clause. In SUBTABLE clause, each auto created subtable will concat 'new-' and source subtable name as their name(Starting from 3.2.3.0, in order to avoid the expression in subtable being unable to distinguish between different subtables, add '_groupId' to the end of subtable name).
|
||||
|
||||
If the output length exceeds the limitation of TDengine(192), the name will be truncated. If the generated name is occupied by some other table, the creation and writing of the new subtable will be failed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -35,9 +35,9 @@ TDengine supports the `UNION` and `UNION ALL` operations. UNION ALL collects all
|
|||
| # | **Operator** | **Supported Data Types** | **Description** |
|
||||
| --- | :---------------: | -------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------- |
|
||||
| 1 | = | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON | Equal to |
|
||||
| 2 | <\>, != | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON; the primary key (timestamp) is also not supported | Not equal to |
|
||||
| 3 | \>, < | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON | Greater than and less than |
|
||||
| 4 | \>=, <= | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON | Greater than or equal to and less than or equal to |
|
||||
| 2 | <>, != | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON; the primary key (timestamp) is also not supported | Not equal to |
|
||||
| 3 | >, < | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON | Greater than and less than |
|
||||
| 4 | >=, <= | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON | Greater than or equal to and less than or equal to |
|
||||
| 5 | IS [NOT] NULL | All types | Indicates whether the value is null |
|
||||
| 6 | [NOT] BETWEEN AND | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, JSON and GEOMETRY | Closed interval comparison |
|
||||
| 7 | IN | All types except BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and JSON; the primary key (timestamp) is also not supported | Equal to any value in the list |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,14 +7,14 @@ description: This document describes the usage of escape characters in TDengine.
|
|||
|
||||
| Escape Character | **Actual Meaning** |
|
||||
| :--------------: | ------------------------ |
|
||||
| `\'` | Single quote ' |
|
||||
| `\"` | Double quote " |
|
||||
| \n | Line Break |
|
||||
| \r | Carriage Return |
|
||||
| \t | tab |
|
||||
| `\\` | Back Slash \ |
|
||||
| `\%` | % see below for details |
|
||||
| `\_` | \_ see below for details |
|
||||
| `\'` | Single quote `'` |
|
||||
| `\"` | Double quote `"` |
|
||||
| `\n` | Line Break |
|
||||
| `\r` | Carriage Return |
|
||||
| `\t` | tab |
|
||||
| `\\` | Back Slash `\ ` |
|
||||
| `\%` | `%` see below for details |
|
||||
| `\_` | `_` see below for details |
|
||||
|
||||
## Restrictions
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,5 +22,5 @@ description: This document describes the usage of escape characters in TDengine.
|
|||
- Identifier without ``: Error will be returned because identifier must be constituted of digits, ASCII characters or underscore and can't be started with digits
|
||||
- Identifier quoted with ``: Original content is kept, no escaping
|
||||
2. If there are escape characters in values
|
||||
- The escape characters will be escaped as the above table. If the escape character doesn't match any supported one, the escape character "\" will be ignored.
|
||||
- "%" and "\_" are used as wildcards in `like`. `\%` and `\_` should be used to represent literal "%" and "\_" in `like`,. If `\%` and `\_` are used out of `like` context, the evaluation result is "`\%`"and "`\_`", instead of "%" and "\_".
|
||||
- The escape characters will be escaped as the above table. If the escape character doesn't match any supported one, the escape character `\ ` will be ignored(`\x` remaining).
|
||||
- `%` and `_` are used as wildcards in `like`. `\%` and `\_` should be used to represent literal `%` and `_` in `like`. If `\%` and `\_` are used out of `like` context, the evaluation result is `\%` and `\_`, instead of `%` and `_`.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ The following data types can be used in the schema for standard tables.
|
|||
| 44 | SHOW STREAMS | Modified | This statement previously showed continuous queries. The continuous query feature has been replaced with the stream processing feature. This statement now shows streams that have been created.
|
||||
| 45 | SHOW SUBSCRIPTIONS | Added | Shows all subscriptions in the current database.
|
||||
| 46 | SHOW TABLES | Modified | Only shows table names.
|
||||
| 47 | SHOW TABLE DISTRIBUTED | Added | Shows how table data is distributed. This replaces the `SELECT _block_dist() FROM { tb_name | stb_name }` command.
|
||||
| 47 | SHOW TABLE DISTRIBUTED | Added | Shows how table data is distributed. This replaces the `SELECT _block_dist() FROM { tb_name | stb_name }` command.
|
||||
| 48 | SHOW TOPICS | Added | Shows all subscribed topics in the current database.
|
||||
| 49 | SHOW TRANSACTIONS | Added | Shows all running transactions in the system.
|
||||
| 50 | SHOW DNODE VARIABLES | Added | Shows the configuration of the specified dnode.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Diagnostic steps:
|
|||
2. On the server side, execute command `taos -n server -P <port> -l <pktlen>` to monitor the port range starting from the port specified by `-P` parameter with the role of "server".
|
||||
3. On the client side, execute command `taos -n client -h <fqdn of server> -P <port> -l <pktlen>` to send a testing package to the specified server and port.
|
||||
|
||||
-l <pktlen\>: The size of the testing package, in bytes. The value range is [11, 64,000] and default value is 1,000.
|
||||
-l <pktlen>: The size of the testing package, in bytes. The value range is [11, 64,000] and default value is 1,000.
|
||||
Please note that the package length must be same in the above 2 commands executed on server side and client side respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
Output of the server side for the example is below:
|
||||
|
|
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ Once this parameter is set to 135 or 143, the log file grows very quickly especi
|
|||
|
||||
## Client Log
|
||||
|
||||
An independent log file, named as "taoslog+<seq num\>" is generated for each client program, i.e. a client process. The parameter `debugFlag` is used to control the log level. The default value is 131. For debugging and tracing, it needs to be set to either 135 or 143 respectively.
|
||||
An independent log file, named as "taoslog+<seq num>" is generated for each client program, i.e. a client process. The parameter `debugFlag` is used to control the log level. The default value is 131. For debugging and tracing, it needs to be set to either 135 or 143 respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
The default value of `debugFlag` is also 131 and only logs at level of INFO/ERROR/WARNING are recorded. As stated above, for debugging and tracing, it needs to be changed to 135 or 143 respectively, so that logs at DEBUG or TRACE level can be recorded.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ Parameter Description:
|
|||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
URL Encoding. Make sure that parameters are properly encoded. For example, when specifying a timezone you must properly encode special characters. ?tz=Etc/GMT+10 will not work because the <+> plus symbol is recognized as a space in the url. It's best practice to encode all special characters in a parameter. Instead use ?tz=Etc%2FGMT%2B10 for the parameter.
|
||||
URL Encoding. Make sure that parameters are properly encoded. For example, when specifying a timezone you must properly encode special characters. ?tz=Etc/GMT+10 will not work because the + plus symbol is recognized as a space in the url. It's best practice to encode all special characters in a parameter. Instead use ?tz=Etc%2FGMT%2B10 for the parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -166,8 +166,8 @@ See [example/config/taosadapter.toml](https://github.com/taosdata/taosadapter/bl
|
|||
- Compatible with InfluxDB v1 write interface
|
||||
[https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/reference/api/influxdb-1x/write/](https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/reference/api/influxdb-1x/write/)
|
||||
- Compatible with OpenTSDB JSON and telnet format writes
|
||||
- <http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_http/put.html>
|
||||
- <http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_telnet/put.html>
|
||||
- [http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_http/put.html](http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_http/put.html)
|
||||
- [http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_telnet/put.html](http://opentsdb.net/docs/build/html/api_telnet/put.html)
|
||||
- Seamless connection to collectd
|
||||
collectd is a system statistics collection daemon, please visit [https://collectd.org/](https://collectd.org/) for more information.
|
||||
- Seamless connection with StatsD
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -94,67 +94,67 @@ taosBenchmark -f <json file>
|
|||
|
||||
## Command-line argument in detail
|
||||
|
||||
- **-f/--file <json file\>** :
|
||||
- **-f/--file <json file>** :
|
||||
specify the configuration file to use. This file includes All parameters. Users should not use this parameter with other parameters on the command-line. There is no default value.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-c/--config-dir <dir\>** :
|
||||
- **-c/--config-dir <dir>** :
|
||||
specify the directory where the TDengine cluster configuration file. The default path is `/etc/taos`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-h/--host <host\>** :
|
||||
- **-h/--host <host>** :
|
||||
Specify the FQDN of the TDengine server to connect to. The default value is localhost.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-P/--port <port\>** :
|
||||
- **-P/--port <port>** :
|
||||
The port number of the TDengine server to connect to, the default value is 6030.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-I/--interface <insertMode\>** :
|
||||
- **-I/--interface <insertMode>** :
|
||||
Insert mode. Options are taosc, rest, stmt, sml, sml-rest, corresponding to normal write, restful interface writing, parameter binding interface writing, schemaless interface writing, RESTful schemaless interface writing (provided by taosAdapter). The default value is taosc.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-u/--user <user\>** :
|
||||
- **-u/--user <user>** :
|
||||
User name to connect to the TDengine server. Default is root.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-U/--supplement-insert ** :
|
||||
Supplementally insert data without create database and table, optional, default is off.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-p/--password <passwd\>** :
|
||||
- **-p/--password <passwd>** :
|
||||
The default password to connect to the TDengine server is `taosdata`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-o/--output <file\>** :
|
||||
- **-o/--output <file>** :
|
||||
specify the path of the result output file, the default value is `. /output.txt`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-T/--thread <threadNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-T/--thread <threadNum>** :
|
||||
The number of threads to insert data. Default is 8.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-B/--interlace-rows <rowNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-B/--interlace-rows <rowNum>** :
|
||||
Enables interleaved insertion mode and specifies the number of rows of data to be inserted into each child table. Interleaved insertion mode means inserting the number of rows specified by this parameter into each sub-table and repeating the process until all sub-tables have been inserted. The default value is 0, i.e., data is inserted into one sub-table before the next sub-table is inserted.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-i/--insert-interval <timeInterval\>** :
|
||||
- **-i/--insert-interval <timeInterval>** :
|
||||
Specify the insert interval in `ms` for interleaved insert mode. The default value is 0. It only works if `-B/--interlace-rows` is greater than 0. After inserting interlaced rows for each child table, the data insertion thread will wait for the interval specified by this value before proceeding to the next round of writes.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-r/--rec-per-req <rowNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-r/--rec-per-req <rowNum>** :
|
||||
Writing the number of rows of records per request to TDengine, the default value is 30000.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-t/--tables <tableNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-t/--tables <tableNum>** :
|
||||
Specify the number of sub-tables. The default is 10000.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-S/--timestampstep <stepLength\>** :
|
||||
- **-S/--timestampstep <stepLength>** :
|
||||
Timestamp step for inserting data in each child table in ms, default is 1.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-n/--records <recordNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-n/--records <recordNum>** :
|
||||
The default value of the number of records inserted in each sub-table is 10000.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-d/--database <dbName\>** :
|
||||
- **-d/--database <dbName>** :
|
||||
The name of the database used, the default value is `test`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-b/--data-type <colType\>** :
|
||||
- **-b/--data-type <colType>** :
|
||||
specify the type of the data columns of the super table. It defaults to three columns of type FLOAT, INT, and FLOAT if not used.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-l/--columns <colNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-l/--columns <colNum>** :
|
||||
specify the number of columns in the super table. If both this parameter and `-b/--data-type` is set, the final result number of columns is the greater of the two. If the number specified by this parameter is greater than the number of columns specified by `-b/--data-type`, the unspecified column type defaults to INT, for example: `-l 5 -b float,double`, then the final column is `FLOAT,DOUBLE,INT,INT,INT`. If the number of columns specified is less than or equal to the number of columns specified by `-b/--data-type`, then the result is the column and type specified by `-b/--data-type`, e.g.: `-l 3 -b float,double,float,bigint`. The last column is `FLOAT,DOUBLE, FLOAT,BIGINT`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-L/--partial-col-num <colNum\> ** :
|
||||
- **-L/--partial-col-num <colNum> ** :
|
||||
Specify first numbers of columns has data. Rest of columns' data are NULL. Default is all columns have data.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-A/--tag-type <tagType\>** :
|
||||
- **-A/--tag-type <tagType>** :
|
||||
The tag column type of the super table. nchar and binary types can both set the length, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -168,10 +168,10 @@ Note: In some shells, such as bash, "()" needs to be escaped, so the above comma
|
|||
taosBenchmark -A INT,DOUBLE,NCHAR,BINARY\(16\)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **-w/--binwidth <length\>**:
|
||||
- **-w/--binwidth <length>**:
|
||||
specify the default length for nchar and binary types. The default value is 64.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-m/--table-prefix <tablePrefix\>** :
|
||||
- **-m/--table-prefix <tablePrefix>** :
|
||||
The prefix of the sub-table name, the default value is "d".
|
||||
|
||||
- **-E/--escape-character** :
|
||||
|
|
@ -192,25 +192,25 @@ taosBenchmark -A INT,DOUBLE,NCHAR,BINARY\(16\)
|
|||
- **-y/--answer-yes** :
|
||||
Switch parameter that requires the user to confirm at the prompt to continue. The default value is false.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-O/--disorder <Percentage\>** :
|
||||
- **-O/--disorder <Percentage>** :
|
||||
Specify the percentage probability of disordered data, with a value range of [0,50]. The default is 0, i.e., there is no disordered data.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-R/--disorder-range <timeRange\>** :
|
||||
- **-R/--disorder-range <timeRange>** :
|
||||
Specify the timestamp range for the disordered data. It leads the resulting disorder timestamp as the ordered timestamp minus a random value in this range. Valid only if the percentage of disordered data specified by `-O/--disorder` is greater than 0.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-F/--prepared_rand <Num\>** :
|
||||
- **-F/--prepared_rand <Num>** :
|
||||
Specify the number of unique values in the generated random data. A value of 1 means that all data are equal. The default value is 10000.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-a/--replica <replicaNum\>** :
|
||||
- **-a/--replica <replicaNum>** :
|
||||
Specify the number of replicas when creating the database. The default value is 1.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-k/--keep-trying <NUMBER\>** :
|
||||
- **-k/--keep-trying <NUMBER>** :
|
||||
Keep trying if failed to insert, default is no. Available with v3.0.9+.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-z/--trying-interval <NUMBER\>** :
|
||||
- **-z/--trying-interval <NUMBER&;gt;** :
|
||||
Specify interval between keep trying insert. Valid value is a positive number. Only valid when keep trying be enabled. Available with v3.0.9+.
|
||||
|
||||
- **-v/--vgroups <NUMBER\>** :
|
||||
- **-v/--vgroups <NUMBER>** :
|
||||
Specify vgroups number for creating a database, only valid with daemon version 3.0+
|
||||
|
||||
- **-V/--version** :
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,7 +226,7 @@ taosBenchmark -A INT,DOUBLE,NCHAR,BINARY\(16\)
|
|||
The parameters listed in this section apply to all function modes.
|
||||
|
||||
- **filetype** : The function to be tested, with optional values `insert`, `query` and `subscribe`. These correspond to the insert, query, and subscribe functions, respectively. Users can specify only one of these in each configuration file.
|
||||
**cfgdir**: specify the TDengine client configuration file's directory. The default path is /etc/taos.
|
||||
**cfgdir**: specify the TDengine client configuration file's directory. The default path is `/etc/taos`.
|
||||
|
||||
- **host**: Specify the FQDN of the TDengine server to connect. The default value is `localhost`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Users should not use taosdump to back up raw data, environment settings, hardwar
|
|||
|
||||
There are two ways to install taosdump:
|
||||
|
||||
- Install the taosTools official installer. Please find taosTools from [Release History](https://docs.taosdata.com/releases/tools/) page and download and install it.
|
||||
- Install the taosTools official installer. Please find taosTools from [Release History](../../releases/tools/) page and download and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
- Compile taos-tools separately and install it. Please refer to the [taos-tools](https://github.com/taosdata/taos-tools) repository for details.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -226,9 +226,10 @@ Please note the `taoskeeper` needs to be installed and running to create the `lo
|
|||
| Attribute | Description |
|
||||
| ------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Applicable | Client only |
|
||||
| Meaning | When the Last, First, LastRow function is queried, whether the returned column name contains the function name. |
|
||||
| Value Range | 0 means including the function name, 1 means not including the function name. |
|
||||
| Default Value | 0 |
|
||||
| Meaning | When the Last, First, and LastRow functions are queried and no alias is specified, the alias is automatically set to the column name (excluding the function name). Therefore, if the order by clause refers to the column name, it will automatically refer to the function corresponding to the column. |
|
||||
| Value Range | 1 means automatically setting the alias to the column name (excluding the function name), 0 means not automatically setting the alias. |
|
||||
| Default Value | 0 |
|
||||
| Notes | When multiple of the above functions act on the same column at the same time and no alias is specified, if the order by clause refers to the column name, column selection ambiguous will occur because the aliases of multiple columns are the same. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Locale Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -288,7 +289,7 @@ A specific type "nchar" is provided in TDengine to store non-ASCII characters su
|
|||
|
||||
The characters input on the client side are encoded using the default system encoding, which is UTF-8 on Linux/macOS, or GB18030 or GBK on some systems in Chinese, POSIX in docker, CP936 on Windows in Chinese. The encoding of the operating system in use must be set correctly so that the characters in nchar type can be converted to UCS4-LE.
|
||||
|
||||
The locale definition standard on Linux/macOS is: <Language\>\_<Region\>.<charset\>, for example, in "zh_CN.UTF-8", "zh" means Chinese, "CN" means China mainland, "UTF-8" means charset. The charset indicates how to display the characters. On Linux/macOS, the charset can be set by locale in the system. On Windows system another configuration parameter `charset` must be used to configure charset because the locale used on Windows is not POSIX standard. Of course, `charset` can also be used on Linux/macOS to specify the charset.
|
||||
The locale definition standard on Linux/macOS is: <Language>\_<Region>.<charset>, for example, in "zh_CN.UTF-8", "zh" means Chinese, "CN" means China mainland, "UTF-8" means charset. The charset indicates how to display the characters. On Linux/macOS, the charset can be set by locale in the system. On Windows system another configuration parameter `charset` must be used to configure charset because the locale used on Windows is not POSIX standard. Of course, `charset` can also be used on Linux/macOS to specify the charset.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -84,18 +84,22 @@ Schemaless writes process row data according to the following principles.
|
|||
|
||||
1. You can use the following rules to generate the subtable names: first, combine the measurement name and the key and value of the label into the next string:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"measurement,tag_key1=tag_value1,tag_key2=tag_value2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"measurement,tag_key1=tag_value1,tag_key2=tag_value2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
Note that tag_key1, tag_key2 are not the original order of the tags entered by the user but the result of using the tag names in ascending order of the strings. Therefore, tag_key1 is not the first tag entered in the line protocol.
|
||||
The string's MD5 hash value "md5_val" is calculated after the ranking is completed. The calculation result is then combined with the string to generate the table name: "t_md5_val". "t\_" is a fixed prefix that every table generated by this mapping relationship has.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
Note that tag_key1, tag_key2 are not the original order of the tags entered by the user but the result of using the tag names in ascending order of the strings. Therefore, tag_key1 is not the first tag entered in the line protocol.
|
||||
The string's MD5 hash value "md5_val" is calculated after the ranking is completed. The calculation result is then combined with the string to generate the table name: "t_md5_val". "t\_" is a fixed prefix that every table generated by this mapping relationship has.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not want to use an automatically generated table name, there are two ways to specify sub table names, the first one has a higher priority.
|
||||
You can configure smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter in taos.cfg(except for `@ # space \r \t \n`), for example, `smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter=tname`. You can insert `st,t0=cpul,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000` and the table name will be cpu1-4.
|
||||
You can configure smlChildTableName in taos.cfg to specify table names, for example, `smlChildTableName=tname`. You can insert `st,tname=cpul,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000` and the cpu1 table will be automatically created. Note that if multiple rows have the same tname but different tag_set values, the tag_set of the first row is used to create the table and the others are ignored.
|
||||
If you do not want to use an automatically generated table name, there are two ways to specify sub table names(the first one has a higher priority).
|
||||
|
||||
1. You can configure smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter in taos.cfg(except for `@ # space \r \t \n`).
|
||||
1. For example, `smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter=tname`. You can insert `st,t0=cpul,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000` and the table name will be cpu1-4.
|
||||
|
||||
2. You can configure smlChildTableName in taos.cfg to specify table names.
|
||||
2. For example, `smlChildTableName=tname`. You can insert `st,tname=cpul,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000` and the cpu1 table will be automatically created. Note that if multiple rows have the same tname but different tag_set values, the tag_set of the first row is used to create the table and the others are ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
2. If the super table obtained by parsing the line protocol does not exist, this super table is created.
|
||||
**Important:** Manually creating supertables for schemaless writing is not supported. Schemaless writing creates appropriate supertables automatically.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ LoadPlugin network
|
|||
</Plugin>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where <taosAdapter's host\> fills in the server's domain name or IP address running taosAdapter. <port for collectd direct\> fills in the port that taosAdapter uses to receive collectd data (default is 6045).
|
||||
where <taosAdapter's host> fills in the server's domain name or IP address running taosAdapter. <port for collectd direct> fills in the port that taosAdapter uses to receive collectd data (default is 6045).
|
||||
|
||||
An example is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ LoadPlugin write_tsdb
|
|||
</Plugin>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where <taosAdapter's host\> is the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter. <port for collectd write_tsdb plugin\> Fill in the data that taosAdapter uses to receive the collectd write_tsdb plugin (default is 6047).
|
||||
Where <taosAdapter's host> is the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter. <port for collectd write_tsdb plugin> Fill in the data that taosAdapter uses to receive the collectd write_tsdb plugin (default is 6047).
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
LoadPlugin write_tsdb
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ The default database name written by the taosAdapter is `icinga2`. You can also
|
|||
### Configure icinga3
|
||||
|
||||
- Enable opentsdb-writer for icinga2 (refer to the link https://icinga.com/docs/icinga-2/latest/doc/14-features/#opentsdb-writer)
|
||||
- Modify the configuration file `/etc/icinga2/features-enabled/opentsdb.conf` by filling in <taosAdapter's host\> as the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter and <port for icinga2\> as the corresponding port on which taosAdapter supports receiving icinga2 data (default is 6048)
|
||||
- Modify the configuration file `/etc/icinga2/features-enabled/opentsdb.conf` by filling in <taosAdapter's host> as the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter and <port for icinga2> as the corresponding port on which taosAdapter supports receiving icinga2 data (default is 6048)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
object OpenTsdbWriter "opentsdb" {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,8 +9,8 @@ Point the `remote_read url` and `remote_write url` to the domain name or IP addr
|
|||
|
||||
### Configure Basic authentication
|
||||
|
||||
- username: <TDengine's username>
|
||||
- password: <TDengine's password>
|
||||
- username: TDengine's username
|
||||
- password: TDengine's password
|
||||
|
||||
### Example configuration of remote_write and remote_read related sections in prometheus.yml file
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ The default database name written by taosAdapter is `statsd`. To specify a diffe
|
|||
|
||||
### Configuring StatsD
|
||||
|
||||
To use StatsD, you need to download its [source code](https://github.com/statsd/statsd). Please refer to the example file `exampleConfig.js` in the root directory of the source download to modify the configuration file. In <taosAdapter's host\>, please fill in the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter, and <port for StatsD\>, please fill in the port where taosAdapter receives StatsD data (default is 6044).
|
||||
To use StatsD, you need to download its [source code](https://github.com/statsd/statsd). Please refer to the example file `exampleConfig.js` in the root directory of the source download to modify the configuration file. In <taosAdapter's host>, please fill in the domain name or IP address of the server running taosAdapter, and <port for StatsD>, please fill in the port where taosAdapter receives StatsD data (default is 6044).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
backends section add ". /backends/repeater"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ In the Telegraf configuration file (default location `/etc/telegraf/telegraf.con
|
|||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where <taosAdapter's host\> please fill in the server's domain name or IP address running the taosAdapter service. <REST service port\> please fill in the port of the REST service (default is 6041). <TDengine's username\> and <TDengine's password\> please fill in the actual configuration of the currently running TDengine. And <database name\> please fill in the database name where you want to store Telegraf data in TDengine.
|
||||
Where <taosAdapter's host> please fill in the server's domain name or IP address running the taosAdapter service. <REST service port> please fill in the port of the REST service (default is 6041). <TDengine's username> and <TDengine's password> please fill in the actual configuration of the currently running TDengine. And <database name> please fill in the database name where you want to store Telegraf data in TDengine.
|
||||
|
||||
An example is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Record these values:
|
|||
|
||||
## Installing Grafana
|
||||
|
||||
TDengine currently supports Grafana versions 7.5 and above. Users can go to the Grafana official website to download the installation package and execute the installation according to the current operating system. The download address is as follows: <https://grafana.com/grafana/download>.
|
||||
TDengine currently supports Grafana versions 7.5 and above. Users can go to the Grafana official website to download the installation package and execute the installation according to the current operating system. The download address is as follows: [https://grafana.com/grafana/download](https://grafana.com/grafana/download).
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring Grafana
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ bash -c "$(curl -fsSL \
|
|||
-p taosdata
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Restart Grafana service and open Grafana in web-browser, usually <http://localhost:3000>.
|
||||
Restart Grafana service and open Grafana in web-browser, usually `http://localhost:3000`.
|
||||
|
||||
Save the script and type `./install.sh --help` for the full usage of the script.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,7 +181,7 @@ You can setup a zero-configuration stack for TDengine + Grafana by [docker-compo
|
|||
|
||||
3. Start TDengine and Grafana services: `docker-compose up -d`.
|
||||
|
||||
Open Grafana <http://localhost:3000>, and you can add dashboard with TDengine now.
|
||||
Open Grafana (http://localhost:3000), and you can add dashboard with TDengine now.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
|
@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ As shown above, select the `TDengine` data source in the `Query` and enter the c
|
|||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
Since the REST connection because is stateless. Grafana plugin can use <db_name>.<table_name> in the SQL command to specify the database name.
|
||||
Since the REST connection because is stateless. Grafana plugin can use <db_name>.<table_name> in the SQL command to specify the database name.
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -345,7 +345,7 @@ The following configuration items apply to TDengine Sink Connector and TDengine
|
|||
### TDengine Sink Connector specific configuration
|
||||
|
||||
1. `connection.database`: The name of the target database. If the specified database does not exist, it will be created automatically. The time precision used for automatic library building is nanoseconds. The default value is null. When it is NULL, refer to the description of the `connection.database.prefix` parameter for the naming rules of the target database
|
||||
2. `connection.database.prefix`: When `connection.database` is null, the prefix of the target database. Can contain placeholder '${topic}'. For example, kafka_${topic}, for topic 'orders' will be written to database 'kafka_orders'. Default null. When null, the name of the target database is the same as the name of the topic.
|
||||
2. `connection.database.prefix`: When `connection.database` is null, the prefix of the target database. Can contain placeholder '${topic}'. For example, kafka_${topic}, for topic 'orders' will be written to database 'kafka_orders'. Default null. When null, the name of the target database is the same as the name of the topic.
|
||||
3. `batch.size`: Write the number of records in each batch in batches. When the data received by the sink connector at one time is larger than this value, it will be written in some batches.
|
||||
4. `max.retries`: The maximum number of retries when an error occurs. Defaults to 1.
|
||||
5. `retry.backoff.ms`: The time interval for retry when sending an error. The unit is milliseconds. The default is 3000.
|
||||
|
|
@ -370,12 +370,12 @@ The following configuration items apply to TDengine Sink Connector and TDengine
|
|||
|
||||
## Other notes
|
||||
|
||||
1. To use Kafka Connect, refer to <https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#connect>.
|
||||
1. To use Kafka Connect, refer to [https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#connect](https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#connect).
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
<https://github.com/taosdata/kafka-connect-tdengine/issues>
|
||||
[https://github.com/taosdata/kafka-connect-tdengine/issues](https://github.com/taosdata/kafka-connect-tdengine/issues)
|
||||
|
||||
## Reference
|
||||
|
||||
1. For more information, see <https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/>
|
||||
1. For more information, see [https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/](https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ With TDengine ODBC driver, PowerBI can access time series data stored in TDengin
|
|||
|
||||
## Install Driver
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your TDengine server version, download appropriate version of TDengine client package from TDengine website [Download Link](https://docs.taosdata.com/get-started/package/), or TDengine explorer if you are using a local TDengine cluster. Install the TDengine client package on same Windows machine where PowerBI is running.
|
||||
Depending on your TDengine server version, download appropriate version of TDengine client package from TDengine website [Download Link](../../get-started/package/), or TDengine explorer if you are using a local TDengine cluster. Install the TDengine client package on same Windows machine where PowerBI is running.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Data Source
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ To better use Power BI to analyze the data stored in TDengine, you need to under
|
|||
|
||||
1. Dimention: it's normally category (text) data to describe such information as device, collection point, model. In the supertable template of TDengine, we use tag columns to store the dimention information. You can use SQL like `select distinct tbname, tag1, tag2 from supertable` to get dimentions.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Metric: quantitive (numeric) fileds that can be calculated, like SUM, AVERAGE, MINIMUM. If the collecting frequency is 1 second, then there are 31,536,000 records in one year, it will be too low efficient to import so big data into Power BI. In TDengine, you can use data partition query, window partition query, in combination with pseudo columns related to window, to import downsampled data into Power BI. For more details, please refer to [TDengine Specialized Queries](https://docs.taosdata.com/taos-sql/distinguished/)。
|
||||
2. Metric: quantitive (numeric) fileds that can be calculated, like SUM, AVERAGE, MINIMUM. If the collecting frequency is 1 second, then there are 31,536,000 records in one year, it will be too low efficient to import so big data into Power BI. In TDengine, you can use data partition query, window partition query, in combination with pseudo columns related to window, to import downsampled data into Power BI. For more details, please refer to [TDengine Specialized Queries](../../taos-sql/distinguished/)。
|
||||
|
||||
- Window partition query: for example, thermal meters collect one data per second, but you need to query the average temperature every 10 minutes, you can use window subclause to get the downsampling data you need. The corresponding SQL is like `select tbname, _wstart date,avg(temperature) temp from table interval(10m)`, in which _wstart is a pseudo column indicting the start time of a widow, 10m is the duration of the window, `avg(temperature)` indicates the aggregate value inside a window.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -184,8 +184,6 @@ TDengine supports the standard JDBC 3.0 interface for manipulating databases, bu
|
|||
|
||||
To facilitate historical data migration, we provide a plug-in for the data synchronization tool DataX, which can automatically write data into TDengine.The automatic data migration of DataX can only support the data migration process of a single value model.
|
||||
|
||||
For the specific usage of DataX and how to use DataX to write data to TDengine, please refer to [DataX-based TDengine Data Migration Tool](https://www.taosdata.com/engineering/16401.html).
|
||||
|
||||
After migrating via DataX, we found that we can significantly improve the efficiency of migrating historical data by starting multiple processes and migrating numerous metrics simultaneously. The following are some records of the migration process. We provide these as a reference for application migration.
|
||||
|
||||
| Number of datax instances (number of concurrent processes) | Migration record speed (pieces/second) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,6 +10,10 @@ For TDengine 2.x installation packages by version, please visit [here](https://t
|
|||
|
||||
import Release from "/components/ReleaseV3";
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.2.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
<Release type="tdengine" version="3.2.3.0" />
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
<Release type="tdengine" version="3.2.2.0" />
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ description: This document provides download links for all released versions of
|
|||
|
||||
taosTools installation packages can be downloaded at the following links:
|
||||
|
||||
For other historical version installers, please visit [here](https://www.taosdata.com/all-downloads).
|
||||
For other historical version installers, please visit [here](https://tdengine.com/downloads/historical/).
|
||||
|
||||
import Release from "/components/ReleaseV3";
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ title: 流式计算
|
|||
|
||||
TDengine 3.0 的流式计算引擎提供了实时处理写入的数据流的能力,使用 SQL 定义实时流变换,当数据被写入流的源表后,数据会被以定义的方式自动处理,并根据定义的触发模式向目的表推送结果。它提供了替代复杂流处理系统的轻量级解决方案,并能够在高吞吐的数据写入的情况下,提供毫秒级的计算结果延迟。
|
||||
|
||||
流式计算可以包含数据过滤,标量函数计算(含UDF),以及窗口聚合(支持滑动窗口、会话窗口与状态窗口),可以以超级表、子表、普通表为源表,写入到目的超级表。在创建流时,目的超级表将被自动创建,随后新插入的数据会被流定义的方式处理并写入其中,通过 partition by 子句,可以以表名或标签划分 partition,不同的 partition 将写入到目的超级表的不同子表。
|
||||
流式计算可以包含数据过滤,标量函数计算(含UDF),以及窗口聚合(支持滑动窗口、会话窗口、状态窗口、事件窗口与计数窗口),可以以超级表、子表、普通表为源表,写入到目的超级表。在创建流时,目的超级表将被自动创建,随后新插入的数据会被流定义的方式处理并写入其中,通过 partition by 子句,可以以表名或标签划分 partition,不同的 partition 将写入到目的超级表的不同子表。
|
||||
|
||||
TDengine 的流式计算能够支持分布在多个 vnode 中的超级表聚合;还能够处理乱序数据的写入:它提供了 watermark 机制以度量容忍数据乱序的程度,并提供了 ignore expired 配置项以决定乱序数据的处理策略——丢弃或者重新计算。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,43 +15,82 @@ import Node from "./_sub_node.mdx";
|
|||
import CSharp from "./_sub_cs.mdx";
|
||||
import CDemo from "./_sub_c.mdx";
|
||||
|
||||
为了帮助应用实时获取写入 TDengine 的数据,或者以事件到达顺序处理数据,TDengine 提供了类似消息队列产品的数据订阅、消费接口。这样在很多场景下,采用 TDengine 的时序数据处理系统不再需要集成消息队列产品,比如 kafka, 从而简化系统设计的复杂度,降低运营维护成本。
|
||||
为了帮助应用实时获取写入 TDengine 的数据,或者以事件到达顺序处理数据,TDengine 提供了类似 kafka 的数据订阅功能。这样在很多场景下,采用 TDengine 的时序数据处理系统不再需要集成消息队列产品,比如 kafka, 从而简化系统设计的复杂度,降低运营维护成本。
|
||||
|
||||
与 kafka 一样,你需要定义 *topic*, 但 TDengine 的 *topic* 是基于一个已经存在的超级表、子表或普通表的查询条件,即一个 `SELECT` 语句。你可以使用 SQL 对标签、表名、列、表达式等条件进行过滤,以及对数据进行标量函数与 UDF 计算(不包括数据聚合)。与其他消息队列软件相比,这是 TDengine 数据订阅功能的最大的优势,它提供了更大的灵活性,数据的颗粒度可以由应用随时调整,而且数据的过滤与预处理交给 TDengine,而不是应用完成,有效的减少传输的数据量与应用的复杂度。
|
||||
## 数据订阅介绍
|
||||
|
||||
消费者订阅 *topic* 后,可以实时获得最新的数据。多个消费者可以组成一个消费者组 (consumer group), 一个消费者组里的多个消费者共享消费进度,便于多线程、分布式地消费数据,提高消费速度。但不同消费者组中的消费者即使消费同一个 topic, 并不共享消费进度。一个消费者可以订阅多个 topic。如果订阅的是超级表,数据可能会分布在多个不同的 vnode 上,也就是多个 shard 上,这样一个消费组里有多个消费者可以提高消费效率。TDengine 的消息队列提供了消息的 ACK 机制,在宕机、重启等复杂环境下确保 at least once 消费。
|
||||
### 主题
|
||||
与 kafka 一样,你需要定义 topic, TDengine 的 topic 有三种,可以是数据库,超级表,或者一个 `SELECT` 语句,具体的语法参见 [CREATE TOPIC](../../taos-sql/tmq)。与其他消息队列软件相比,这是 TDengine 数据订阅功能的最大的优势,它提供了更大的灵活性,数据的颗粒度可以由应用随时调整,而且数据的过滤与预处理交给 TDengine,而不是应用完成,有效的减少传输的数据量与应用的复杂度。
|
||||
|
||||
为了实现上述功能,TDengine 会为 WAL (Write-Ahead-Log) 文件自动创建索引以支持快速随机访问,并提供了灵活可配置的文件切换与保留机制:用户可以按需指定 WAL 文件保留的时间以及大小(详见 create database 语句)。通过以上方式将 WAL 改造成了一个保留事件到达顺序的、可持久化的存储引擎(但由于 TSDB 具有远比 WAL 更高的压缩率,我们不推荐保留太长时间,一般来说,不超过几天)。 对于以 topic 形式创建的查询,TDengine 将对接 WAL 而不是 TSDB 作为其存储引擎。在消费时,TDengine 根据当前消费进度从 WAL 直接读取数据,并使用统一的查询引擎实现过滤、变换等操作,将数据推送给消费者。
|
||||
如下图,每个 topic 涉及到的数据表可能分布在多个 vnode(相当于 kafka 里的 partition) 上,每个 vnode 上的数据保存在 WAL(Write-Ahead-Log) 文件中,WAL 文件里的数据是顺序写入的(由于 WAL 文件中存储的不只有数据,还有元数据,写入消息等,所以数据的版本号不是连续的)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面为关于数据订阅的一些说明,需要对TDengine的架构有一些了解,结合各个语言链接器的接口使用。(可使用时再了解)
|
||||
- 一个消费组消费同一个topic下的所有数据,不同消费组之间相互独立;
|
||||
- 一个消费组消费同一个topic所有的vgroup,消费组可由多个消费者组成,但一个vgroup仅被一个消费者消费,如果消费者数量超过了vgroup数量,多余的消费者不消费数据;
|
||||
- 在服务端每个vgroup仅保存一个offset,每个vgroup的offset是单调递增的,但不一定连续。各个vgroup的offset之间没有关联;
|
||||
- 每次poll服务端会返回一个结果block,该block属于一个vgroup,可能包含多个wal版本的数据,可以通过 offset 接口获得是该block第一条记录的offset;
|
||||
- 一个消费组如果从未commit过offset,当其成员消费者重启重新拉取数据时,均从参数auto.offset.reset设定值开始消费;在一个消费者生命周期中,客户端本地记录了最近一次拉取数据的offset,不会拉取重复数据;
|
||||
- 消费者如果异常终止(没有调用tmq_close),需等约12秒后触发其所属消费组rebalance,该消费者在服务端状态变为LOST,约1天后该消费者自动被删除;正常退出,退出后就会删除消费者;新增消费者,需等约2秒触发rebalance,该消费者在服务端状态变为ready;
|
||||
- 消费组rebalance会对该组所有ready状态的消费者成员重新进行vgroup分配,消费者仅能对自己负责的vgroup进行assignment/seek/commit/poll操作;
|
||||
- 消费者可利用 position 获得当前消费的offset,并seek到指定offset,重新消费;
|
||||
- seek将position指向指定offset,不执行commit操作,一旦seek成功,可poll拉取指定offset及以后的数据;
|
||||
- seek 操作之前须调用 assignment 接口获取该consumer的vgroup ID和offset范围。seek 操作会检测vgroup ID 和 offset是否合法,如非法将报错;
|
||||
- position是获取当前的消费位置,是下次要取的位置,不是当前消费到的位置
|
||||
- commit是提交消费位置,不带参数的话,是提交当前消费位置(下次要取的位置,不是当前消费到的位置),带参数的话,是提交参数里的位置(也即下次退出重启后要取的位置)
|
||||
- seek是设置consumer消费位置,seek到哪,position就返回哪,都是下次要取的位置
|
||||
- seek不会影响commit,commit不影响seek,相互独立,两个是不同的概念
|
||||
- begin接口为wal 第一条数据的offset,end 接口为wal 最后一条数据的offset + 1
|
||||
- offset接口获取的是记录所在结果block块里的第一条数据的offset,当seek至该offset时,将消费到这个block里的全部数据。参见第四点;
|
||||
- 由于存在 WAL 过期删除机制,即使seek 操作成功,poll数据时有可能offset已失效。如果poll 的offset 小于 WAL 最小版本号,将会从WAL最小版本号消费;
|
||||
- 数据订阅是从 WAL 消费数据,如果一些 WAL 文件被基于 WAL 保留策略删除,则已经删除的 WAL 文件中的数据就无法再消费到。需要根据业务需要在创建数据库时合理设置 `WAL_RETENTION_PERIOD` 或 `WAL_RETENTION_SIZE` ,并确保应用及时消费数据,这样才不会产生数据丢失的现象。数据订阅的行为与 Kafka 等广泛使用的消息队列类产品的行为相似;
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
本文档不对消息队列本身的知识做更多的介绍,如果需要了解,请自行搜索。
|
||||
TDengine 会为 WAL 文件自动创建索引以支持快速随机访问,并提供了灵活可配置的文件切换与保留机制,用户可以按需指定 WAL 文件保留的时间以及大小(详见 [CREATE DATABASE](../../taos-sql/database) 语句,由于消费是通过 WAL 实现的,所以应该根据写入消费速度来确定 WAL 的保存时长)。通过以上方式将 WAL 改造成了一个保留事件到达顺序的、可持久化的存储引擎。
|
||||
|
||||
说明:
|
||||
对于 `SELECT` 语句形式的 topic,在消费时,TDengine 根据当前消费进度从 WAL 直接读取数据,并使用统一的查询引擎实现过滤、变换等操作,将数据推送给消费者。
|
||||
|
||||
### 生产者
|
||||
写入 topic 相关联的数据表中数据的都是生产者,生产者实际生产的数据写入到了子表或普通表中,即表所在 vnode 的 WAL 里。
|
||||
|
||||
### 消费者
|
||||
|
||||
#### 消费者组
|
||||
消费者订阅 topic 后,可以消费 topic 里的所有数据(这些数据所在的表可能分布在多个 vnode 上,即 db 所在的所有 vnode)。订阅 topic 时,需要指定一个消费者组 (consumer group),如果这个消费者组里只有一个消费者,那么这个消费者会顺序的消费这些 vnode 上的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
为了提高消费速度,便于多线程、分布式地消费数据,可以在一个消费组里添加多个消费者,这些消费者将均分数据所在的 vnode 进行消费(比如数据分布在 4 个 vnode 上,有 2 个消费者的话,那么每个消费者消费 2 个 vnode;有 3 个消费者的话,2 个消费者各消费 1 个 vnode,1 个消费者消费 2 个 vnode;有 5 个消费者的话,4 个各分配 1 个 vnode 消费,另外 1 个不消费),如下图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在一个消费组里添加一个消费者后,在 Mnode 上通过 rebalance 的机制实现消费者的重新分配,该操作对用户是透明的。
|
||||
|
||||
一个消费者可以订阅多个 topic。TDengine 的数据订阅在宕机、重启等复杂环境下确保 at least once 消费。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 消费进度
|
||||
在 topic 的一个消费组的一个 vnode 上有消费进度。消费者消费的同时,可以提交消费进度,消费进度即 vnode 上 WAL 的版本号(对于 kafka 里的 offset),消费进度可以手动提交,也可以通过参数(auto.commit.interval.ms)设置为周期性自动提交。
|
||||
|
||||
首次消费数据时通过订阅参数(auto.offset.reset)来确定消费位置为最新数据(latest)还是最旧数据(earliest)。
|
||||
|
||||
消费进度在一个 vnode 上对于同一个 topic 和 消费者组是唯一的。所以如果同一个 topic 和 消费者组在一个 vnode 上的消费者退出了,并且提交了消费进度。然后同一个 topic 和 消费者组里重新建了一个新的消费者消费这个 vnode,那么这个新消费者将继承之前的消费进度继续消费。
|
||||
|
||||
如果之前的消费者没有提交消费进度,那个新的消费者将根据订阅参数(auto.offset.reset)设置的值来确定起始消费位置。
|
||||
|
||||
不同消费者组中的消费者即使消费同一个 topic, 并不共享消费进度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
作为一个数据库产品, WAL 文件中存储的不全是数据,也包括其他写入消息,元数据等,所以消费进度不是连续的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 说明
|
||||
从3.2.0.0版本开始,数据订阅支持vnode迁移和分裂。
|
||||
由于数据订阅依赖wal文件,而在vnode迁移和分裂的过程中,wal并不会同步过去,所以迁移或分裂后,之前没消费完的wal数据后消费不到。所以请保证之前把数据全部消费完后,再进行vnode迁移或分裂,否则,消费会丢失数据。
|
||||
|
||||
## 主要数据结构和 API
|
||||
由于数据订阅依赖wal文件,而在vnode迁移和分裂的过程中,wal并不会同步过去,所以迁移或分裂后,之前没消费完的wal数据后消费不到。所以请保证迁移和分裂之前把数据全部消费完后,再进行vnode迁移或分裂,否则,消费会丢失数据。
|
||||
|
||||
不同语言下, TMQ 订阅相关的 API 及数据结构如下(注意consumer结构不是线程安全的,在一个线程使用consumer时,不要在另一个线程close这个consumer):
|
||||
## 数据订阅语法说明
|
||||
|
||||
具体的语法参见 [数据订阅](../../taos-sql/tmq)
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据订阅相关参数
|
||||
|
||||
消费参数主要用于消费者创建时指定,基础配置项如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 参数说明 | 备注 |
|
||||
| :----------------------------: | :-----: | -------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `td.connect.ip` | string | 服务端的 IP 地址 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.user` | string | 用户名 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.pass` | string | 密码 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.port` | integer | 服务端的端口号 | |
|
||||
| `group.id` | string | 消费组 ID,同一消费组共享消费进度 | <br />**必填项**。最大长度:192。<br />每个topic最多可建立100个 consumer group |
|
||||
| `client.id` | string | 客户端 ID | 最大长度:192。 |
|
||||
| `auto.offset.reset` | enum | 消费组订阅的初始位置 | <br />`earliest`: default(version < 3.2.0.0);从头开始订阅; <br/>`latest`: default(version >= 3.2.0.0);仅从最新数据开始订阅; <br/>`none`: 没有提交的 offset 无法订阅 |
|
||||
| `enable.auto.commit` | boolean | 是否启用消费位点自动提交,true: 自动提交,客户端应用无需commit;false:客户端应用需要自行commit | 默认值为 true |
|
||||
| `auto.commit.interval.ms` | integer | 消费记录自动提交消费位点时间间隔,单位为毫秒 | 默认值为 5000 |
|
||||
| `msg.with.table.name` | boolean | 是否允许从消息中解析表名, 不适用于列订阅(列订阅时可将 tbname 作为列写入 subquery 语句)(从3.2.0.0版本该参数废弃,恒为true) |默认关闭 |
|
||||
| `enable.replay` | boolean | 是否开启数据回放功能 |默认关闭 |
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据订阅主要 API 接口
|
||||
|
||||
不同语言下, TMQ 订阅相关的 API 及数据结构如下(详细的接口说明可以参考连接器章节数据订阅部分,注意consumer结构不是线程安全的,在一个线程使用consumer时,不要在另一个线程close这个consumer):
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs defaultValue="java" groupId="lang">
|
||||
<TabItem value="c" label="C">
|
||||
|
|
@ -273,7 +312,8 @@ void Close()
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 写入数据
|
||||
## 数据订阅示例
|
||||
### 写入数据
|
||||
|
||||
首先完成建库、建一张超级表和多张子表操作,然后就可以写入数据了,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -282,81 +322,19 @@ DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS tmqdb;
|
|||
CREATE DATABASE tmqdb WAL_RETENTION_PERIOD 3600;
|
||||
CREATE TABLE tmqdb.stb (ts TIMESTAMP, c1 INT, c2 FLOAT, c3 VARCHAR(16)) TAGS(t1 INT, t3 VARCHAR(16));
|
||||
CREATE TABLE tmqdb.ctb0 USING tmqdb.stb TAGS(0, "subtable0");
|
||||
CREATE TABLE tmqdb.ctb1 USING tmqdb.stb TAGS(1, "subtable1");
|
||||
CREATE TABLE tmqdb.ctb1 USING tmqdb.stb TAGS(1, "subtable1");
|
||||
INSERT INTO tmqdb.ctb0 VALUES(now, 0, 0, 'a0')(now+1s, 0, 0, 'a00');
|
||||
INSERT INTO tmqdb.ctb1 VALUES(now, 1, 1, 'a1')(now+1s, 11, 11, 'a11');
|
||||
```
|
||||
### 创建 topic
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建 *topic*
|
||||
|
||||
TDengine 使用 SQL 创建一个 topic:
|
||||
使用 SQL 创建一个 topic:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC topic_name AS SELECT ts, c1, c2, c3 FROM tmqdb.stb WHERE c1 > 1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
- topic创建个数有上限,通过参数 tmqMaxTopicNum 控制,默认 20 个
|
||||
|
||||
TMQ 支持多种订阅类型:
|
||||
|
||||
### 列订阅
|
||||
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC topic_name as subquery
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过 `SELECT` 语句订阅(包括 `SELECT *`,或 `SELECT ts, c1` 等指定列订阅,可以带条件过滤、标量函数计算,但不支持聚合函数、不支持时间窗口聚合)。需要注意的是:
|
||||
|
||||
- 该类型 TOPIC 一旦创建则订阅数据的结构确定。
|
||||
- 被订阅或用于计算的列或标签不可被删除(`ALTER table DROP`)、修改(`ALTER table MODIFY`)。
|
||||
- 若发生表结构变更,新增的列不出现在结果中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 超级表订阅
|
||||
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC topic_name [with meta] AS STABLE stb_name [where_condition]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
与 `SELECT * from stbName` 订阅的区别是:
|
||||
|
||||
- 不会限制用户的表结构变更。
|
||||
- 返回的是非结构化的数据:返回数据的结构会随之超级表的表结构变化而变化。
|
||||
- with meta 参数可选,选择时将返回创建超级表,子表等语句,主要用于taosx做超级表迁移
|
||||
- where_condition 参数可选,选择时将用来过滤符合条件的子表,订阅这些子表。where 条件里不能有普通列,只能是tag或tbname,where条件里可以用函数,用来过滤tag,但是不能是聚合函数,因为子表tag值无法做聚合。也可以是常量表达式,比如 2 > 1(订阅全部子表),或者 false(订阅0个子表)
|
||||
- 返回数据不包含标签。
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据库订阅
|
||||
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC topic_name [with meta] AS DATABASE db_name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过该语句可创建一个包含数据库所有表数据的订阅
|
||||
|
||||
- with meta 参数可选,选择时将返回创建数据库里所有超级表,子表的语句,主要用于taosx做数据库迁移
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建消费者 *consumer*
|
||||
|
||||
消费者需要通过一系列配置选项创建,基础配置项如下表所示:
|
||||
|
||||
| 参数名称 | 类型 | 参数说明 | 备注 |
|
||||
| :----------------------------: | :-----: | -------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `td.connect.ip` | string | 服务端的 IP 地址 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.user` | string | 用户名 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.pass` | string | 密码 | |
|
||||
| `td.connect.port` | integer | 服务端的端口号 | |
|
||||
| `group.id` | string | 消费组 ID,同一消费组共享消费进度 | <br />**必填项**。最大长度:192。<br />每个topic最多可建立100个 consumer group |
|
||||
| `client.id` | string | 客户端 ID | 最大长度:192。 |
|
||||
| `auto.offset.reset` | enum | 消费组订阅的初始位置 | <br />`earliest`: default(version < 3.2.0.0);从头开始订阅; <br/>`latest`: default(version >= 3.2.0.0);仅从最新数据开始订阅; <br/>`none`: 没有提交的 offset 无法订阅 |
|
||||
| `enable.auto.commit` | boolean | 是否启用消费位点自动提交,true: 自动提交,客户端应用无需commit;false:客户端应用需要自行commit | 默认值为 true |
|
||||
| `auto.commit.interval.ms` | integer | 消费记录自动提交消费位点时间间隔,单位为毫秒 | 默认值为 5000 |
|
||||
| `msg.with.table.name` | boolean | 是否允许从消息中解析表名, 不适用于列订阅(列订阅时可将 tbname 作为列写入 subquery 语句)(从3.2.0.0版本该参数废弃,恒为true) |默认关闭 |
|
||||
| `enable.replay` | boolean | 是否开启数据回放功能 |默认关闭 |
|
||||
### 创建消费者 consumer
|
||||
|
||||
对于不同编程语言,其设置方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -520,31 +498,13 @@ var consumer = new ConsumerBuilder<Dictionary<string, object>>(cfg).Build();
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上述配置中包括 consumer group ID,如果多个 consumer 指定的 consumer group ID 一样,则自动形成一个 consumer group,共享消费进度。
|
||||
|
||||
数据回放功能说明:
|
||||
- 订阅增加 replay 功能,按照数据写入的时间回放。
|
||||
比如,如下时间写入三条数据
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:00.000
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:05.000
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:08.000
|
||||
```
|
||||
则订阅出第一条数据 5s 后返回第二条数据,获取第二条数据 3s 后返回第三条数据。
|
||||
- 仅列订阅支持数据回放
|
||||
- 回放需要保证独立时间线
|
||||
- 如果是子表订阅或者普通表订阅,只有一个vnode上有数据,保证是一个时间线
|
||||
- 如果超级表订阅,则需保证该 DB 只有一个vnode,否则报错(因为多个vnode上订阅出的数据不在一个时间线上)
|
||||
- 超级表和库订阅不支持回放
|
||||
- 增加 enable.replay 参数,true表示开启订阅回放功能,false表示不开启订阅回放功能,默认不开启。
|
||||
- 回放不支持进度保存,所以回放参数 enable.replay = true 时,auto commit 自动关闭
|
||||
- 因为数据回放本身需要处理时间,所以回放的精度存在几十ms的误差
|
||||
|
||||
## 订阅 *topics*
|
||||
|
||||
### 订阅 topics
|
||||
|
||||
一个 consumer 支持同时订阅多个 topic。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs defaultValue="java" groupId="lang">
|
||||
<TabItem value="c" label="C">
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -620,7 +580,7 @@ consumer.Subscribe(topics);
|
|||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 消费
|
||||
### 消费
|
||||
|
||||
以下代码展示了不同语言下如何对 TMQ 消息进行消费。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -756,7 +716,7 @@ while (true)
|
|||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 结束消费
|
||||
### 结束消费
|
||||
|
||||
消费结束后,应当取消订阅。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -837,36 +797,7 @@ consumer.Close();
|
|||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除 *topic*
|
||||
|
||||
如果不再需要订阅数据,可以删除 topic,需要注意:只有当前未在订阅中的 TOPIC 才能被删除。
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
/* 删除 topic */
|
||||
DROP TOPIC topic_name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 状态查看
|
||||
|
||||
1、*topics*:查询已经创建的 topic
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW TOPICS;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2、consumers:查询 consumer 的状态及其订阅的 topic
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW CONSUMERS;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3、subscriptions:查询 consumer 与 vgroup 之间的分配关系
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW SUBSCRIPTIONS;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例代码
|
||||
### 完整示例代码
|
||||
|
||||
以下是各语言的完整示例代码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -908,3 +839,22 @@ SHOW SUBSCRIPTIONS;
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据订阅高级功能
|
||||
### 数据回放
|
||||
- 订阅支持 replay 功能,按照数据写入的时间回放。
|
||||
比如,如下时间写入三条数据
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:00.000
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:05.000
|
||||
2023/09/22 00:00:08.000
|
||||
```
|
||||
则订阅出第一条数据 5s 后返回第二条数据,获取第二条数据 3s 后返回第三条数据。
|
||||
- 仅查询订阅支持数据回放
|
||||
- 回放需要保证独立时间线
|
||||
- 如果是子表订阅或者普通表订阅,只有一个vnode上有数据,保证是一个时间线
|
||||
- 如果超级表订阅,则需保证该 DB 只有一个vnode,否则报错(因为多个vnode上订阅出的数据不在一个时间线上)
|
||||
- 超级表和库订阅不支持回放
|
||||
- enable.replay 参数,true表示开启订阅回放功能,false表示不开启订阅回放功能,默认不开启。
|
||||
- 回放不支持进度保存,所以回放参数 enable.replay = true 时,auto commit 自动关闭
|
||||
- 因为数据回放本身需要处理时间,所以回放的精度存在几十ms的误差
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,3 +6,4 @@
|
|||
```
|
||||
```java
|
||||
{{#include docs/examples/java/src/main/java/com/taos/example/Meters.java}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 48 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
|
|
@ -856,7 +856,7 @@ taosws `Consumer` API 提供了基于 Websocket 订阅 TMQ 数据的 API。创
|
|||
```python
|
||||
import taosws
|
||||
|
||||
consumer = taosws.(conf={"group.id": "local", "td.connect.websocket.scheme": "ws"})
|
||||
consumer = taosws.Consumer(conf={"group.id": "local", "td.connect.websocket.scheme": "ws"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
|
@ -896,13 +896,13 @@ Consumer API 的 `poll` 方法用于消费数据,`poll` 方法接收一个 flo
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
res = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not res:
|
||||
message = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not message:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
err = res.error()
|
||||
err = message.error()
|
||||
if err is not None:
|
||||
raise err
|
||||
val = res.value()
|
||||
val = message.value()
|
||||
|
||||
for block in val:
|
||||
print(block.fetchall())
|
||||
|
|
@ -911,16 +911,14 @@ while True:
|
|||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="websocket" label="WebSocket 连接">
|
||||
|
||||
Consumer API 的 `poll` 方法用于消费数据,`poll` 方法接收一个 float 类型的超时时间,超时时间单位为秒(s),`poll` 方法在超时之前返回一条 Message 类型的数据或超时返回 `None`。消费者必须通过 Message 的 `error()` 方法校验返回数据的 error 信息。
|
||||
Consumer API 的 `poll` 方法用于消费数据,`poll` 方法接收一个 float 类型的超时时间,超时时间单位为秒(s),`poll` 方法在超时之前返回一条 Message 类型的数据或超时返回 `None`。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
res = consumer.poll(timeout=1.0)
|
||||
if not res:
|
||||
message = consumer.poll(1)
|
||||
if not message:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
err = res.error()
|
||||
if err is not None:
|
||||
raise err
|
||||
|
||||
for block in message:
|
||||
for row in block:
|
||||
print(row)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ SELECT [hints] [DISTINCT] [TAGS] select_list
|
|||
hints: /*+ [hint([hint_param_list])] [hint([hint_param_list])] */
|
||||
|
||||
hint:
|
||||
BATCH_SCAN | NO_BATCH_SCAN | SORT_FOR_GROUP
|
||||
BATCH_SCAN | NO_BATCH_SCAN | SORT_FOR_GROUP | PARTITION_FIRST | PARA_TABLES_SORT | SMALLDATA_TS_SORT
|
||||
|
||||
select_list:
|
||||
select_expr [, select_expr] ...
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,6 +93,8 @@ Hints 是用户控制单个语句查询优化的一种手段,当 Hint 不适
|
|||
| NO_BATCH_SCAN | 无 | 采用顺序读表的方式 | 超级表 JOIN 语句 |
|
||||
| SORT_FOR_GROUP| 无 | 采用sort方式进行分组, 与PARTITION_FIRST冲突 | partition by 列表有普通列时 |
|
||||
| PARTITION_FIRST| 无 | 在聚合之前使用PARTITION计算分组, 与SORT_FOR_GROUP冲突 | partition by 列表有普通列时 |
|
||||
| PARA_TABLES_SORT| 无 | 超级表的数据按时间戳排序时, 不使用临时磁盘空间, 只使用内存。当子表数量多, 行长比较大时候, 会使用大量内存, 可能发生OOM | 超级表的数据按时间戳排序时 |
|
||||
| SMALLDATA_TS_SORT| 无 | 超级表的数据按时间戳排序时, 查询列长度大于等于256, 但是行数不多, 使用这个提示, 可以提高性能 | 超级表的数据按时间戳排序时 |
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,6 +102,8 @@ Hints 是用户控制单个语句查询优化的一种手段,当 Hint 不适
|
|||
SELECT /*+ BATCH_SCAN() */ a.ts FROM stable1 a, stable2 b where a.tag0 = b.tag0 and a.ts = b.ts;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ SORT_FOR_GROUP() */ count(*), c1 FROM stable1 PARTITION BY c1;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ PARTITION_FIRST() */ count(*), c1 FROM stable1 PARTITION BY c1;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ PARA_TABLES_SORT() */ * from stable1 order by ts;
|
||||
SELECT /*+ SMALLDATA_TS_SORT() */ * from stable1 order by ts;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 列表
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -491,6 +491,8 @@ TO_CHAR(ts, format_str_literal)
|
|||
|
||||
**功能说明**: 将timestamp类型按照指定格式转换为字符串
|
||||
|
||||
**版本**: ver-3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
**返回结果数据类型**: VARCHAR
|
||||
|
||||
**应用字段**: TIMESTAMP
|
||||
|
|
@ -550,6 +552,8 @@ TO_TIMESTAMP(ts_str_literal, format_str_literal)
|
|||
|
||||
**功能说明**: 将字符串按照指定格式转化为时间戳.
|
||||
|
||||
**版本**: ver-3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
**返回结果数据类型**: TIMESTAMP
|
||||
|
||||
**应用字段**: VARCHAR
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -49,6 +49,7 @@ window_clause: {
|
|||
| STATE_WINDOW(col)
|
||||
| INTERVAL(interval_val [, interval_offset]) [SLIDING (sliding_val)] [FILL(fill_mod_and_val)]
|
||||
| EVENT_WINDOW START WITH start_trigger_condition END WITH end_trigger_condition
|
||||
| COUNT_WINDOW(count_val[, sliding_val])
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,6 +181,19 @@ select _wstart, _wend, count(*) from t event_window start with c1 > 0 end with c
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 计数窗口
|
||||
|
||||
计数窗口按固定的数据行数来划分窗口。默认将数据按时间戳排序,再按照count_val的值,将数据划分为多个窗口,然后做聚合计算。count_val表示每个count window包含的最大数据行数,总数据行数不能整除count_val时,最后一个窗口的行数会小于count_val。sliding_val是常量,表示窗口滑动的数量,类似于 interval的SLIDING。
|
||||
|
||||
以下面的 SQL 语句为例,计数窗口切分如图所示:
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select _wstart, _wend, count(*) from t count_window(4);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
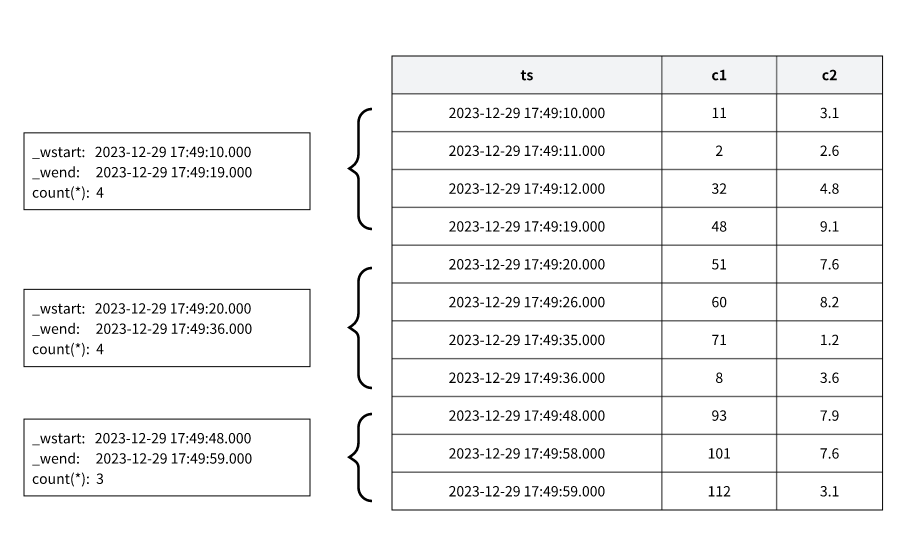
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 时间戳伪列
|
||||
|
||||
窗口聚合查询结果中,如果 SQL 语句中没有指定输出查询结果中的时间戳列,那么最终结果中不会自动包含窗口的时间列信息。如果需要在结果中输出聚合结果所对应的时间窗口信息,需要在 SELECT 子句中使用时间戳相关的伪列: 时间窗口起始时间 (\_WSTART), 时间窗口结束时间 (\_WEND), 时间窗口持续时间 (\_WDURATION), 以及查询整体窗口相关的伪列: 查询窗口起始时间(\_QSTART) 和查询窗口结束时间(\_QEND)。需要注意的是时间窗口起始时间和结束时间均是闭区间,时间窗口持续时间是数据当前时间分辨率下的数值。例如,如果当前数据库的时间分辨率是毫秒,那么结果中 500 就表示当前时间窗口的持续时间是 500毫秒 (500 ms)。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,32 +6,68 @@ description: TDengine 消息队列提供的数据订阅功能
|
|||
|
||||
TDengine 3.0.0.0 开始对消息队列做了大幅的优化和增强以简化用户的解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建订阅主题
|
||||
## 创建 topic
|
||||
|
||||
TDengine 创建 topic 的个数上限通过参数 tmqMaxTopicNum 控制,默认 20 个。
|
||||
|
||||
TDengine 使用 SQL 创建一个 topic,共有三种类型的 topic:
|
||||
|
||||
### 查询 topic
|
||||
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC [IF NOT EXISTS] topic_name AS subquery;
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC [IF NOT EXISTS] topic_name as subquery
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过 `SELECT` 语句订阅(包括 `SELECT *`,或 `SELECT ts, c1` 等指定查询订阅,可以带条件过滤、标量函数计算,但不支持聚合函数、不支持时间窗口聚合)。需要注意的是:
|
||||
|
||||
TOPIC 支持过滤和标量函数和 UDF 标量函数,不支持 JOIN、GROUP BY、窗口切分子句、聚合函数和 UDF 聚合函数。列订阅规则如下:
|
||||
- 该类型 TOPIC 一旦创建则订阅数据的结构确定。
|
||||
- 被订阅或用于计算的列或标签不可被删除(`ALTER table DROP`)、修改(`ALTER table MODIFY`)。
|
||||
- 若发生表结构变更,新增的列不出现在结果中。
|
||||
- 对于 select \*,则订阅展开为创建时所有的列(子表、普通表为数据列,超级表为数据列加标签列)
|
||||
### 超级表 topic
|
||||
|
||||
1. TOPIC 一旦创建则返回结果的字段确定
|
||||
2. 被订阅或用于计算的列不可被删除、修改
|
||||
3. 列可以新增,但新增的列不出现在订阅结果字段中
|
||||
4. 对于 select \*,则订阅展开为创建时所有的列(子表、普通表为数据列,超级表为数据列加标签列)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除订阅主题
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC [IF NOT EXISTS] topic_name [with meta] AS STABLE stb_name [where_condition]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
与 `SELECT * from stbName` 订阅的区别是:
|
||||
|
||||
- 不会限制用户的表结构变更。
|
||||
- 返回的是非结构化的数据:返回数据的结构会随之超级表的表结构变化而变化。
|
||||
- with meta 参数可选,选择时将返回创建超级表,子表等语句,主要用于taosx做超级表迁移
|
||||
- where_condition 参数可选,选择时将用来过滤符合条件的子表,订阅这些子表。where 条件里不能有普通列,只能是tag或tbname,where条件里可以用函数,用来过滤tag,但是不能是聚合函数,因为子表tag值无法做聚合。也可以是常量表达式,比如 2 > 1(订阅全部子表),或者 false(订阅0个子表)
|
||||
- 返回数据不包含标签。
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据库 topic
|
||||
|
||||
语法:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TOPIC [IF NOT EXISTS] topic_name [with meta] AS DATABASE db_name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过该语句可创建一个包含数据库所有表数据的订阅
|
||||
|
||||
- with meta 参数可选,选择时将返回创建数据库里所有超级表,子表的语句,主要用于taosx做数据库迁移
|
||||
|
||||
说明: 超级表订阅和库订阅属于高级订阅模式,容易出错,如确实要使用,请咨询专业人员。
|
||||
|
||||
## 删除 topic
|
||||
|
||||
如果不再需要订阅数据,可以删除 topic,需要注意:只有当前未在订阅中的 TOPIC 才能被删除。
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
/* 删除 topic */
|
||||
DROP TOPIC [IF EXISTS] topic_name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此时如果该订阅主题上存在 consumer,则此 consumer 会收到一个错误。
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看订阅主题
|
||||
|
||||
## SHOW TOPICS
|
||||
## 查看 topic
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW TOPICS;
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,3 +94,11 @@ SHOW CONSUMERS;
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
显示当前数据库下所有活跃的消费者的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看订阅信息
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SHOW SUBSCRIPTIONS;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
显示 consumer 与 vgroup 之间的分配关系和消费信息
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ subquery: SELECT select_list
|
|||
[window_clause]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
支持会话窗口、状态窗口与滑动窗口,其中,会话窗口与状态窗口搭配超级表时必须与partition by tbname一起使用
|
||||
支持会话窗口、状态窗口、滑动窗口、事件窗口和计数窗口,其中,状态窗口、事件窗口和计数窗口搭配超级表时必须与partition by tbname一起使用
|
||||
|
||||
stb_name 是保存计算结果的超级表的表名,如果该超级表不存在,会自动创建;如果已存在,则检查列的schema信息。详见 写入已存在的超级表
|
||||
|
||||
TAGS 字句定义了流计算中创建TAG的规则,可以为每个partition对应的子表生成自定义的TAG值,详见 自定义TAG
|
||||
TAGS 子句定义了流计算中创建TAG的规则,可以为每个partition对应的子表生成自定义的TAG值,详见 自定义TAG
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
create_definition:
|
||||
col_name column_definition
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,18 +49,32 @@ window_clause: {
|
|||
SESSION(ts_col, tol_val)
|
||||
| STATE_WINDOW(col)
|
||||
| INTERVAL(interval_val [, interval_offset]) [SLIDING (sliding_val)]
|
||||
| EVENT_WINDOW START WITH start_trigger_condition END WITH end_trigger_condition
|
||||
| COUNT_WINDOW(count_val[, sliding_val])
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其中,SESSION 是会话窗口,tol_val 是时间间隔的最大范围。在 tol_val 时间间隔范围内的数据都属于同一个窗口,如果连续的两条数据的时间超过 tol_val,则自动开启下一个窗口。
|
||||
EVENT_WINDOW 是事件窗口,根据开始条件和结束条件来划定窗口。当 start_trigger_condition 满足时则窗口开始,直到 end_trigger_condition 满足时窗口关闭。 start_trigger_condition 和 end_trigger_condition 可以是任意 TDengine 支持的条件表达式,且可以包含不同的列。
|
||||
COUNT_WINDOW 是计数窗口,按固定的数据行数来划分窗口。 count_val 是常量,是正整数,必须大于等于2,小于2147483648。 count_val 表示每个 COUNT_WINDOW 包含的最大数据行数,总数据行数不能整除 count_val 时,最后一个窗口的行数会小于 count_val 。 sliding_val 是常量,表示窗口滑动的数量,类似于 INTERVAL 的 SLIDING 。
|
||||
|
||||
窗口的定义与时序数据特色查询中的定义完全相同,详见 [TDengine 特色查询](../distinguished)
|
||||
|
||||
例如,如下语句创建流式计算,同时自动创建名为 avg_vol 的超级表,此流计算以一分钟为时间窗口、30 秒为前向增量统计这些电表的平均电压,并将来自 meters 表的数据的计算结果写入 avg_vol 表,不同 partition 的数据会分别创建子表并写入不同子表。
|
||||
例如,如下语句创建流式计算。第一个流计算,自动创建名为 avg_vol 的超级表,以一分钟为时间窗口、30 秒为前向增量统计这些电表的平均电压,并将来自 meters 表的数据的计算结果写入 avg_vol 表,不同 partition 的数据会分别创建子表并写入不同子表。
|
||||
|
||||
第二个流计算,自动创建名为 streamt0 的超级表,将数据按时间戳的顺序,以 voltage < 0 作为窗口的开始条件,voltage > 9作为窗口的结束条件,划分窗口做聚合运算,并将来自 meters 表的数据的计算结果写入 streamt0 表,不同 partition 的数据会分别创建子表并写入不同子表。
|
||||
|
||||
第三个流计算,自动创建名为 streamt1 的超级表,将数据按时间戳的顺序,以10条数据为一组,划分窗口做聚合运算,并将来自 meters 表的数据的计算结果写入 streamt1 表,不同 partition 的数据会分别创建子表并写入不同子表。
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE STREAM avg_vol_s INTO avg_vol AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) FROM meters PARTITION BY tbname INTERVAL(1m) SLIDING(30s);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE STREAM streams0 INTO streamt0 AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) from meters PARTITION BY tbname EVENT_WINDOW START WITH voltage < 0 END WITH voltage > 9;
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE STREAM streams1 IGNORE EXPIRED 1 WATERMARK 100s INTO streamt1 AS
|
||||
SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) from meters PARTITION BY tbname COUNT_WINDOW(10);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 流式计算的 partition
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,7 +91,7 @@ SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) FROM meters PARTITION BY tbname INTERVAL(
|
|||
CREATE STREAM avg_vol_s INTO avg_vol SUBTABLE(CONCAT('new-', tname)) AS SELECT _wstart, count(*), avg(voltage) FROM meters PARTITION BY tbname tname INTERVAL(1m);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PARTITION 子句中,为 tbname 定义了一个别名 tname, 在PARTITION 子句中的别名可以用于 SUBTABLE 子句中的表达式计算,在上述示例中,流新创建的子表将以前缀 'new-' 连接原表名作为表名。
|
||||
PARTITION 子句中,为 tbname 定义了一个别名 tname, 在PARTITION 子句中的别名可以用于 SUBTABLE 子句中的表达式计算,在上述示例中,流新创建的子表将以前缀 'new-' 连接原表名作为表名(从3.2.3.0开始,为了避免 sutable 中的表达式无法区分各个子表,即误将多个相同时间线写入一个子表,在指定的子表名后面加上 _groupId)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,子表名的长度若超过 TDengine 的限制,将被截断。若要生成的子表名已经存在于另一超级表,由于 TDengine 的子表名是唯一的,因此对应新子表的创建以及数据的写入将会失败。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,8 +226,8 @@ CREATE STREAM streams2 trigger at_once INTO st1 TAGS(cc varchar(100)) as select
|
|||
PARTITION 子句中,为 concat("tag-", tbname)定义了一个别名cc, 对应超级表st1的自定义TAG的名字。在上述示例中,流新创建的子表的TAG将以前缀 'new-' 连接原表名作为TAG的值。
|
||||
|
||||
会对TAG信息进行如下检查
|
||||
1.检查tag的schema信息是否匹配,对于不匹配的,则自动进行数据类型转换,当前只有数据长度大于4096byte时才报错,其余场景都能进行类型转换。
|
||||
2.检查tag的个数是否相同,如果不同,需要显示的指定超级表与subquery的tag的对应关系,否则报错;如果相同,可以指定对应关系,也可以不指定,不指定则按位置顺序对应。
|
||||
1. 检查tag的schema信息是否匹配,对于不匹配的,则自动进行数据类型转换,当前只有数据长度大于4096byte时才报错,其余场景都能进行类型转换。
|
||||
2. 检查tag的个数是否相同,如果不同,需要显示的指定超级表与subquery的tag的对应关系,否则报错;如果相同,可以指定对应关系,也可以不指定,不指定则按位置顺序对应。
|
||||
|
||||
## 清理中间状态
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,16 +8,15 @@ description: TDengine 中使用转义字符的详细规则
|
|||
|
||||
| 字符序列 | **代表的字符** |
|
||||
| :------: | -------------- |
|
||||
| `\'` | 单引号' |
|
||||
| `\"` | 双引号" |
|
||||
| \n | 换行符 |
|
||||
| \r | 回车符 |
|
||||
| \t | tab 符 |
|
||||
| `\\` | 斜杠\ |
|
||||
| `\%` | % 规则见下 |
|
||||
| `\_` | \_ 规则见下 |
|
||||
| `\'` | 单引号`'` |
|
||||
| `\"` | 双引号`"` |
|
||||
| `\n` | 换行符 |
|
||||
| `\r` | 回车符 |
|
||||
| `\t` | tab 符 |
|
||||
| `\\` | 斜杠 `\ ` |
|
||||
| `\%` | `%` 规则见下 |
|
||||
| `\_` | `_` 规则见下 |
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 转义字符使用规则
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,5 +24,5 @@ description: TDengine 中使用转义字符的详细规则
|
|||
1. 普通标识符: 直接提示错误的标识符,因为标识符规定必须是数字、字母和下划线,并且不能以数字开头。
|
||||
2. 反引号``标识符: 保持原样,不转义
|
||||
2. 数据里有转义字符
|
||||
1. 遇到上面定义的转义字符会转义(%和\_见下面说明),如果没有匹配的转义字符会忽略掉转义符\。
|
||||
2. 对于%和\_,因为在 like 里这两个字符是通配符,所以在模式匹配 like 里用`\%`%和`\_`表示字符里本身的%和\_,如果在 like 模式匹配上下文之外使用`\%`或`\_`,则它们的计算结果为字符串`\%`和`\_`,而不是%和\_。
|
||||
1. 遇到上面定义的转义字符会转义(`%`和`_`见下面说明),如果没有匹配的转义字符会忽略掉转义符`\ `(`\x`保持原样)。
|
||||
2. 对于`%`和`_`,因为在`like`里这两个字符是通配符,所以在模式匹配`like`里用`\%`和`\_`表示字符里本身的`%`和`_`,如果在`like`模式匹配上下文之外使用`\%`或`\_`,则它们的计算结果为字符串`\%`和`\_`,而不是`%`和`_`。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -215,9 +215,10 @@ taos -C
|
|||
| 属性 | 说明 |
|
||||
| -------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 适用范围 | 仅客户端适用 |
|
||||
| 含义 | Last、First、LastRow 函数查询时,返回的列名是否包含函数名。 |
|
||||
| 取值范围 | 0 表示包含函数名,1 表示不包含函数名。 |
|
||||
| 缺省值 | 0 |
|
||||
| 含义 | Last、First、LastRow 函数查询且未指定别名时,自动设置别名为列名(不含函数名),因此 order by 子句如果引用了该列名将自动引用该列对应的函数 |
|
||||
| 取值范围 | 1 表示自动设置别名为列名(不包含函数名), 0 表示不自动设置别名。 |
|
||||
| 缺省值 | 0 |
|
||||
| 补充说明 | 当同时出现多个上述函数作用于同一列且未指定别名时,如果 order by 子句引用了该列名,将会因为多列别名相同引发列选择冲突|
|
||||
|
||||
### countAlwaysReturnValue
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -87,19 +87,20 @@ st,t1=3,t2=4,t3=t3 c1=3i64,c3="passit",c2=false,c4=4f64 1626006833639000000
|
|||
|
||||
1. 将使用如下规则来生成子表名:首先将 measurement 的名称和标签的 key 和 value 组合成为如下的字符串
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"measurement,tag_key1=tag_value1,tag_key2=tag_value2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"measurement,tag_key1=tag_value1,tag_key2=tag_value2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
需要注意的是,这里的 tag_key1, tag_key2 并不是用户输入的标签的原始顺序,而是使用了标签名称按照字符串升序排列后的结果。所以,tag_key1 并不是在行协议中输入的第一个标签。
|
||||
排列完成以后计算该字符串的 MD5 散列值 "md5_val"。然后将计算的结果与字符串组合生成表名:“t_md5_val”。其中的 “t_” 是固定的前缀,每个通过该映射关系自动生成的表都具有该前缀。
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
如果不想用自动生成的表名,有两种指定子表名的方式,第一种优先级更高:
|
||||
通过在taos.cfg里配置 smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter 参数来指定(`@ # 空格 回车 换行 制表符`除外)。
|
||||
举例如下:配置 smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter=- 插入数据为 st,t0=cpu1,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000 则创建的表名为 cpu1-4。
|
||||
通过在taos.cfg里配置 smlChildTableName 参数来指定。
|
||||
举例如下:配置 smlChildTableName=tname 插入数据为 st,tname=cpu1,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000 则创建的表名为 cpu1,注意如果多行数据 tname 相同,但是后面的 tag_set 不同,则使用第一行自动建表时指定的 tag_set,其他的行会忽略)。
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
需要注意的是,这里的 tag_key1, tag_key2 并不是用户输入的标签的原始顺序,而是使用了标签名称按照字符串升序排列后的结果。所以,tag_key1 并不是在行协议中输入的第一个标签。
|
||||
排列完成以后计算该字符串的 MD5 散列值 "md5_val"。然后将计算的结果与字符串组合生成表名:“t_md5_val”。其中的 “t_” 是固定的前缀,每个通过该映射关系自动生成的表都具有该前缀。
|
||||
:::tip
|
||||
|
||||
如果不想用自动生成的表名,有两种指定子表名的方式(第一种优先级更高)。
|
||||
1. 通过在taos.cfg里配置 smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter 参数来指定(`@ # 空格 回车 换行 制表符`除外)。
|
||||
1. 举例如下:配置 smlAutoChildTableNameDelimiter=- 插入数据为 st,t0=cpu1,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000 则创建的表名为 cpu1-4。
|
||||
2. 通过在taos.cfg里配置 smlChildTableName 参数来指定。
|
||||
1. 举例如下:配置 smlChildTableName=tname 插入数据为 st,tname=cpu1,t1=4 c1=3 1626006833639000000 则创建的表名为 cpu1,注意如果多行数据 tname 相同,但是后面的 tag_set 不同,则使用第一行自动建表时指定的 tag_set,其他的行会忽略。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 如果解析行协议获得的超级表不存在,则会创建这个超级表(不建议手动创建超级表,不然插入数据可能异常)。
|
||||
3. 如果解析行协议获得子表不存在,则 Schemaless 会按照步骤 1 或 2 确定的子表名来创建子表。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,6 +10,10 @@ TDengine 2.x 各版本安装包请访问[这里](https://www.taosdata.com/all-do
|
|||
|
||||
import Release from "/components/ReleaseV3";
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.2.3.0
|
||||
|
||||
<Release type="tdengine" version="3.2.3.0" />
|
||||
|
||||
## 3.2.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
<Release type="tdengine" version="3.2.2.0" />
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,6 +29,7 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_QNODES "ins_qnodes"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_BNODES "ins_bnodes" // no longer used
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_SNODES "ins_snodes"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_ARBGROUPS "ins_arbgroups"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_CLUSTER "ins_cluster"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_DATABASES "ins_databases"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_FUNCTIONS "ins_functions"
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,6 +53,9 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_VIEWS "ins_views"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_COMPACTS "ins_compacts"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_COMPACT_DETAILS "ins_compact_details"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_GRANTS_FULL "ins_grants_full"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_GRANTS_LOGS "ins_grants_logs"
|
||||
#define TSDB_INS_TABLE_MACHINES "ins_machines"
|
||||
|
||||
#define TSDB_PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA_DB "performance_schema"
|
||||
#define TSDB_PERFS_TABLE_SMAS "perf_smas"
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,6 +66,11 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
#define TSDB_PERFS_TABLE_TRANS "perf_trans"
|
||||
#define TSDB_PERFS_TABLE_APPS "perf_apps"
|
||||
|
||||
#define TSDB_AUDIT_DB "audit"
|
||||
#define TSDB_AUDIT_STB_OPERATION "operations"
|
||||
#define TSDB_AUDIT_CTB_OPERATION "t_operations_"
|
||||
#define TSDB_AUDIT_CTB_OPERATION_LEN 13
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SSysDbTableSchema {
|
||||
const char* name;
|
||||
const int32_t type;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,6 +54,8 @@ typedef struct SSessionKey {
|
|||
uint64_t groupId;
|
||||
} SSessionKey;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef int64_t COUNT_TYPE;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SVersionRange {
|
||||
int64_t minVer;
|
||||
int64_t maxVer;
|
||||
|
|
@ -171,6 +173,7 @@ typedef enum EStreamType {
|
|||
STREAM_CHECKPOINT,
|
||||
STREAM_CREATE_CHILD_TABLE,
|
||||
STREAM_TRANS_STATE,
|
||||
STREAM_MID_RETRIEVE,
|
||||
} EStreamType;
|
||||
|
||||
#pragma pack(push, 1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -206,6 +209,7 @@ typedef struct SDataBlockInfo {
|
|||
int16_t hasVarCol;
|
||||
int16_t dataLoad; // denote if the data is loaded or not
|
||||
uint8_t scanFlag;
|
||||
bool blankFill;
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: optimize and remove following
|
||||
int64_t version; // used for stream, and need serialization
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,6 +32,9 @@ typedef struct SBlockOrderInfo {
|
|||
SColumnInfoData* pColData;
|
||||
} SBlockOrderInfo;
|
||||
|
||||
#define BLOCK_VERSION_1 1
|
||||
#define BLOCK_VERSION_2 2
|
||||
|
||||
#define NBIT (3u)
|
||||
#define BitPos(_n) ((_n) & ((1 << NBIT) - 1))
|
||||
#define BMCharPos(bm_, r_) ((bm_)[(r_) >> NBIT])
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,7 +267,7 @@ int32_t buildSubmitReqFromDataBlock(SSubmitReq2** pReq, const SSDataBlock* pData
|
|||
|
||||
bool alreadyAddGroupId(char* ctbName);
|
||||
bool isAutoTableName(char* ctbName);
|
||||
void buildCtbNameAddGruopId(char* ctbName, uint64_t groupId);
|
||||
void buildCtbNameAddGroupId(char* ctbName, uint64_t groupId);
|
||||
char* buildCtbNameByGroupId(const char* stbName, uint64_t groupId);
|
||||
int32_t buildCtbNameByGroupIdImpl(const char* stbName, uint64_t groupId, char* pBuf);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -76,6 +76,11 @@ extern int32_t tsHeartbeatInterval;
|
|||
extern int32_t tsHeartbeatTimeout;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsSnapReplMaxWaitN;
|
||||
|
||||
// arbitrator
|
||||
extern int32_t tsArbHeartBeatIntervalSec;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsArbCheckSyncIntervalSec;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsArbSetAssignedTimeoutSec;
|
||||
|
||||
// vnode
|
||||
extern int64_t tsVndCommitMaxIntervalMs;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,6 +111,9 @@ extern char tsMonitorFqdn[];
|
|||
extern uint16_t tsMonitorPort;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsMonitorMaxLogs;
|
||||
extern bool tsMonitorComp;
|
||||
extern bool tsMonitorLogProtocol;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsMonitorIntervalForBasic;
|
||||
extern bool tsMonitorForceV2;
|
||||
|
||||
// audit
|
||||
extern bool tsEnableAudit;
|
||||
|
|
@ -211,6 +219,7 @@ extern int32_t tsUptimeInterval;
|
|||
|
||||
extern bool tsDisableStream;
|
||||
extern int64_t tsStreamBufferSize;
|
||||
extern int tsStreamAggCnt;
|
||||
extern bool tsFilterScalarMode;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsMaxStreamBackendCache;
|
||||
extern int32_t tsPQSortMemThreshold;
|
||||
|
|
@ -229,10 +238,10 @@ int32_t taosCfgDynamicOptions(SConfig *pCfg, char *name, bool forServer);
|
|||
|
||||
struct SConfig *taosGetCfg();
|
||||
|
||||
void taosSetAllDebugFlag(int32_t flag);
|
||||
void taosSetDebugFlag(int32_t *pFlagPtr, const char *flagName, int32_t flagVal);
|
||||
void taosLocalCfgForbiddenToChange(char *name, bool *forbidden);
|
||||
int8_t taosGranted();
|
||||
void taosSetGlobalDebugFlag(int32_t flag);
|
||||
void taosSetDebugFlag(int32_t *pFlagPtr, const char *flagName, int32_t flagVal);
|
||||
void taosLocalCfgForbiddenToChange(char *name, bool *forbidden);
|
||||
int8_t taosGranted(int8_t type);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,15 +22,17 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
|
||||
#include "os.h"
|
||||
#include "taoserror.h"
|
||||
#ifdef GRANTS_CFG
|
||||
#include "tgrantCfg.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include "tdef.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN
|
||||
#define GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN 196
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define GRANT_HEART_BEAT_MIN 2
|
||||
#define GRANT_ACTIVE_CODE "activeCode"
|
||||
#define GRANT_FLAG_ALL (0x01)
|
||||
#define GRANT_FLAG_AUDIT (0x02)
|
||||
#define GRANT_FLAG_VIEW (0x04)
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum {
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_ALL,
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,63 +50,52 @@ typedef enum {
|
|||
TSDB_GRANT_CPU_CORES,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_STABLE,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_TABLE,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_SUBSCRIPTION,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_AUDIT,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_CSV,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_VIEW,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_MULTI_TIER,
|
||||
TSDB_GRANT_BACKUP_RESTORE,
|
||||
} EGrantType;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t grantCheck(EGrantType grant);
|
||||
int32_t grantAlterActiveCode(int32_t did, const char* old, const char* newer, char* out, int8_t type);
|
||||
int32_t grantCheckExpire(EGrantType grant);
|
||||
char* tGetMachineId();
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef GRANTS_CFG
|
||||
// #ifndef GRANTS_CFG
|
||||
#ifdef TD_ENTERPRISE
|
||||
#define GRANTS_SCHEMA \
|
||||
static const SSysDbTableSchema grantsSchema[] = { \
|
||||
{.name = "version", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expire_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expired", .bytes = 5 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "storage", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "timeseries", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "databases", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "users", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "accounts", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "dnodes", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "connections", .bytes = 11 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "streams", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "cpu_cores", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "speed", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "querytime", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "opc_da", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "opc_ua", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "pi", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "kafka", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "influxdb", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "mqtt", .bytes = GRANTS_COL_MAX_LEN + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
#define GRANTS_SCHEMA \
|
||||
static const SSysDbTableSchema grantsSchema[] = { \
|
||||
{.name = "version", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expire_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "service_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expired", .bytes = 5 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "state", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "timeseries", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "dnodes", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "cpu_cores", .bytes = 13 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define GRANTS_SCHEMA \
|
||||
static const SSysDbTableSchema grantsSchema[] = { \
|
||||
{.name = "version", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expire_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expired", .bytes = 5 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "storage", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "timeseries", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "databases", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "users", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "accounts", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "dnodes", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "connections", .bytes = 11 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "streams", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "cpu_cores", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "speed", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
{.name = "querytime", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR}, \
|
||||
#define GRANTS_SCHEMA \
|
||||
static const SSysDbTableSchema grantsSchema[] = { \
|
||||
{.name = "version", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expire_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "service_time", .bytes = 19 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "expired", .bytes = 5 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "state", .bytes = 9 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "timeseries", .bytes = 21 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "dnodes", .bytes = 10 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
{.name = "cpu_cores", .bytes = 13 + VARSTR_HEADER_SIZE, .type = TSDB_DATA_TYPE_VARCHAR, .sysInfo = true}, \
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_ADD
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_SET
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_GET
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_CHECK
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_SKIP
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_DECLARE
|
||||
#define GRANT_CFG_EXTERN
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_ADD
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_SET
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_GET
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_CHECK
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_SKIP
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_DECLARE
|
||||
// #define GRANT_CFG_EXTERN
|
||||
// #endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -47,10 +47,11 @@ typedef struct SCorEpSet {
|
|||
int32_t taosGetFqdnPortFromEp(const char* ep, SEp* pEp);
|
||||
void addEpIntoEpSet(SEpSet* pEpSet, const char* fqdn, uint16_t port);
|
||||
|
||||
bool isEpsetEqual(const SEpSet* s1, const SEpSet* s2);
|
||||
void epsetAssign(SEpSet* dst, const SEpSet* pSrc);
|
||||
void updateEpSet_s(SCorEpSet* pEpSet, SEpSet* pNewEpSet);
|
||||
SEpSet getEpSet_s(SCorEpSet* pEpSet);
|
||||
bool isEpsetEqual(const SEpSet* s1, const SEpSet* s2);
|
||||
void epsetAssign(SEpSet* dst, const SEpSet* pSrc);
|
||||
void updateEpSet_s(SCorEpSet* pEpSet, SEpSet* pNewEpSet);
|
||||
SEpSet getEpSet_s(SCorEpSet* pEpSet);
|
||||
void epsetSort(SEpSet* pEpSet);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -147,6 +147,10 @@ typedef enum _mgmt_table {
|
|||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_VIEWS,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_COMPACT,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_COMPACT_DETAIL,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_GRANTS_FULL,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_GRANTS_LOGS,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_MACHINES,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_ARBGROUP,
|
||||
TSDB_MGMT_TABLE_MAX,
|
||||
} EShowType;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -204,9 +208,6 @@ typedef enum _mgmt_table {
|
|||
#define TD_CHILD_TABLE TSDB_CHILD_TABLE
|
||||
#define TD_NORMAL_TABLE TSDB_NORMAL_TABLE
|
||||
|
||||
#define TD_REQ_FROM_APP 0
|
||||
#define TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX 1
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum ENodeType {
|
||||
// Syntax nodes are used in parser and planner module, and some are also used in executor module, such as COLUMN,
|
||||
// VALUE, OPERATOR, FUNCTION and so on.
|
||||
|
|
@ -244,6 +245,7 @@ typedef enum ENodeType {
|
|||
QUERY_NODE_EVENT_WINDOW,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_HINT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_VIEW,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_COUNT_WINDOW,
|
||||
|
||||
// Statement nodes are used in parser and planner module.
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SET_OPERATOR = 100,
|
||||
|
|
@ -298,7 +300,8 @@ typedef enum ENodeType {
|
|||
QUERY_NODE_SYNCDB_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_GRANT_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_REVOKE_STMT,
|
||||
// placeholder for [152, 180]
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_ALTER_CLUSTER_STMT,
|
||||
// placeholder for [153, 180]
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_CREATE_VIEW_STMT = 181,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_CREATE_DATABASE_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_CREATE_TABLE_STMT,
|
||||
|
|
@ -334,6 +337,7 @@ typedef enum ENodeType {
|
|||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_QNODES_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_SNODES_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_BNODES_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_ARBGROUPS_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_CLUSTER_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_DATABASES_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_FUNCTIONS_STMT,
|
||||
|
|
@ -359,6 +363,9 @@ typedef enum ENodeType {
|
|||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_VIEWS_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_COMPACTS_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_COMPACT_DETAILS_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_GRANTS_FULL_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_GRANTS_LOGS_STMT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_SHOW_CLUSTER_MACHINES_STMT,
|
||||
|
||||
// logic plan node
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_LOGIC_PLAN_SCAN = 1000,
|
||||
|
|
@ -424,7 +431,10 @@ typedef enum ENodeType {
|
|||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_STREAM_EVENT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_HASH_JOIN,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_GROUP_CACHE,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_DYN_QUERY_CTRL
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_DYN_QUERY_CTRL,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_MERGE_COUNT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_STREAM_COUNT,
|
||||
QUERY_NODE_PHYSICAL_PLAN_STREAM_MID_INTERVAL,
|
||||
} ENodeType;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -573,9 +583,9 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
};
|
||||
} SSubmitRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tEncodeSSubmitRsp(SEncoder* pEncoder, const SSubmitRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDecodeSSubmitRsp(SDecoder* pDecoder, SSubmitRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSSubmitBlkRsp(void* param);
|
||||
// int32_t tEncodeSSubmitRsp(SEncoder* pEncoder, const SSubmitRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// int32_t tDecodeSSubmitRsp(SDecoder* pDecoder, SSubmitRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// void tFreeSSubmitBlkRsp(void* param);
|
||||
void tFreeSSubmitRsp(SSubmitRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
#define COL_SMA_ON ((int8_t)0x1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -748,7 +758,7 @@ static FORCE_INLINE int32_t tDecodeSSchemaWrapperEx(SDecoder* pDecoder, SSchemaW
|
|||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char name[TSDB_TABLE_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
int8_t igExists;
|
||||
int8_t source; // 1-taosX or 0-taosClient
|
||||
int8_t source; // TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX-taosX or TD_REQ_FROM_APP-taosClient
|
||||
int8_t reserved[6];
|
||||
tb_uid_t suid;
|
||||
int64_t delay1;
|
||||
|
|
@ -791,7 +801,7 @@ void tFreeSMCreateStbRsp(SMCreateStbRsp* pRsp);
|
|||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char name[TSDB_TABLE_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
int8_t igNotExists;
|
||||
int8_t source; // 1-taosX or 0-taosClient
|
||||
int8_t source; // TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX-taosX or TD_REQ_FROM_APP-taosClient
|
||||
int8_t reserved[6];
|
||||
tb_uid_t suid;
|
||||
int32_t sqlLen;
|
||||
|
|
@ -877,8 +887,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int64_t maxStorage;
|
||||
} SCreateAcctReq, SAlterAcctReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSCreateAcctReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateAcctReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSCreateAcctReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateAcctReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSCreateAcctReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateAcctReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSCreateAcctReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateAcctReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char user[TSDB_USER_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
@ -1144,6 +1154,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t tsdbPageSize;
|
||||
int32_t sqlLen;
|
||||
char* sql;
|
||||
int8_t withArbitrator;
|
||||
} SCreateDbReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSCreateDbReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateDbReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1172,6 +1183,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t walRetentionSize;
|
||||
int32_t sqlLen;
|
||||
char* sql;
|
||||
int8_t withArbitrator;
|
||||
} SAlterDbReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSAlterDbReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SAlterDbReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1294,6 +1306,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
SArray* pRetensions;
|
||||
int8_t schemaless;
|
||||
int16_t sstTrigger;
|
||||
int8_t withArbitrator;
|
||||
} SDbCfgRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef SDbCfgRsp SDbCfgInfo;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1316,14 +1329,13 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SDnodeListReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSDnodeListReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDnodeListReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSDnodeListReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDnodeListReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t useless; // useless
|
||||
} SServerVerReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSServerVerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SServerVerReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSServerVerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SServerVerReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSServerVerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SServerVerReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char ver[TSDB_VERSION_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
@ -1392,7 +1404,7 @@ void tFreeSCompactDbReq(SCompactDbReq* pReq);
|
|||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t compactId;
|
||||
int8_t bAccepted;
|
||||
int8_t bAccepted;
|
||||
} SCompactDbRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSCompactDbRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCompactDbRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1406,7 +1418,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSKillCompactReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SKillCompactReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSKillCompactReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SKillCompactReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSKillCompactReq(SKillCompactReq *pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSKillCompactReq(SKillCompactReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char name[TSDB_FUNC_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
@ -1557,9 +1569,11 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int64_t updateTime;
|
||||
float numOfCores;
|
||||
int32_t numOfSupportVnodes;
|
||||
int32_t numOfDiskCfg;
|
||||
int64_t memTotal;
|
||||
int64_t memAvail;
|
||||
char dnodeEp[TSDB_EP_LEN];
|
||||
char machineId[TSDB_MACHINE_ID_LEN + 1];
|
||||
SMnodeLoad mload;
|
||||
SQnodeLoad qload;
|
||||
SClusterCfg clusterCfg;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1572,6 +1586,15 @@ int32_t tSerializeSStatusReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SStatusReq* pReq);
|
|||
int32_t tDeserializeSStatusReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SStatusReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSStatusReq(SStatusReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t contLen;
|
||||
char* pCont;
|
||||
} SStatisReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSStatisReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SStatisReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSStatisReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SStatisReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSStatisReq(SStatisReq *pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
int64_t clusterId;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1619,14 +1642,14 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SMTimerReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMTimerMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMTimerReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMTimerMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMTimerReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSMTimerMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMTimerReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int64_t tick;
|
||||
} SMStreamTickReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMStreamTickMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMStreamTickReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMStreamTickMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMStreamTickReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSMStreamTickMsg(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMStreamTickReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t id;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1740,9 +1763,9 @@ int32_t tSerializeSCompactVnodeReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCompactVnodeReq*
|
|||
int32_t tDeserializeSCompactVnodeReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCompactVnodeReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t compactId;
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
int32_t compactId;
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
} SVKillCompactReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVKillCompactReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVKillCompactReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1897,7 +1920,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SShowVariablesReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSShowVariablesReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowVariablesReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSShowVariablesReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowVariablesReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSShowVariablesReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowVariablesReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char name[TSDB_CONFIG_OPTION_LEN + 1];
|
||||
|
|
@ -1927,7 +1950,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SShowReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSShowReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSShowReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSShowReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSShowReq(SShowReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1935,17 +1958,17 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
STableMetaRsp tableMeta;
|
||||
} SShowRsp, SVShowTablesRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSShowRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSShowRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSShowRsp(SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSShowRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSShowRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// void tFreeSShowRsp(SShowRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char db[TSDB_DB_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
char tb[TSDB_TABLE_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
char user[TSDB_USER_LEN];
|
||||
char filterTb[TSDB_TABLE_NAME_LEN]; // for ins_columns
|
||||
char filterTb[TSDB_TABLE_NAME_LEN]; // for ins_columns
|
||||
int64_t showId;
|
||||
int64_t compactId; // for compact
|
||||
int64_t compactId; // for compact
|
||||
} SRetrieveTableReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SSysTableSchema {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1975,6 +1998,14 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
char data[];
|
||||
} SRetrieveTableRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int64_t version;
|
||||
int64_t numOfRows;
|
||||
int8_t compressed;
|
||||
int8_t precision;
|
||||
char data[];
|
||||
} SRetrieveTableRspForTmq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int64_t handle;
|
||||
int64_t useconds;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2023,6 +2054,17 @@ int32_t tSerializeSExplainRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SExplainRsp* pRsp);
|
|||
int32_t tDeserializeSExplainRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SExplainRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSExplainRsp(SExplainRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char config[TSDB_DNODE_CONFIG_LEN];
|
||||
char value[TSDB_CLUSTER_VALUE_LEN];
|
||||
int32_t sqlLen;
|
||||
char* sql;
|
||||
} SMCfgClusterReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMCfgClusterReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMCfgClusterReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMCfgClusterReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMCfgClusterReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSMCfgClusterReq(SMCfgClusterReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char fqdn[TSDB_FQDN_LEN]; // end point, hostname:port
|
||||
int32_t port;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2108,6 +2150,99 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t tSerializeSDCreateMnodeReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDCreateMnodeReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSDCreateMnodeReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDCreateMnodeReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int32_t hbSeq;
|
||||
} SVArbHbReqMember;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
char* arbToken;
|
||||
int64_t arbTerm;
|
||||
SArray* hbMembers; // SVArbHbReqMember
|
||||
} SVArbHeartBeatReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbHeartBeatReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbHeartBeatReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbHeartBeatReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbHeartBeatReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbHeartBeatReq(SVArbHeartBeatReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
char memberToken[TSDB_ARB_TOKEN_SIZE];
|
||||
int32_t hbSeq;
|
||||
} SVArbHbRspMember;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char arbToken[TSDB_ARB_TOKEN_SIZE];
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
SArray* hbMembers; // SVArbHbRspMember
|
||||
} SVArbHeartBeatRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbHeartBeatRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbHeartBeatRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbHeartBeatRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbHeartBeatRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbHeartBeatRsp(SVArbHeartBeatRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char* arbToken;
|
||||
int64_t arbTerm;
|
||||
char* member0Token;
|
||||
char* member1Token;
|
||||
} SVArbCheckSyncReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbCheckSyncReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbCheckSyncReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbCheckSyncReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbCheckSyncReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbCheckSyncReq(SVArbCheckSyncReq* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char* arbToken;
|
||||
char* member0Token;
|
||||
char* member1Token;
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int32_t errCode;
|
||||
} SVArbCheckSyncRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbCheckSyncRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbCheckSyncRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbCheckSyncRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbCheckSyncRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbCheckSyncRsp(SVArbCheckSyncRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char* arbToken;
|
||||
int64_t arbTerm;
|
||||
char* memberToken;
|
||||
} SVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq(SVArbSetAssignedLeaderReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char* arbToken;
|
||||
char* memberToken;
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
} SVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tFreeSVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp(SVArbSetAssignedLeaderRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t dnodeId;
|
||||
char* token;
|
||||
} SMArbUpdateGroupReqMember;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int64_t dbUid;
|
||||
SMArbUpdateGroupReqMember members[2];
|
||||
int8_t isSync;
|
||||
SMArbUpdateGroupReqMember assignedLeader;
|
||||
int64_t version;
|
||||
} SMArbUpdateGroupReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMArbUpdateGroupReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMArbUpdateGroupReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMArbUpdateGroupReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMArbUpdateGroupReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tFreeSMArbUpdateGroupReq(SMArbUpdateGroupReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char queryStrId[TSDB_QUERY_ID_LEN];
|
||||
} SKillQueryReq;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2176,7 +2311,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SForceBecomeFollowerReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSForceBecomeFollowerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SForceBecomeFollowerReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSForceBecomeFollowerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SForceBecomeFollowerReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSForceBecomeFollowerReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SForceBecomeFollowerReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2193,8 +2328,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
char ckey[TSDB_PASSWORD_LEN];
|
||||
} SAuthReq, SAuthRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSAuthReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SAuthReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSAuthReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SAuthReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSAuthReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SAuthReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSAuthReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SAuthReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t statusCode;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2400,6 +2535,11 @@ typedef struct SColLocation {
|
|||
int8_t type;
|
||||
} SColLocation;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SVgroupVer {
|
||||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
int64_t ver;
|
||||
} SVgroupVer;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char name[TSDB_STREAM_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
char sourceDB[TSDB_DB_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
@ -2423,6 +2563,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int64_t deleteMark;
|
||||
int8_t igUpdate;
|
||||
int64_t lastTs;
|
||||
SArray* pVgroupVerList;
|
||||
} SCMCreateStreamReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2622,6 +2763,7 @@ typedef struct SVCreateStbReq {
|
|||
SRSmaParam rsmaParam;
|
||||
int32_t alterOriDataLen;
|
||||
void* alterOriData;
|
||||
int8_t source;
|
||||
} SVCreateStbReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int tEncodeSVCreateStbReq(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVCreateStbReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -2691,6 +2833,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
SVCreateTbReq* pReqs;
|
||||
SArray* pArray;
|
||||
};
|
||||
int8_t source; // TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX-taosX or TD_REQ_FROM_APP-taosClient
|
||||
} SVCreateTbBatchReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int tEncodeSVCreateTbBatchReq(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVCreateTbBatchReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -2719,8 +2862,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int tEncodeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int tDecodeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(SDecoder* pCoder, SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSVCreateTbBatchRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVCreateTbBatchRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
// TDMT_VND_DROP_TABLE =================
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2775,14 +2918,17 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
char* tagName;
|
||||
int8_t isNull;
|
||||
int8_t tagType;
|
||||
int8_t tagFree;
|
||||
uint32_t nTagVal;
|
||||
uint8_t* pTagVal;
|
||||
SArray* pTagArray;
|
||||
// TSDB_ALTER_TABLE_UPDATE_OPTIONS
|
||||
int8_t updateTTL;
|
||||
int32_t newTTL;
|
||||
int32_t newCommentLen;
|
||||
char* newComment;
|
||||
int64_t ctimeMs; // fill by vnode
|
||||
int8_t source; // TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX-taosX or TD_REQ_FROM_APP-taosClient
|
||||
} SVAlterTbReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tEncodeSVAlterTbReq(SEncoder* pEncoder, const SVAlterTbReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -3146,18 +3292,11 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
SMsgHead head;
|
||||
int64_t leftForVer;
|
||||
int64_t resetRelHalt; // reset related stream task halt status
|
||||
int64_t streamId;
|
||||
int32_t taskId;
|
||||
} SVDropStreamTaskReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
SMsgHead head;
|
||||
int64_t streamId;
|
||||
int32_t taskId;
|
||||
int64_t dataVer;
|
||||
} SVStreamTaskVerUpdateReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int8_t reserved;
|
||||
} SVDropStreamTaskRsp;
|
||||
|
|
@ -3181,8 +3320,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t hasCheckPoint;
|
||||
} SMVStreamGatherInfoReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMRecoverStreamReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, const SMRecoverStreamReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMRecoverStreamReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMRecoverStreamReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSMRecoverStreamReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, const SMRecoverStreamReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSMRecoverStreamReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMRecoverStreamReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int64_t leftForVer;
|
||||
|
|
@ -3323,7 +3462,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
SMsgHead head;
|
||||
int64_t streamId;
|
||||
int32_t taskId;
|
||||
} SVPauseStreamTaskReq, SVResetStreamTaskReq, SVDropHTaskReq;
|
||||
} SVPauseStreamTaskReq, SVResetStreamTaskReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int8_t reserved;
|
||||
|
|
@ -3407,7 +3546,7 @@ int32_t tDeserializeSCreateTagIdxReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SCreateTagIndexR
|
|||
|
||||
typedef SMDropSmaReq SDropTagIndexReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSDropTagIdxReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDropTagIndexReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSDropTagIdxReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDropTagIndexReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSDropTagIdxReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SDropTagIndexReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -3459,7 +3598,7 @@ void* tDeserializeSVDropTSmaReq(void* buf, SVDropTSmaReq* pReq);
|
|||
int32_t tEncodeSVCreateTSmaReq(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVCreateTSmaReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDecodeSVCreateTSmaReq(SDecoder* pCoder, SVCreateTSmaReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tEncodeSVDropTSmaReq(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVDropTSmaReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDecodeSVDropTSmaReq(SDecoder* pCoder, SVDropTSmaReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDecodeSVDropTSmaReq(SDecoder* pCoder, SVDropTSmaReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t number;
|
||||
|
|
@ -3528,8 +3667,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int8_t igNotExists;
|
||||
} SMDropFullTextReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMDropFullTextReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMDropFullTextReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMDropFullTextReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMDropFullTextReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tSerializeSMDropFullTextReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMDropFullTextReq* pReq);
|
||||
// int32_t tDeserializeSMDropFullTextReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMDropFullTextReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char indexFName[TSDB_INDEX_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
@ -3603,6 +3742,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int64_t timeout;
|
||||
STqOffsetVal reqOffset;
|
||||
int8_t enableReplay;
|
||||
int8_t sourceExcluded;
|
||||
} SMqPollReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMqPollReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqPollReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -3732,6 +3872,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t vgId;
|
||||
STqOffsetVal offset;
|
||||
int64_t rows;
|
||||
int64_t ever;
|
||||
} OffsetRows;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -3746,7 +3887,12 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SMqHbReq;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int8_t reserved;
|
||||
char topic[TSDB_TOPIC_FNAME_LEN];
|
||||
int8_t noPrivilege;
|
||||
} STopicPrivilege;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
SArray* topicPrivileges; // SArray<STopicPrivilege>
|
||||
} SMqHbRsp;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -3765,18 +3911,6 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
SVCreateTbReq cTbReq;
|
||||
} SVSubmitBlk;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t flags;
|
||||
int32_t nBlocks;
|
||||
union {
|
||||
SArray* pArray;
|
||||
SVSubmitBlk* pBlocks;
|
||||
};
|
||||
} SVSubmitReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tEncodeSVSubmitReq(SEncoder* pCoder, const SVSubmitReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDecodeSVSubmitReq(SDecoder* pCoder, SVSubmitReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
SMsgHead header;
|
||||
uint64_t sId;
|
||||
|
|
@ -3786,6 +3920,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
uint32_t phyLen;
|
||||
char* sql;
|
||||
char* msg;
|
||||
int8_t source;
|
||||
} SVDeleteReq;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSVDeleteReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SVDeleteReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
|
@ -3807,6 +3942,7 @@ typedef struct SDeleteRes {
|
|||
char tableFName[TSDB_TABLE_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
char tsColName[TSDB_COL_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
int64_t ctimeMs; // fill by vnode
|
||||
int8_t source;
|
||||
} SDeleteRes;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tEncodeDeleteRes(SEncoder* pCoder, const SDeleteRes* pRes);
|
||||
|
|
@ -3883,13 +4019,22 @@ int32_t tSerializeSMqAskEpReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqAskEpReq* pReq);
|
|||
int32_t tDeserializeSMqAskEpReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqAskEpReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMqHbReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqHbReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMqHbReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqHbReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeatroySMqHbReq(SMqHbReq* pReq);
|
||||
void tDestroySMqHbReq(SMqHbReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMqHbRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqHbRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMqHbRsp(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqHbRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
void tDestroySMqHbRsp(SMqHbRsp* pRsp);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tSerializeSMqSeekReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqSeekReq* pReq);
|
||||
int32_t tDeserializeSMqSeekReq(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SMqSeekReq* pReq);
|
||||
|
||||
#define TD_REQ_FROM_APP 0x0
|
||||
#define SUBMIT_REQ_AUTO_CREATE_TABLE 0x1
|
||||
#define SUBMIT_REQ_COLUMN_DATA_FORMAT 0x2
|
||||
#define SUBMIT_REQ_FROM_FILE 0x4
|
||||
#define TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX 0x8
|
||||
|
||||
#define TD_REQ_FROM_TAOX_OLD 0x1 // for compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t flags;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,9 +36,11 @@ typedef enum {
|
|||
SYNC_QUEUE,
|
||||
SYNC_RD_QUEUE,
|
||||
STREAM_QUEUE,
|
||||
ARB_QUEUE,
|
||||
QUEUE_MAX,
|
||||
} EQueueType;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef void (*GetDnodeEp)(void* pData, int32_t dnodeId, char* pEp, char* pFqdn, uint16_t* pPort);
|
||||
typedef bool (*UpdateDnodeInfoFp)(void* pData, int32_t* dnodeId, int64_t* clusterId, char* fqdn, uint16_t* port);
|
||||
typedef int32_t (*PutToQueueFp)(void* pMgmt, EQueueType qtype, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
typedef int32_t (*GetQueueSizeFp)(void* pMgmt, int32_t vgId, EQueueType qtype);
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,6 +66,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
ReleaseHandleFp releaseHandleFp;
|
||||
ReportStartup reportStartupFp;
|
||||
UpdateDnodeInfoFp updateDnodeInfoFp;
|
||||
GetDnodeEp getDnodeEpFp;
|
||||
} SMsgCb;
|
||||
|
||||
void tmsgSetDefault(const SMsgCb* msgcb);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -215,8 +215,11 @@
|
|||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_CREATE_VIEW, "create-view", SCMCreateViewReq, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_DROP_VIEW, "drop-view", SCMDropViewReq, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_VIEW_META, "view-meta", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_STATIS, "statis", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_KILL_COMPACT, "kill-compact", SKillCompactReq, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_COMPACT_TIMER, "compact-tmr", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_STREAM_REQ_CHKPT, "stream-req-checkpoint", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_CONFIG_CLUSTER, "config-cluster", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_MAX_MSG, "mnd-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_MND_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -269,6 +272,8 @@
|
|||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_DISABLE_WRITE, "vnode-disable-write", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_QUERY_COMPACT_PROGRESS, "vnode-query-compact-progress", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_KILL_COMPACT, "kill-compact", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_ARB_HEARTBEAT, "vnode-arb-hb", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_ARB_CHECK_SYNC, "vnode-arb-check-sync", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_MAX_MSG, "vnd-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_VND_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -301,7 +306,6 @@
|
|||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_STREAM_TASK_PAUSE, "stream-task-pause", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_STREAM_TASK_RESUME, "stream-task-resume", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_STREAM_TASK_STOP, "stream-task-stop", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_STREAM_HTASK_DROP, "stream-htask-drop", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_STREAM_MAX_MSG, "stream-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_STREAM_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -337,13 +341,14 @@
|
|||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_LOCAL_CMD, "sync-local-cmd", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_PREP_SNAPSHOT, "sync-prep-snapshot", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_PREP_SNAPSHOT_REPLY, "sync-prep-snapshot-reply", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_MAX_MSG, "sync-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_UNUSED_CODE, "sync-unused", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_FORCE_FOLLOWER, "sync-force-become-follower", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_SET_ASSIGNED_LEADER, "sync-set-assigned-leader", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_SYNC_MAX_MSG, "sync-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_SYNC_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
TD_NEW_MSG_SEG(TDMT_VND_STREAM_MSG) //7 << 8
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_STREAM_SCAN_HISTORY, "vnode-stream-scan-history", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_STREAM_SCAN_HISTORY_FINISH, "vnode-stream-scan-history-finish", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_STREAM_CHECK_POINT_SOURCE, "vnode-stream-checkpoint-source", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_STREAM_TASK_UPDATE, "vnode-stream-update", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_STREAM_TASK_RESET, "vnode-stream-reset", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
|
|
@ -365,6 +370,13 @@
|
|||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_VND_TMQ_MAX_MSG, "vnd-tmq-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_TMQ_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
TD_NEW_MSG_SEG(TDMT_MND_ARB_MSG) //9 << 8
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_ARB_HEARTBEAT_TIMER, "mnd-arb-hb-tmr", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_ARB_CHECK_SYNC_TIMER, "mnd-arb-check-sync-tmr", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_ARB_UPDATE_GROUP, "mnd-arb-update-group", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_DEF_MSG_TYPE(TDMT_MND_ARB_MAX_MSG, "mnd-arb-max", NULL, NULL)
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_ARB_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
TD_NEW_MSG_SEG(TDMT_MAX_MSG) // msg end mark
|
||||
TD_CLOSE_MSG_SEG(TDMT_END_MAX_MSG)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -289,7 +289,7 @@ int32_t tdGetBitmapValType(const void *pBitmap, int16_t colIdx, TDRowValT *pValT
|
|||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
static FORCE_INLINE void tdSRowInit(SRowBuilder *pBuilder, int16_t sver) {
|
||||
pBuilder->rowType = TD_ROW_TP; // default STpRow
|
||||
pBuilder->rowType = pBuilder->rowType;
|
||||
pBuilder->sver = sver;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int32_t tdSRowSetInfo(SRowBuilder *pBuilder, int32_t nCols, int32_t nBoundCols, int32_t flen);
|
||||
|
|
@ -331,7 +331,7 @@ void tdSTSRowIterReset(STSRowIter *pIter, STSRow *pRow);
|
|||
bool tdSTSRowIterFetch(STSRowIter *pIter, col_id_t colId, col_type_t colType, SCellVal *pVal);
|
||||
bool tdSTSRowIterNext(STSRowIter *pIter, SCellVal *pVal);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t tdSTSRowNew(SArray *pArray, STSchema *pTSchema, STSRow **ppRow);
|
||||
int32_t tdSTSRowNew(SArray *pArray, STSchema *pTSchema, STSRow **ppRow, int8_t rowType);
|
||||
bool tdSTSRowGetVal(STSRowIter *pIter, col_id_t colId, col_type_t colType, SCellVal *pVal);
|
||||
void tdSRowPrint(STSRow *row, STSchema *pSchema, const char *tag);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -74,307 +74,315 @@
|
|||
#define TK_NK_IPTOKEN 55
|
||||
#define TK_FORCE 56
|
||||
#define TK_UNSAFE 57
|
||||
#define TK_LOCAL 58
|
||||
#define TK_QNODE 59
|
||||
#define TK_BNODE 60
|
||||
#define TK_SNODE 61
|
||||
#define TK_MNODE 62
|
||||
#define TK_VNODE 63
|
||||
#define TK_DATABASE 64
|
||||
#define TK_USE 65
|
||||
#define TK_FLUSH 66
|
||||
#define TK_TRIM 67
|
||||
#define TK_COMPACT 68
|
||||
#define TK_IF 69
|
||||
#define TK_NOT 70
|
||||
#define TK_EXISTS 71
|
||||
#define TK_BUFFER 72
|
||||
#define TK_CACHEMODEL 73
|
||||
#define TK_CACHESIZE 74
|
||||
#define TK_COMP 75
|
||||
#define TK_DURATION 76
|
||||
#define TK_NK_VARIABLE 77
|
||||
#define TK_MAXROWS 78
|
||||
#define TK_MINROWS 79
|
||||
#define TK_KEEP 80
|
||||
#define TK_PAGES 81
|
||||
#define TK_PAGESIZE 82
|
||||
#define TK_TSDB_PAGESIZE 83
|
||||
#define TK_PRECISION 84
|
||||
#define TK_REPLICA 85
|
||||
#define TK_VGROUPS 86
|
||||
#define TK_SINGLE_STABLE 87
|
||||
#define TK_RETENTIONS 88
|
||||
#define TK_SCHEMALESS 89
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_LEVEL 90
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_FSYNC_PERIOD 91
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_RETENTION_PERIOD 92
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_RETENTION_SIZE 93
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_ROLL_PERIOD 94
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_SEGMENT_SIZE 95
|
||||
#define TK_STT_TRIGGER 96
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE_PREFIX 97
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE_SUFFIX 98
|
||||
#define TK_KEEP_TIME_OFFSET 99
|
||||
#define TK_NK_COLON 100
|
||||
#define TK_BWLIMIT 101
|
||||
#define TK_START 102
|
||||
#define TK_TIMESTAMP 103
|
||||
#define TK_END 104
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE 105
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LP 106
|
||||
#define TK_NK_RP 107
|
||||
#define TK_STABLE 108
|
||||
#define TK_COLUMN 109
|
||||
#define TK_MODIFY 110
|
||||
#define TK_RENAME 111
|
||||
#define TK_TAG 112
|
||||
#define TK_SET 113
|
||||
#define TK_NK_EQ 114
|
||||
#define TK_USING 115
|
||||
#define TK_TAGS 116
|
||||
#define TK_BOOL 117
|
||||
#define TK_TINYINT 118
|
||||
#define TK_SMALLINT 119
|
||||
#define TK_INT 120
|
||||
#define TK_INTEGER 121
|
||||
#define TK_BIGINT 122
|
||||
#define TK_FLOAT 123
|
||||
#define TK_DOUBLE 124
|
||||
#define TK_BINARY 125
|
||||
#define TK_NCHAR 126
|
||||
#define TK_UNSIGNED 127
|
||||
#define TK_JSON 128
|
||||
#define TK_VARCHAR 129
|
||||
#define TK_MEDIUMBLOB 130
|
||||
#define TK_BLOB 131
|
||||
#define TK_VARBINARY 132
|
||||
#define TK_GEOMETRY 133
|
||||
#define TK_DECIMAL 134
|
||||
#define TK_COMMENT 135
|
||||
#define TK_MAX_DELAY 136
|
||||
#define TK_WATERMARK 137
|
||||
#define TK_ROLLUP 138
|
||||
#define TK_TTL 139
|
||||
#define TK_SMA 140
|
||||
#define TK_DELETE_MARK 141
|
||||
#define TK_FIRST 142
|
||||
#define TK_LAST 143
|
||||
#define TK_SHOW 144
|
||||
#define TK_PRIVILEGES 145
|
||||
#define TK_DATABASES 146
|
||||
#define TK_TABLES 147
|
||||
#define TK_STABLES 148
|
||||
#define TK_MNODES 149
|
||||
#define TK_QNODES 150
|
||||
#define TK_FUNCTIONS 151
|
||||
#define TK_INDEXES 152
|
||||
#define TK_ACCOUNTS 153
|
||||
#define TK_APPS 154
|
||||
#define TK_CONNECTIONS 155
|
||||
#define TK_LICENCES 156
|
||||
#define TK_GRANTS 157
|
||||
#define TK_QUERIES 158
|
||||
#define TK_SCORES 159
|
||||
#define TK_TOPICS 160
|
||||
#define TK_VARIABLES 161
|
||||
#define TK_CLUSTER 162
|
||||
#define TK_BNODES 163
|
||||
#define TK_SNODES 164
|
||||
#define TK_TRANSACTIONS 165
|
||||
#define TK_DISTRIBUTED 166
|
||||
#define TK_CONSUMERS 167
|
||||
#define TK_SUBSCRIPTIONS 168
|
||||
#define TK_VNODES 169
|
||||
#define TK_ALIVE 170
|
||||
#define TK_VIEWS 171
|
||||
#define TK_VIEW 172
|
||||
#define TK_COMPACTS 173
|
||||
#define TK_NORMAL 174
|
||||
#define TK_CHILD 175
|
||||
#define TK_LIKE 176
|
||||
#define TK_TBNAME 177
|
||||
#define TK_QTAGS 178
|
||||
#define TK_AS 179
|
||||
#define TK_SYSTEM 180
|
||||
#define TK_INDEX 181
|
||||
#define TK_FUNCTION 182
|
||||
#define TK_INTERVAL 183
|
||||
#define TK_COUNT 184
|
||||
#define TK_LAST_ROW 185
|
||||
#define TK_META 186
|
||||
#define TK_ONLY 187
|
||||
#define TK_TOPIC 188
|
||||
#define TK_CONSUMER 189
|
||||
#define TK_GROUP 190
|
||||
#define TK_DESC 191
|
||||
#define TK_DESCRIBE 192
|
||||
#define TK_RESET 193
|
||||
#define TK_QUERY 194
|
||||
#define TK_CACHE 195
|
||||
#define TK_EXPLAIN 196
|
||||
#define TK_ANALYZE 197
|
||||
#define TK_VERBOSE 198
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BOOL 199
|
||||
#define TK_RATIO 200
|
||||
#define TK_NK_FLOAT 201
|
||||
#define TK_OUTPUTTYPE 202
|
||||
#define TK_AGGREGATE 203
|
||||
#define TK_BUFSIZE 204
|
||||
#define TK_LANGUAGE 205
|
||||
#define TK_REPLACE 206
|
||||
#define TK_STREAM 207
|
||||
#define TK_INTO 208
|
||||
#define TK_PAUSE 209
|
||||
#define TK_RESUME 210
|
||||
#define TK_TRIGGER 211
|
||||
#define TK_AT_ONCE 212
|
||||
#define TK_WINDOW_CLOSE 213
|
||||
#define TK_IGNORE 214
|
||||
#define TK_EXPIRED 215
|
||||
#define TK_FILL_HISTORY 216
|
||||
#define TK_UPDATE 217
|
||||
#define TK_SUBTABLE 218
|
||||
#define TK_UNTREATED 219
|
||||
#define TK_KILL 220
|
||||
#define TK_CONNECTION 221
|
||||
#define TK_TRANSACTION 222
|
||||
#define TK_BALANCE 223
|
||||
#define TK_VGROUP 224
|
||||
#define TK_LEADER 225
|
||||
#define TK_MERGE 226
|
||||
#define TK_REDISTRIBUTE 227
|
||||
#define TK_SPLIT 228
|
||||
#define TK_DELETE 229
|
||||
#define TK_INSERT 230
|
||||
#define TK_NULL 231
|
||||
#define TK_NK_QUESTION 232
|
||||
#define TK_NK_ALIAS 233
|
||||
#define TK_NK_ARROW 234
|
||||
#define TK_ROWTS 235
|
||||
#define TK_QSTART 236
|
||||
#define TK_QEND 237
|
||||
#define TK_QDURATION 238
|
||||
#define TK_WSTART 239
|
||||
#define TK_WEND 240
|
||||
#define TK_WDURATION 241
|
||||
#define TK_IROWTS 242
|
||||
#define TK_ISFILLED 243
|
||||
#define TK_CAST 244
|
||||
#define TK_NOW 245
|
||||
#define TK_TODAY 246
|
||||
#define TK_TIMEZONE 247
|
||||
#define TK_CLIENT_VERSION 248
|
||||
#define TK_SERVER_VERSION 249
|
||||
#define TK_SERVER_STATUS 250
|
||||
#define TK_CURRENT_USER 251
|
||||
#define TK_CASE 252
|
||||
#define TK_WHEN 253
|
||||
#define TK_THEN 254
|
||||
#define TK_ELSE 255
|
||||
#define TK_BETWEEN 256
|
||||
#define TK_IS 257
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LT 258
|
||||
#define TK_NK_GT 259
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LE 260
|
||||
#define TK_NK_GE 261
|
||||
#define TK_NK_NE 262
|
||||
#define TK_MATCH 263
|
||||
#define TK_NMATCH 264
|
||||
#define TK_CONTAINS 265
|
||||
#define TK_IN 266
|
||||
#define TK_JOIN 267
|
||||
#define TK_INNER 268
|
||||
#define TK_SELECT 269
|
||||
#define TK_NK_HINT 270
|
||||
#define TK_DISTINCT 271
|
||||
#define TK_WHERE 272
|
||||
#define TK_PARTITION 273
|
||||
#define TK_BY 274
|
||||
#define TK_SESSION 275
|
||||
#define TK_STATE_WINDOW 276
|
||||
#define TK_EVENT_WINDOW 277
|
||||
#define TK_SLIDING 278
|
||||
#define TK_FILL 279
|
||||
#define TK_VALUE 280
|
||||
#define TK_VALUE_F 281
|
||||
#define TK_NONE 282
|
||||
#define TK_PREV 283
|
||||
#define TK_NULL_F 284
|
||||
#define TK_LINEAR 285
|
||||
#define TK_NEXT 286
|
||||
#define TK_HAVING 287
|
||||
#define TK_RANGE 288
|
||||
#define TK_EVERY 289
|
||||
#define TK_ORDER 290
|
||||
#define TK_SLIMIT 291
|
||||
#define TK_SOFFSET 292
|
||||
#define TK_LIMIT 293
|
||||
#define TK_OFFSET 294
|
||||
#define TK_ASC 295
|
||||
#define TK_NULLS 296
|
||||
#define TK_ABORT 297
|
||||
#define TK_AFTER 298
|
||||
#define TK_ATTACH 299
|
||||
#define TK_BEFORE 300
|
||||
#define TK_BEGIN 301
|
||||
#define TK_BITAND 302
|
||||
#define TK_BITNOT 303
|
||||
#define TK_BITOR 304
|
||||
#define TK_BLOCKS 305
|
||||
#define TK_CHANGE 306
|
||||
#define TK_COMMA 307
|
||||
#define TK_CONCAT 308
|
||||
#define TK_CONFLICT 309
|
||||
#define TK_COPY 310
|
||||
#define TK_DEFERRED 311
|
||||
#define TK_DELIMITERS 312
|
||||
#define TK_DETACH 313
|
||||
#define TK_DIVIDE 314
|
||||
#define TK_DOT 315
|
||||
#define TK_EACH 316
|
||||
#define TK_FAIL 317
|
||||
#define TK_FILE 318
|
||||
#define TK_FOR 319
|
||||
#define TK_GLOB 320
|
||||
#define TK_ID 321
|
||||
#define TK_IMMEDIATE 322
|
||||
#define TK_IMPORT 323
|
||||
#define TK_INITIALLY 324
|
||||
#define TK_INSTEAD 325
|
||||
#define TK_ISNULL 326
|
||||
#define TK_KEY 327
|
||||
#define TK_MODULES 328
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BITNOT 329
|
||||
#define TK_NK_SEMI 330
|
||||
#define TK_NOTNULL 331
|
||||
#define TK_OF 332
|
||||
#define TK_PLUS 333
|
||||
#define TK_PRIVILEGE 334
|
||||
#define TK_RAISE 335
|
||||
#define TK_RESTRICT 336
|
||||
#define TK_ROW 337
|
||||
#define TK_SEMI 338
|
||||
#define TK_STAR 339
|
||||
#define TK_STATEMENT 340
|
||||
#define TK_STRICT 341
|
||||
#define TK_STRING 342
|
||||
#define TK_TIMES 343
|
||||
#define TK_VALUES 344
|
||||
#define TK_VARIABLE 345
|
||||
#define TK_WAL 346
|
||||
#define TK_CLUSTER 58
|
||||
#define TK_LOCAL 59
|
||||
#define TK_QNODE 60
|
||||
#define TK_BNODE 61
|
||||
#define TK_SNODE 62
|
||||
#define TK_MNODE 63
|
||||
#define TK_VNODE 64
|
||||
#define TK_DATABASE 65
|
||||
#define TK_USE 66
|
||||
#define TK_FLUSH 67
|
||||
#define TK_TRIM 68
|
||||
#define TK_COMPACT 69
|
||||
#define TK_IF 70
|
||||
#define TK_NOT 71
|
||||
#define TK_EXISTS 72
|
||||
#define TK_BUFFER 73
|
||||
#define TK_CACHEMODEL 74
|
||||
#define TK_CACHESIZE 75
|
||||
#define TK_COMP 76
|
||||
#define TK_DURATION 77
|
||||
#define TK_NK_VARIABLE 78
|
||||
#define TK_MAXROWS 79
|
||||
#define TK_MINROWS 80
|
||||
#define TK_KEEP 81
|
||||
#define TK_PAGES 82
|
||||
#define TK_PAGESIZE 83
|
||||
#define TK_TSDB_PAGESIZE 84
|
||||
#define TK_PRECISION 85
|
||||
#define TK_REPLICA 86
|
||||
#define TK_VGROUPS 87
|
||||
#define TK_SINGLE_STABLE 88
|
||||
#define TK_RETENTIONS 89
|
||||
#define TK_SCHEMALESS 90
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_LEVEL 91
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_FSYNC_PERIOD 92
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_RETENTION_PERIOD 93
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_RETENTION_SIZE 94
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_ROLL_PERIOD 95
|
||||
#define TK_WAL_SEGMENT_SIZE 96
|
||||
#define TK_STT_TRIGGER 97
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE_PREFIX 98
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE_SUFFIX 99
|
||||
#define TK_KEEP_TIME_OFFSET 100
|
||||
#define TK_NK_COLON 101
|
||||
#define TK_BWLIMIT 102
|
||||
#define TK_START 103
|
||||
#define TK_TIMESTAMP 104
|
||||
#define TK_END 105
|
||||
#define TK_TABLE 106
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LP 107
|
||||
#define TK_NK_RP 108
|
||||
#define TK_STABLE 109
|
||||
#define TK_COLUMN 110
|
||||
#define TK_MODIFY 111
|
||||
#define TK_RENAME 112
|
||||
#define TK_TAG 113
|
||||
#define TK_SET 114
|
||||
#define TK_NK_EQ 115
|
||||
#define TK_USING 116
|
||||
#define TK_TAGS 117
|
||||
#define TK_BOOL 118
|
||||
#define TK_TINYINT 119
|
||||
#define TK_SMALLINT 120
|
||||
#define TK_INT 121
|
||||
#define TK_INTEGER 122
|
||||
#define TK_BIGINT 123
|
||||
#define TK_FLOAT 124
|
||||
#define TK_DOUBLE 125
|
||||
#define TK_BINARY 126
|
||||
#define TK_NCHAR 127
|
||||
#define TK_UNSIGNED 128
|
||||
#define TK_JSON 129
|
||||
#define TK_VARCHAR 130
|
||||
#define TK_MEDIUMBLOB 131
|
||||
#define TK_BLOB 132
|
||||
#define TK_VARBINARY 133
|
||||
#define TK_GEOMETRY 134
|
||||
#define TK_DECIMAL 135
|
||||
#define TK_COMMENT 136
|
||||
#define TK_MAX_DELAY 137
|
||||
#define TK_WATERMARK 138
|
||||
#define TK_ROLLUP 139
|
||||
#define TK_TTL 140
|
||||
#define TK_SMA 141
|
||||
#define TK_DELETE_MARK 142
|
||||
#define TK_FIRST 143
|
||||
#define TK_LAST 144
|
||||
#define TK_SHOW 145
|
||||
#define TK_PRIVILEGES 146
|
||||
#define TK_DATABASES 147
|
||||
#define TK_TABLES 148
|
||||
#define TK_STABLES 149
|
||||
#define TK_MNODES 150
|
||||
#define TK_QNODES 151
|
||||
#define TK_ARBGROUPS 152
|
||||
#define TK_FUNCTIONS 153
|
||||
#define TK_INDEXES 154
|
||||
#define TK_ACCOUNTS 155
|
||||
#define TK_APPS 156
|
||||
#define TK_CONNECTIONS 157
|
||||
#define TK_LICENCES 158
|
||||
#define TK_GRANTS 159
|
||||
#define TK_FULL 160
|
||||
#define TK_LOGS 161
|
||||
#define TK_MACHINES 162
|
||||
#define TK_QUERIES 163
|
||||
#define TK_SCORES 164
|
||||
#define TK_TOPICS 165
|
||||
#define TK_VARIABLES 166
|
||||
#define TK_BNODES 167
|
||||
#define TK_SNODES 168
|
||||
#define TK_TRANSACTIONS 169
|
||||
#define TK_DISTRIBUTED 170
|
||||
#define TK_CONSUMERS 171
|
||||
#define TK_SUBSCRIPTIONS 172
|
||||
#define TK_VNODES 173
|
||||
#define TK_ALIVE 174
|
||||
#define TK_VIEWS 175
|
||||
#define TK_VIEW 176
|
||||
#define TK_COMPACTS 177
|
||||
#define TK_NORMAL 178
|
||||
#define TK_CHILD 179
|
||||
#define TK_LIKE 180
|
||||
#define TK_TBNAME 181
|
||||
#define TK_QTAGS 182
|
||||
#define TK_AS 183
|
||||
#define TK_SYSTEM 184
|
||||
#define TK_INDEX 185
|
||||
#define TK_FUNCTION 186
|
||||
#define TK_INTERVAL 187
|
||||
#define TK_COUNT 188
|
||||
#define TK_LAST_ROW 189
|
||||
#define TK_META 190
|
||||
#define TK_ONLY 191
|
||||
#define TK_TOPIC 192
|
||||
#define TK_CONSUMER 193
|
||||
#define TK_GROUP 194
|
||||
#define TK_DESC 195
|
||||
#define TK_DESCRIBE 196
|
||||
#define TK_RESET 197
|
||||
#define TK_QUERY 198
|
||||
#define TK_CACHE 199
|
||||
#define TK_EXPLAIN 200
|
||||
#define TK_ANALYZE 201
|
||||
#define TK_VERBOSE 202
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BOOL 203
|
||||
#define TK_RATIO 204
|
||||
#define TK_NK_FLOAT 205
|
||||
#define TK_OUTPUTTYPE 206
|
||||
#define TK_AGGREGATE 207
|
||||
#define TK_BUFSIZE 208
|
||||
#define TK_LANGUAGE 209
|
||||
#define TK_REPLACE 210
|
||||
#define TK_STREAM 211
|
||||
#define TK_INTO 212
|
||||
#define TK_PAUSE 213
|
||||
#define TK_RESUME 214
|
||||
#define TK_TRIGGER 215
|
||||
#define TK_AT_ONCE 216
|
||||
#define TK_WINDOW_CLOSE 217
|
||||
#define TK_IGNORE 218
|
||||
#define TK_EXPIRED 219
|
||||
#define TK_FILL_HISTORY 220
|
||||
#define TK_UPDATE 221
|
||||
#define TK_SUBTABLE 222
|
||||
#define TK_UNTREATED 223
|
||||
#define TK_KILL 224
|
||||
#define TK_CONNECTION 225
|
||||
#define TK_TRANSACTION 226
|
||||
#define TK_BALANCE 227
|
||||
#define TK_VGROUP 228
|
||||
#define TK_LEADER 229
|
||||
#define TK_MERGE 230
|
||||
#define TK_REDISTRIBUTE 231
|
||||
#define TK_SPLIT 232
|
||||
#define TK_DELETE 233
|
||||
#define TK_INSERT 234
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BIN 235
|
||||
#define TK_NK_HEX 236
|
||||
#define TK_NULL 237
|
||||
#define TK_NK_QUESTION 238
|
||||
#define TK_NK_ALIAS 239
|
||||
#define TK_NK_ARROW 240
|
||||
#define TK_ROWTS 241
|
||||
#define TK_QSTART 242
|
||||
#define TK_QEND 243
|
||||
#define TK_QDURATION 244
|
||||
#define TK_WSTART 245
|
||||
#define TK_WEND 246
|
||||
#define TK_WDURATION 247
|
||||
#define TK_IROWTS 248
|
||||
#define TK_ISFILLED 249
|
||||
#define TK_CAST 250
|
||||
#define TK_NOW 251
|
||||
#define TK_TODAY 252
|
||||
#define TK_TIMEZONE 253
|
||||
#define TK_CLIENT_VERSION 254
|
||||
#define TK_SERVER_VERSION 255
|
||||
#define TK_SERVER_STATUS 256
|
||||
#define TK_CURRENT_USER 257
|
||||
#define TK_CASE 258
|
||||
#define TK_WHEN 259
|
||||
#define TK_THEN 260
|
||||
#define TK_ELSE 261
|
||||
#define TK_BETWEEN 262
|
||||
#define TK_IS 263
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LT 264
|
||||
#define TK_NK_GT 265
|
||||
#define TK_NK_LE 266
|
||||
#define TK_NK_GE 267
|
||||
#define TK_NK_NE 268
|
||||
#define TK_MATCH 269
|
||||
#define TK_NMATCH 270
|
||||
#define TK_CONTAINS 271
|
||||
#define TK_IN 272
|
||||
#define TK_JOIN 273
|
||||
#define TK_INNER 274
|
||||
#define TK_SELECT 275
|
||||
#define TK_NK_HINT 276
|
||||
#define TK_DISTINCT 277
|
||||
#define TK_WHERE 278
|
||||
#define TK_PARTITION 279
|
||||
#define TK_BY 280
|
||||
#define TK_SESSION 281
|
||||
#define TK_STATE_WINDOW 282
|
||||
#define TK_EVENT_WINDOW 283
|
||||
#define TK_COUNT_WINDOW 284
|
||||
#define TK_SLIDING 285
|
||||
#define TK_FILL 286
|
||||
#define TK_VALUE 287
|
||||
#define TK_VALUE_F 288
|
||||
#define TK_NONE 289
|
||||
#define TK_PREV 290
|
||||
#define TK_NULL_F 291
|
||||
#define TK_LINEAR 292
|
||||
#define TK_NEXT 293
|
||||
#define TK_HAVING 294
|
||||
#define TK_RANGE 295
|
||||
#define TK_EVERY 296
|
||||
#define TK_ORDER 297
|
||||
#define TK_SLIMIT 298
|
||||
#define TK_SOFFSET 299
|
||||
#define TK_LIMIT 300
|
||||
#define TK_OFFSET 301
|
||||
#define TK_ASC 302
|
||||
#define TK_NULLS 303
|
||||
#define TK_ABORT 304
|
||||
#define TK_AFTER 305
|
||||
#define TK_ATTACH 306
|
||||
#define TK_BEFORE 307
|
||||
#define TK_BEGIN 308
|
||||
#define TK_BITAND 309
|
||||
#define TK_BITNOT 310
|
||||
#define TK_BITOR 311
|
||||
#define TK_BLOCKS 312
|
||||
#define TK_CHANGE 313
|
||||
#define TK_COMMA 314
|
||||
#define TK_CONCAT 315
|
||||
#define TK_CONFLICT 316
|
||||
#define TK_COPY 317
|
||||
#define TK_DEFERRED 318
|
||||
#define TK_DELIMITERS 319
|
||||
#define TK_DETACH 320
|
||||
#define TK_DIVIDE 321
|
||||
#define TK_DOT 322
|
||||
#define TK_EACH 323
|
||||
#define TK_FAIL 324
|
||||
#define TK_FILE 325
|
||||
#define TK_FOR 326
|
||||
#define TK_GLOB 327
|
||||
#define TK_ID 328
|
||||
#define TK_IMMEDIATE 329
|
||||
#define TK_IMPORT 330
|
||||
#define TK_INITIALLY 331
|
||||
#define TK_INSTEAD 332
|
||||
#define TK_ISNULL 333
|
||||
#define TK_KEY 334
|
||||
#define TK_MODULES 335
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BITNOT 336
|
||||
#define TK_NK_SEMI 337
|
||||
#define TK_NOTNULL 338
|
||||
#define TK_OF 339
|
||||
#define TK_PLUS 340
|
||||
#define TK_PRIVILEGE 341
|
||||
#define TK_RAISE 342
|
||||
#define TK_RESTRICT 343
|
||||
#define TK_ROW 344
|
||||
#define TK_SEMI 345
|
||||
#define TK_STAR 346
|
||||
#define TK_STATEMENT 347
|
||||
#define TK_STRICT 348
|
||||
#define TK_STRING 349
|
||||
#define TK_TIMES 350
|
||||
#define TK_VALUES 351
|
||||
#define TK_VARIABLE 352
|
||||
#define TK_WAL 353
|
||||
|
||||
#define TK_NK_SPACE 600
|
||||
#define TK_NK_COMMENT 601
|
||||
#define TK_NK_ILLEGAL 602
|
||||
#define TK_NK_HEX 603 // hex number 0x123
|
||||
// #define TK_NK_HEX 603 // hex number 0x123
|
||||
#define TK_NK_OCT 604 // oct number
|
||||
#define TK_NK_BIN 605 // bin format data 0b111
|
||||
// #define TK_NK_BIN 605 // bin format data 0b111
|
||||
#define TK_BATCH_SCAN 606
|
||||
#define TK_NO_BATCH_SCAN 607
|
||||
#define TK_SORT_FOR_GROUP 608
|
||||
#define TK_PARTITION_FIRST 609
|
||||
|
||||
#define TK_PARA_TABLES_SORT 610
|
||||
#define TK_SMALLDATA_TS_SORT 611
|
||||
|
||||
#define TK_NK_NIL 65535
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -44,6 +44,11 @@ int32_t toDoubleEx(const char *z, int32_t n, uint32_t type, double *value);
|
|||
int32_t toInteger(const char *z, int32_t n, int32_t base, int64_t *value);
|
||||
int32_t toUInteger(const char *z, int32_t n, int32_t base, uint64_t *value);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* non floating point integers
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int32_t toIntegerPure(const char *z, int32_t n, int32_t base, int64_t *value);
|
||||
|
||||
void taosVariantCreateFromBinary(SVariant *pVar, const char *pz, size_t len, uint32_t type);
|
||||
|
||||
void taosVariantDestroy(SVariant *pV);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -75,6 +75,9 @@ void mndStop(SMnode *pMnode);
|
|||
|
||||
int32_t mndIsCatchUp(SMnode *pMnode);
|
||||
ESyncRole mndGetRole(SMnode *pMnode);
|
||||
int64_t mndGetTerm(SMnode *pMnode);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t mndGetArbToken(SMnode *pMnode, char *outToken);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Get mnode monitor info.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,22 +18,24 @@
|
|||
|
||||
// message process
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskStartAsync(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SMsgCb* cb, bool restart);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamOneTaskStartAsync(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SMsgCb* cb, int64_t streamId, int32_t taskId);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamStartOneTaskAsync(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SMsgCb* cb, int64_t streamId, int32_t taskId);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessUpdateReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SMsgCb* cb, SRpcMsg* pMsg, bool restored);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessDispatchReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessDispatchRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessRetrieveReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessScanHistoryFinishReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessScanHistoryFinishRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessCheckReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessCheckRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg, bool isLeader);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessCheckpointReadyMsg(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamProcessStreamHbRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamProcessReqCheckpointRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamProcessCheckpointReadyRsp(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessDeployReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SMsgCb* cb, int64_t sversion, char* msg, int32_t msgLen,
|
||||
bool isLeader, bool restored);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessDropReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, char* msg, int32_t msgLen);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessRunReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg, bool isLeader);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskResetStatus(SStreamMeta* pMeta, int32_t* numOfTasks);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskResetStatus(SStreamMeta* pMeta);
|
||||
int32_t tqStartTaskCompleteCallback(SStreamMeta* pMeta);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTasksGetTotalNum(SStreamMeta* pMeta);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessTaskResetReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, SRpcMsg* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessTaskPauseReq(SStreamMeta* pMeta, char* pMsg);
|
||||
int32_t tqStreamTaskProcessTaskResumeReq(void* handle, int64_t sversion, char* pMsg, bool fromVnode);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -358,7 +358,7 @@ int32_t catalogGetUdfInfo(SCatalog* pCtg, SRequestConnInfo* pConn, const char* f
|
|||
|
||||
int32_t catalogChkAuth(SCatalog* pCtg, SRequestConnInfo* pConn, SUserAuthInfo *pAuth, SUserAuthRes* pRes);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t catalogChkAuthFromCache(SCatalog* pCtg, SUserAuthInfo *pAuth, SUserAuthRes* pRes, bool* exists);
|
||||
int32_t catalogChkAuthFromCache(SCatalog* pCtg, SUserAuthInfo *pAuth, SUserAuthRes* pRes, bool* exists);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t catalogUpdateUserAuthInfo(SCatalog* pCtg, SGetUserAuthRsp* pAuth);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -197,6 +197,8 @@ int32_t qStreamPrepareScan(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, STqOffsetVal* pOffset, int8_t subT
|
|||
|
||||
void qStreamSetOpen(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
|
||||
void qStreamSetSourceExcluded(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, int8_t sourceExcluded);
|
||||
|
||||
void qStreamExtractOffset(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, STqOffsetVal* pOffset);
|
||||
|
||||
SMqMetaRsp* qStreamExtractMetaMsg(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
|
|
@ -210,11 +212,9 @@ void* qExtractReaderFromStreamScanner(void* scanner);
|
|||
int32_t qExtractStreamScanner(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, void** scanner);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t qSetStreamOperatorOptionForScanHistory(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
int32_t qResetStreamOperatorOptionForScanHistory(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
int32_t qStreamSourceScanParamForHistoryScanStep1(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, SVersionRange *pVerRange, STimeWindow* pWindow);
|
||||
int32_t qStreamSourceScanParamForHistoryScanStep2(qTaskInfo_t tinfo, SVersionRange *pVerRange, STimeWindow* pWindow);
|
||||
int32_t qStreamRecoverFinish(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
int32_t qRestoreStreamOperatorOption(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
bool qStreamScanhistoryFinished(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
int32_t qStreamInfoResetTimewindowFilter(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
void resetTaskInfo(qTaskInfo_t tinfo);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,6 +36,7 @@ extern "C" {
|
|||
#define CACHESCAN_RETRIEVE_LAST_ROW 0x4
|
||||
#define CACHESCAN_RETRIEVE_LAST 0x8
|
||||
|
||||
#define META_READER_LOCK 0x0
|
||||
#define META_READER_NOLOCK 0x1
|
||||
|
||||
#define STREAM_STATE_BUFF_HASH 1
|
||||
|
|
@ -189,7 +190,8 @@ typedef struct TsdReader {
|
|||
|
||||
typedef struct SStoreCacheReader {
|
||||
int32_t (*openReader)(void *pVnode, int32_t type, void *pTableIdList, int32_t numOfTables, int32_t numOfCols,
|
||||
SArray *pCidList, int32_t *pSlotIds, uint64_t suid, void **pReader, const char *idstr);
|
||||
SArray *pCidList, int32_t *pSlotIds, uint64_t suid, void **pReader, const char *idstr,
|
||||
SArray *pFuncTypeList);
|
||||
void *(*closeReader)(void *pReader);
|
||||
int32_t (*retrieveRows)(void *pReader, SSDataBlock *pResBlock, const int32_t *slotIds, const int32_t *dstSlotIds,
|
||||
SArray *pTableUidList);
|
||||
|
|
@ -210,6 +212,7 @@ typedef struct SStoreTqReader {
|
|||
bool (*tqNextBlockImpl)(); // todo remove it
|
||||
SSDataBlock* (*tqGetResultBlock)();
|
||||
int64_t (*tqGetResultBlockTime)();
|
||||
int32_t (*tqGetStreamExecProgress)();
|
||||
|
||||
void (*tqReaderSetColIdList)();
|
||||
int32_t (*tqReaderSetQueryTableList)();
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,10 +224,10 @@ typedef struct SStoreTqReader {
|
|||
bool (*tqReaderCurrentBlockConsumed)();
|
||||
|
||||
struct SWalReader* (*tqReaderGetWalReader)(); // todo remove it
|
||||
int32_t (*tqReaderRetrieveTaosXBlock)(); // todo remove it
|
||||
// int32_t (*tqReaderRetrieveTaosXBlock)(); // todo remove it
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t (*tqReaderSetSubmitMsg)(); // todo remove it
|
||||
bool (*tqReaderNextBlockFilterOut)();
|
||||
// bool (*tqReaderNextBlockFilterOut)();
|
||||
} SStoreTqReader;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SStoreSnapshotFn {
|
||||
|
|
@ -235,12 +238,12 @@ typedef struct SStoreSnapshotFn {
|
|||
} SStoreSnapshotFn;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SStoreMeta {
|
||||
SMTbCursor* (*openTableMetaCursor)(void* pVnode); // metaOpenTbCursor
|
||||
void (*closeTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur); // metaCloseTbCursor
|
||||
void (*pauseTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur); // metaPauseTbCursor
|
||||
void (*resumeTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, int8_t first); // metaResumeTbCursor
|
||||
int32_t (*cursorNext)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, ETableType jumpTableType); // metaTbCursorNext
|
||||
int32_t (*cursorPrev)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, ETableType jumpTableType); // metaTbCursorPrev
|
||||
SMTbCursor* (*openTableMetaCursor)(void* pVnode); // metaOpenTbCursor
|
||||
void (*closeTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur); // metaCloseTbCursor
|
||||
void (*pauseTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur); // metaPauseTbCursor
|
||||
void (*resumeTableMetaCursor)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, int8_t first, int8_t move); // metaResumeTbCursor
|
||||
int32_t (*cursorNext)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, ETableType jumpTableType); // metaTbCursorNext
|
||||
int32_t (*cursorPrev)(SMTbCursor* pTbCur, ETableType jumpTableType); // metaTbCursorPrev
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t (*getTableTags)(void* pVnode, uint64_t suid, SArray* uidList);
|
||||
int32_t (*getTableTagsByUid)(void* pVnode, int64_t suid, SArray* uidList);
|
||||
|
|
@ -265,16 +268,11 @@ typedef struct SStoreMeta {
|
|||
// support filter and non-filter cases. [vnodeGetCtbIdList & vnodeGetCtbIdListByFilter]
|
||||
int32_t (*getChildTableList)(void* pVnode, int64_t suid, SArray* list);
|
||||
int32_t (*storeGetTableList)(void* pVnode, int8_t type, SArray* pList);
|
||||
void* storeGetVersionRange;
|
||||
void* storeGetLastTimestamp;
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t (*getTableSchema)(void* pVnode, int64_t uid, STSchema** pSchema, int64_t* suid); // tsdbGetTableSchema
|
||||
int32_t (*getTableSchema)(void* pVnode, int64_t uid, STSchema** pSchema, int64_t* suid);
|
||||
int32_t (*getNumOfChildTables)(void* pVnode, int64_t uid, int64_t* numOfTables, int32_t* numOfCols);
|
||||
void (*getBasicInfo)(void* pVnode, const char** dbname, int32_t* vgId, int64_t* numOfTables,
|
||||
int64_t* numOfNormalTables);
|
||||
|
||||
int64_t (*getNumOfRowsInMem)(void* pVnode);
|
||||
|
||||
SMCtbCursor* (*openCtbCursor)(void* pVnode, tb_uid_t uid, int lock);
|
||||
int32_t (*resumeCtbCursor)(SMCtbCursor* pCtbCur, int8_t first);
|
||||
void (*pauseCtbCursor)(SMCtbCursor* pCtbCur);
|
||||
|
|
@ -355,14 +353,19 @@ typedef struct SStateStore {
|
|||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionPut)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* key, void* value, int32_t vLen);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionGet)(SStreamState* pState, SSessionKey* key, void** pVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionDel)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* key);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionReset)(SStreamState* pState, void* pVal);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionClear)(SStreamState* pState);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionGetKVByCur)(SStreamStateCur* pCur, SSessionKey* pKey, void** pVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateStateAddIfNotExist)(SStreamState* pState, SSessionKey* key, char* pKeyData, int32_t keyDataLen,
|
||||
state_key_cmpr_fn fn, void** pVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionGetKeyByRange)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* range, SSessionKey* curKey);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateCountGetKeyByRange)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* range, SSessionKey* curKey);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateSessionAllocWinBuffByNextPosition)(SStreamState* pState, SStreamStateCur* pCur,
|
||||
const SSessionKey* pKey, void** pVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateCountWinAddIfNotExist)(SStreamState* pState, SSessionKey* pKey, COUNT_TYPE winCount, void** ppVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
int32_t (*streamStateCountWinAdd)(SStreamState* pState, SSessionKey* pKey, void** pVal, int32_t* pVLen);
|
||||
|
||||
SUpdateInfo* (*updateInfoInit)(int64_t interval, int32_t precision, int64_t watermark, bool igUp);
|
||||
TSKEY (*updateInfoFillBlockData)(SUpdateInfo* pInfo, SSDataBlock* pBlock, int32_t primaryTsCol);
|
||||
bool (*updateInfoIsUpdated)(SUpdateInfo* pInfo, uint64_t tableId, TSKEY ts);
|
||||
|
|
@ -380,6 +383,7 @@ typedef struct SStateStore {
|
|||
int32_t (*updateInfoDeserialize)(void* buf, int32_t bufLen, SUpdateInfo* pInfo);
|
||||
|
||||
SStreamStateCur* (*streamStateSessionSeekKeyNext)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* key);
|
||||
SStreamStateCur* (*streamStateCountSeekKeyPrev)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* pKey, COUNT_TYPE count);
|
||||
SStreamStateCur* (*streamStateSessionSeekKeyCurrentPrev)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* key);
|
||||
SStreamStateCur* (*streamStateSessionSeekKeyCurrentNext)(SStreamState* pState, const SSessionKey* key);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -114,6 +114,7 @@ typedef struct SInputColumnInfoData {
|
|||
int32_t totalRows; // total rows in current columnar data
|
||||
int32_t startRowIndex; // handle started row index
|
||||
int64_t numOfRows; // the number of rows needs to be handled
|
||||
bool blankFill; // fill blank data to block for empty table
|
||||
int32_t numOfInputCols; // PTS is not included
|
||||
bool colDataSMAIsSet; // if agg is set or not
|
||||
SColumnInfoData *pPTS; // primary timestamp column
|
||||
|
|
@ -249,6 +250,10 @@ typedef struct SPoint {
|
|||
int32_t taosGetLinearInterpolationVal(SPoint *point, int32_t outputType, SPoint *point1, SPoint *point2,
|
||||
int32_t inputType);
|
||||
|
||||
#define LEASTSQUARES_DOUBLE_ITEM_LENGTH 25
|
||||
#define LEASTSQUARES_BUFF_LENGTH 128
|
||||
#define DOUBLE_PRECISION_DIGITS "16e"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -126,6 +126,7 @@ typedef enum EFunctionType {
|
|||
FUNCTION_TYPE_TAGS,
|
||||
FUNCTION_TYPE_TBUID,
|
||||
FUNCTION_TYPE_VGID,
|
||||
FUNCTION_TYPE_VGVER,
|
||||
|
||||
// internal function
|
||||
FUNCTION_TYPE_SELECT_VALUE = 3750,
|
||||
|
|
@ -243,7 +244,7 @@ bool fmIsSkipScanCheckFunc(int32_t funcId);
|
|||
void getLastCacheDataType(SDataType* pType);
|
||||
SFunctionNode* createFunction(const char* pName, SNodeList* pParameterList);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t fmGetDistMethod(const SFunctionNode* pFunc, SFunctionNode** pPartialFunc, SFunctionNode** pMergeFunc);
|
||||
int32_t fmGetDistMethod(const SFunctionNode* pFunc, SFunctionNode** pPartialFunc, SFunctionNode** pMidFunc, SFunctionNode** pMergeFunc);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum EFuncDataRequired {
|
||||
FUNC_DATA_REQUIRED_DATA_LOAD = 1,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TDENGINE_CLIENT_MONITOR_H
|
||||
#define TDENGINE_CLIENT_MONITOR_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
extern "C" {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_monitor.h"
|
||||
#include "thash.h"
|
||||
#include "query.h"
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum SQL_RESULT_CODE {
|
||||
SQL_RESULT_SUCCESS = 0,
|
||||
SQL_RESULT_FAILED = 1,
|
||||
SQL_RESULT_CANCEL = 2,
|
||||
} SQL_RESULT_CODE;
|
||||
|
||||
const char* resultStr(SQL_RESULT_CODE code);
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char clusterKey[512];
|
||||
SEpSet epSet;
|
||||
void* pTransporter;
|
||||
taos_collector_registry_t* registry;
|
||||
taos_collector_t* colector;
|
||||
SHashObj* counters;
|
||||
} ClientMonitor;
|
||||
|
||||
void clusterMonitorInit(const char* clusterKey, SEpSet epSet, void* pTransporter);
|
||||
void clusterMonitorClose(const char* clusterKey);
|
||||
taos_counter_t* createClusterCounter(const char* clusterKey, const char* name, const char* help, size_t label_key_count,
|
||||
const char** label_keys);
|
||||
int taosClusterCounterInc(const char* clusterKey, const char* counterName, const char** label_values);
|
||||
void cluster_monitor_stop();
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TDENGINE_CLIENT_MONITOR_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,7 +76,8 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SMonBasicInfo;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
float uptime; // day
|
||||
//float uptime; // day
|
||||
int64_t uptime; // second
|
||||
int8_t has_mnode;
|
||||
int8_t has_qnode;
|
||||
int8_t has_snode;
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,13 +101,15 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
int32_t mnode_id;
|
||||
char mnode_ep[TSDB_EP_LEN];
|
||||
char role[MON_ROLE_LEN];
|
||||
int32_t syncState;
|
||||
} SMonMnodeDesc;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
char first_ep[TSDB_EP_LEN];
|
||||
int32_t first_ep_dnode_id;
|
||||
char version[MON_VER_LEN];
|
||||
float master_uptime; // day
|
||||
//float master_uptime; // day
|
||||
int64_t master_uptime; //second
|
||||
int32_t monitor_interval; // sec
|
||||
int32_t dbs_total;
|
||||
int32_t stbs_total;
|
||||
|
|
@ -125,6 +128,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int32_t dnode_id;
|
||||
char vnode_role[MON_ROLE_LEN];
|
||||
int32_t syncState;
|
||||
} SMonVnodeDesc;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,7 +153,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
} SMonStbInfo;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
uint32_t expire_time;
|
||||
int64_t expire_time;
|
||||
int64_t timeseries_used;
|
||||
int64_t timeseries_total;
|
||||
} SMonGrantInfo;
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,7 +225,9 @@ void monSetVmInfo(SMonVmInfo *pInfo);
|
|||
void monSetQmInfo(SMonQmInfo *pInfo);
|
||||
void monSetSmInfo(SMonSmInfo *pInfo);
|
||||
void monSetBmInfo(SMonBmInfo *pInfo);
|
||||
void monSendReport();
|
||||
void monGenAndSendReport();
|
||||
void monGenAndSendReportBasic();
|
||||
void monSendContent(char *pCont);
|
||||
|
||||
void tFreeSMonMmInfo(SMonMmInfo *pInfo);
|
||||
void tFreeSMonVmInfo(SMonVmInfo *pInfo);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_alloc.h
|
||||
* @brief memory management
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_ALLOC_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_ALLOC_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Redefine this macro if you wish to override it. The default value is malloc.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define taos_malloc malloc
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Redefine this macro if you wish to override it. The default value is realloc.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define taos_realloc realloc
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Redefine this macro if you wish to override it. The default value is strdup.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define taos_strdup strdup
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Redefine this macro if you wish to override it. The default value is free.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define taos_free free
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_ALLOC_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_COLLECTOR_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_COLLECTOR_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_map.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_collector.h
|
||||
* @brief A Prometheus collector returns a collection of metrics
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief A prometheus collector calls collect to prepare metrics and return them to the registry to which it is
|
||||
* registered.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct taos_collector taos_collector_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief The function responsible for preparing metric data and returning metrics for a given collector.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* If you use the default collector registry, this should not concern you. If you are using a custom collector, you may
|
||||
* set this function on your collector to do additional work before returning the contained metrics.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_t*
|
||||
* @return The taos_map_t* containing the collected metrics
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef taos_map_t *taos_collect_fn(taos_collector_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Create a collector
|
||||
* @param name The name of the collector. The name MUST NOT be default or process.
|
||||
* @return The constructed taos_collector_t*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_collector_t *taos_collector_new(const char *name);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Destroy a collector. You MUST set self to NULL after destruction.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_t*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_destroy(taos_collector_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Frees a collector passed as a void pointer. You MUST set self to NULL after destruction.
|
||||
* @param gen The target taos_collector_t* represented as a void*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void taos_collector_free_generic(void *gen);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Destroys a collector passed as a void pointer. You MUST set self to NULL after destruction.
|
||||
* @param gen The target taos_collector_t* represented as a void*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_destroy_generic(void *gen);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Add a metric to a collector
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_t*
|
||||
* @param metric the taos_metric_t* to add to the taos_collector_t* passed as self.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_add_metric(taos_collector_t *self, taos_metric_t *metric);
|
||||
|
||||
int taos_collector_remove_metric(taos_collector_t *self, const char* key);
|
||||
|
||||
taos_metric_t* taos_collector_get_metric(taos_collector_t *self, char *metric_name);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief The collect function is responsible for doing any work involving a set of metrics and then returning them
|
||||
* for metric exposition.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_t*
|
||||
* @param fn The taos_collect_fn* which will be responsible for handling any metric collection operations before
|
||||
* returning the collected metrics for exposition.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_set_collect_fn(taos_collector_t *self, taos_collect_fn *fn);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_COLLECTOR_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_collector_registry.h
|
||||
* @brief The collector registry registers collectors for metric exposition.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_REGISTRY_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_REGISTRY_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_collector.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief A taos_registry_t is responsible for registering metrics and briding them to the string exposition format
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct taos_collector_registry taos_collector_registry_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Initialize the default registry by calling taos_collector_registry_init within your program. You MUST NOT
|
||||
* modify this value.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern taos_collector_registry_t *TAOS_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY_DEFAULT;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Initializes the default collector registry and enables metric collection on the executing process
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_default_init(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Constructs a taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @param name The name of the collector registry. It MUST NOT be default.
|
||||
* @return The constructed taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_collector_registry_t *taos_collector_registry_new(const char *name);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Destroy a collector registry. You MUST set self to NULL after destruction.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_destroy(taos_collector_registry_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Enable process metrics on the given collector registry
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_enable_process_metrics(taos_collector_registry_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Registers a metric with the default collector on TAOS_DEFAULT_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The metric to be registered MUST NOT already be registered with the given . If so, the program will
|
||||
* halt. It returns a taos_metric_t* to simplify metric creation and registration. Furthermore,
|
||||
* TAOS_DEFAULT_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY must be registered via taos_collector_registry_default_init() prior to calling this
|
||||
* function. The metric will be added to the default registry's default collector.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param metric The metric to register on TAOS_DEFAULT_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY*
|
||||
* @return The registered taos_metric_t*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_metric_t *taos_collector_registry_must_register_metric(taos_metric_t *metric);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Registers a metric with the default collector on TAOS_DEFAULT_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY. Returns an non-zero integer
|
||||
* value on failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* See taos_collector_registry_must_register_metric.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param metric The metric to register on TAOS_DEFAULT_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_register_metric(taos_metric_t *metric);
|
||||
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_deregister_metric(const char *key);
|
||||
|
||||
taos_metric_t *taos_collector_registry_get_metric(char* metric_name);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Register a collector with the given registry. Returns a non-zero integer value on failure.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @param collector The taos_collector_t* to register onto the taos_collector_registry_t* as self
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_register_collector(taos_collector_registry_t *self, taos_collector_t *collector);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Returns a string in the default metric exposition format. The string MUST be freed to avoid unnecessary heap
|
||||
* memory growth.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Reference: https://prometheus.io/docs/instrumenting/exposition_formats/
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @return The string int he default metric exposition format.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const char *taos_collector_registry_bridge(taos_collector_registry_t *self, char *ts, char *format);
|
||||
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_clear_batch(taos_collector_registry_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
const char *taos_collector_registry_bridge_new(taos_collector_registry_t *self, char *ts, char *format, char** prom_str);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*@brief Validates that the given metric name complies with the specification:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Reference: https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/data_model/#metric-names-and-labels
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Returns a non-zero integer value on failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_collector_registry_t*
|
||||
* @param metric_name The metric name to validate
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_collector_registry_validate_metric_name(taos_collector_registry_t *self, const char *metric_name);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_COUNTER_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_COUNTER_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_counter.h
|
||||
* @brief https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#counter
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief A prometheus counter.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* References
|
||||
* * See https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#counter
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef taos_metric_t taos_counter_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Construct a taos_counter_t*
|
||||
* @param name The name of the metric
|
||||
* @param help The metric description
|
||||
* @param label_key_count The number of labels associated with the given metric. Pass 0 if the metric does not
|
||||
* require labels.
|
||||
* @param label_keys A collection of label keys. The number of keys MUST match the value passed as label_key_count. If
|
||||
* no labels are required, pass NULL. Otherwise, it may be convenient to pass this value as a
|
||||
* literal.
|
||||
* @return The constructed taos_counter_t*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_new("foo", "foo is a counter with labels", 2, (const char**) { "one", "two" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_new("foo", "foo is a counter without labels", 0, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_counter_t *taos_counter_new(const char *name, const char *help, size_t label_key_count, const char **label_keys);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Destroys a taos_counter_t*. You must set self to NULL after destruction. A non-zero integer value will be
|
||||
* returned on failure.
|
||||
* @param self A taos_counter_t*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_counter_destroy(taos_counter_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Increment the taos_counter_t by 1. A non-zero integer value will be returned on failure.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_counter_t*
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the counter's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_inc(foo_counter, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
**
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_inc(foo_counter, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_counter_inc(taos_counter_t *self, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Add the value to the taos_counter_t*. A non-zero integer value will be returned on failure.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_counter_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to add to the taos_counter_t passed as self. The value MUST be greater than or equal to 0.
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the counter's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_add(foo_counter, 22, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_counter_add(foo_counter, 22, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_counter_add(taos_counter_t *self, double r_value, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_COUNTER_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_gauge.h
|
||||
* @brief https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#gauge
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_GAUGE_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_GAUGE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief A prometheus gauge.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* References
|
||||
* * See https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#gauge
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef taos_metric_t taos_gauge_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Constructs a taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @param name The name of the metric
|
||||
* @param help The metric description
|
||||
* @param label_key_count The number of labels associated with the given metric. Pass 0 if the metric does not
|
||||
* require labels.
|
||||
* @param label_keys A collection of label keys. The number of keys MUST match the value passed as label_key_count. If
|
||||
* no labels are required, pass NULL. Otherwise, it may be convenient to pass this value as a
|
||||
* literal.
|
||||
* @return The constructed taos_guage_t*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_new("foo", "foo is a gauge with labels", 2, (const char**) { "one", "two" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_new("foo", "foo is a gauge without labels", 0, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_gauge_t *taos_gauge_new(const char *name, const char *help, size_t label_key_count, const char **label_keys);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Destroys a taos_gauge_t*. You must set self to NULL after destruction. A non-zero integer value will be
|
||||
* returned on failure.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_destroy(taos_gauge_t *self);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Increment the taos_gauge_t* by 1.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauger_t*
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the gauge's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_inc(foo_gauge, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_inc(foo_gauge, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_inc(taos_gauge_t *self, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Decrement the taos_gauge_t* by 1.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauger_t*
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the gauge's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_dec(foo_gauge, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_dec(foo_gauge, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_dec(taos_gauge_t *self, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Add the value to the taos_gauge_t*.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to add to the taos_gauge_t passed as self.
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the gauge's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_add(foo_gauge 22, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_add(foo_gauge, 22, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_add(taos_gauge_t *self, double r_value, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Subtract the value to the taos_gauge. A non-zero integer value will be returned on failure.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to add to the taos_gauge_t passed as self.
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the gauge's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_sub(foo_gauge 22, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_sub(foo_gauge, 22, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_sub(taos_gauge_t *self, double r_value, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Set the value for the taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_gauge_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to which the taos_gauge_t* passed as self will be set
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the gauge's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A non-zero integer value upon failure.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* *Example*
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example with labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_set(foo_gauge 22, (const char**) { "bar", "bang" });
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // An example without labels
|
||||
* taos_gauge_set(foo_gauge, 22, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_gauge_set(taos_gauge_t *self, double r_value, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_GAUGE_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_LIST_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_LIST_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct taos_linked_list;
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Provides a generic linked list
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct taos_linked_list taos_linked_list_t;
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_LIST_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_MAP_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_MAP_H
|
||||
|
||||
struct taos_map;
|
||||
typedef struct taos_map taos_map_t;
|
||||
|
||||
struct taos_map_node;
|
||||
typedef struct taos_map_node taos_map_node_t;
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_MAP_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_metric.h
|
||||
* @brief Functions for retrieving metric samples from metrics given an ordered set of labels
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_METRIC_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_METRIC_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_metric_sample.h"
|
||||
|
||||
struct taos_metric;
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief A prometheus metric.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Reference: https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/data_model
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct taos_metric taos_metric_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Returns a taos_metric_sample_t*. The order of label_values is significant.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You may use this function to cache metric samples to avoid sample lookup. Metric samples are stored in a hash map
|
||||
* with O(1) lookups in average case; nonethless, caching metric samples and updating them directly might be
|
||||
* preferrable in performance-sensitive situations.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_metric_t*
|
||||
* @param label_values The label values associated with the metric sample being updated. The number of labels must
|
||||
* match the value passed to label_key_count in the counter's constructor. If no label values are
|
||||
* necessary, pass NULL. Otherwise, It may be convenient to pass this value as a literal.
|
||||
* @return A taos_metric_sample_t*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
taos_metric_sample_t *taos_metric_sample_from_labels(taos_metric_t *self, const char **label_values);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_METRIC_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_metric_sample.h
|
||||
* @brief Functions for interfacting with metric samples directly
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_METRIC_SAMPLE_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_METRIC_SAMPLE_H
|
||||
|
||||
struct taos_metric_sample;
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Contains the specific metric and value given the name and label set
|
||||
* Reference: https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/data_model/#metric-names-and-labels
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct taos_metric_sample taos_metric_sample_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Add the r_value to the sample. The value must be greater than or equal to zero.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_metric_sample_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to add to taos_metric_sample_t* provided by self
|
||||
* @return Non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_metric_sample_add(taos_metric_sample_t *self, double r_value);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Subtract the r_value from the sample.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This operation MUST be called a sample derived from a gauge metric.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_metric_sample_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double to subtract from the taos_metric_sample_t* provided by self
|
||||
* @return Non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_metric_sample_sub(taos_metric_sample_t *self, double r_value);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @brief Set the r_value of the sample.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This operation MUST be called on a sample derived from a gauge metric.
|
||||
* @param self The target taos_metric_sample_t*
|
||||
* @param r_value The double which will be set to the taos_metric_sample_t* provided by self
|
||||
* @return Non-zero integer value upon failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int taos_metric_sample_set(taos_metric_sample_t *self, double r_value);
|
||||
|
||||
int taos_metric_sample_exchange(taos_metric_sample_t *self, double r_value, double* old_value);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_METRIC_SAMPLE_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
Copyright 2019 DigitalOcean Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_monitor.h
|
||||
* @brief Include taos_monitor.h to include the entire public API
|
||||
* @mainpage Welcome to the documentation site for prometheus-client-c!
|
||||
* @tableofcontents
|
||||
* @section Introduction
|
||||
*
|
||||
* prometheus-client-c is a small suite of Prometheus client libraries targeted for the C programming language.
|
||||
* In this brief tutorial you will learn how to create and register metrics, update metric samples, and expose metrics
|
||||
* over HTTP.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @section Creating-and-Registering-Metrics Creating and Registering Metrics
|
||||
*
|
||||
* prometheus-client-c supports the following metric types:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * [Counter](https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#counter)
|
||||
* * [Gauge](https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#gauge)
|
||||
* * [Histogram](https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/metric_types/#histogram)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* To get started using one of the metric types, declare the metric at file scope. For example:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @code{.c}
|
||||
*
|
||||
* #incldue "taos_monitor.h"
|
||||
*
|
||||
* taos_counter_t *my_counter;
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @endcode
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Next, create a metric initialization function. You can create the metric and register it with the default metric
|
||||
* collector registry in one chain of functions. A metric collector is responsible for collecting metrics and returning
|
||||
* them. A metric collector registry is declared in global scope and contains metric collectors. More on this later...
|
||||
*
|
||||
* To create a metric and register it with the default metric collector registry in one shot, you may chain the metric
|
||||
* constructor into the taos_collector_registry_must_register_metric function. For example:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @code{.c}
|
||||
*
|
||||
* void foo_metric_init(void) {
|
||||
* my_counter = taos_collector_registry_must_register_metric(taos_counter_new("my_counter", "counts things", 0, NULL));
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @endcode
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The first argument to taos_counter_new is the counter name. The second argument is the counter description. The third
|
||||
* argument is the number of metric labels. In this case, we will only have one metric sample for this metric so we pass
|
||||
* 0 to specify that no labels will be used. The 4th argument is an array of strings storing the metric labels. Since we
|
||||
* have none, we pass NULL. A call to foo_metric_init within the program's main function will initialize the metrics
|
||||
* for the file we just created to the default prometheus metric collector registery called
|
||||
* TAOS_COLLECTOR_REGISTRY_DEFAULT
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @section Updating-Metric-Sample-Values Updating Metric Sample Values
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Now that we have a metric configured for creation and registration, we can update our metric within any of the
|
||||
* functions of the file in which it was declared. For example:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @code{.c}
|
||||
*
|
||||
* void my_lib_do_something(void) {
|
||||
* printf("I did a really important thing!\n");
|
||||
* taos_counter_inc(my_counter, NULL);
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* @endcode
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This function will increment the default metric sample for my_counter. Since we are not using metric labels, we pass
|
||||
* NULL as the second argument.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @section Program-Initialization Program Initialization
|
||||
*
|
||||
* At the start of the program's main function you need to do two things:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * Initialize the default metric collector registry:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @code{.c}
|
||||
*
|
||||
* taos_collector_registry_default_init();
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @endcode
|
||||
*
|
||||
* * For each file containing prometheus metrics, call its corresponding metric initialization function
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @code{.c}
|
||||
*
|
||||
* foo_metric_init()
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @endcode
|
||||
*
|
||||
* After initialization is complete, you may proceed to do work and update your metrics.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @section Metric-Exposition-Over-HTTP Metric Exposition Over HTTP
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @todo Describe how to use libpromhttp to expose metrics over HTTP
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @section Where-To-Go-From-Here Where to Go From Here?
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Take a look at the [Files](https://github.internal.digitalocean.com/pages/timeseries/prometheus-client-c/files.html)
|
||||
* tab in this documentation site for more information about the public API available to you. Also, you can take a look
|
||||
* at the examples directory at the
|
||||
* [Github repository](https://github.internal.digitalocean.com/timeseries/prometheus-client-c) for inspiration.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_INCLUDED
|
||||
#define TAOS_INCLUDED
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_alloc.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_collector.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_collector_registry.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_counter.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_linked_list.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_map.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_metric_sample.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_monitor_util.h"
|
||||
#include "taos_gauge.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_INCLUDED
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2019 TAOS Data, Inc. <jhtao@taosdata.com>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is free software: you can use, redistribute, and/or modify
|
||||
* it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3
|
||||
* or later ("AGPL"), as published by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
|
||||
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @file taos_monitor_util.h
|
||||
* @brief Functions for retrieving metric samples from metrics given an ordered set of labels
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TAOS_MONITOR_UTIL_H
|
||||
#define TAOS_MONITOR_UTIL_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "taos_metric.h"
|
||||
#include "tjson.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void taos_monitor_split_str(char** arr, char* str, const char* del);
|
||||
void taos_monitor_split_str_metric(char** arr, taos_metric_t* metric, const char* del, char** buf);
|
||||
char* taos_monitor_get_metric_name(taos_metric_t* metric);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // TAOS_MONITOR_UTIL_H
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,6 +100,7 @@ typedef struct SDatabaseOptions {
|
|||
int32_t sstTrigger;
|
||||
int32_t tablePrefix;
|
||||
int32_t tableSuffix;
|
||||
int8_t withArbitrator;
|
||||
} SDatabaseOptions;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SCreateDatabaseStmt {
|
||||
|
|
@ -420,6 +421,12 @@ typedef struct SDropCGroupStmt {
|
|||
bool ignoreNotExists;
|
||||
} SDropCGroupStmt;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SAlterClusterStmt {
|
||||
ENodeType type;
|
||||
char config[TSDB_DNODE_CONFIG_LEN];
|
||||
char value[TSDB_CLUSTER_VALUE_LEN];
|
||||
} SAlterClusterStmt;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SAlterLocalStmt {
|
||||
ENodeType type;
|
||||
char config[TSDB_DNODE_CONFIG_LEN];
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -149,6 +149,8 @@ void nodesRewriteExprPostOrder(SNode** pNode, FNodeRewriter rewriter, void* pCon
|
|||
void nodesRewriteExprsPostOrder(SNodeList* pList, FNodeRewriter rewriter, void* pContext);
|
||||
|
||||
bool nodesEqualNode(const SNode* a, const SNode* b);
|
||||
bool nodeListNodeEqual(const SNodeList* a, const SNode* b);
|
||||
|
||||
bool nodesMatchNode(const SNode* pSub, const SNode* pNode);
|
||||
|
||||
SNode* nodesCloneNode(const SNode* pNode);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -120,6 +120,9 @@ typedef struct SScanLogicNode {
|
|||
bool onlyMetaCtbIdx; // for tag scan with no tbname
|
||||
bool filesetDelimited; // returned blocks delimited by fileset
|
||||
bool isCountByTag; // true if selectstmt hasCountFunc & part by tag/tbname
|
||||
SArray* pFuncTypes; // for last, last_row
|
||||
bool paraTablesSort; // for table merge scan
|
||||
bool smallDataTsSort; // disable row id sort for table merge scan
|
||||
} SScanLogicNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SJoinLogicNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -155,6 +158,7 @@ typedef struct SProjectLogicNode {
|
|||
SNodeList* pProjections;
|
||||
char stmtName[TSDB_TABLE_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
bool ignoreGroupId;
|
||||
bool inputIgnoreGroup;
|
||||
} SProjectLogicNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SIndefRowsFuncLogicNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -242,7 +246,8 @@ typedef enum EWindowType {
|
|||
WINDOW_TYPE_INTERVAL = 1,
|
||||
WINDOW_TYPE_SESSION,
|
||||
WINDOW_TYPE_STATE,
|
||||
WINDOW_TYPE_EVENT
|
||||
WINDOW_TYPE_EVENT,
|
||||
WINDOW_TYPE_COUNT
|
||||
} EWindowType;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum EWindowAlgorithm {
|
||||
|
|
@ -255,6 +260,7 @@ typedef enum EWindowAlgorithm {
|
|||
SESSION_ALGO_STREAM_FINAL,
|
||||
SESSION_ALGO_STREAM_SINGLE,
|
||||
SESSION_ALGO_MERGE,
|
||||
INTERVAL_ALGO_STREAM_MID,
|
||||
} EWindowAlgorithm;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SWindowLogicNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -279,6 +285,8 @@ typedef struct SWindowLogicNode {
|
|||
int8_t igCheckUpdate;
|
||||
EWindowAlgorithm windowAlgo;
|
||||
bool isPartTb;
|
||||
int64_t windowCount;
|
||||
int64_t windowSliding;
|
||||
} SWindowLogicNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SFillLogicNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -401,6 +409,7 @@ typedef struct SLastRowScanPhysiNode {
|
|||
bool groupSort;
|
||||
bool ignoreNull;
|
||||
SNodeList* pTargets;
|
||||
SArray* pFuncTypes;
|
||||
} SLastRowScanPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef SLastRowScanPhysiNode STableCountScanPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
|
@ -436,6 +445,8 @@ typedef struct STableScanPhysiNode {
|
|||
int8_t igCheckUpdate;
|
||||
bool filesetDelimited;
|
||||
bool needCountEmptyTable;
|
||||
bool paraTablesSort;
|
||||
bool smallDataTsSort;
|
||||
} STableScanPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef STableScanPhysiNode STableSeqScanPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
|
@ -447,6 +458,7 @@ typedef struct SProjectPhysiNode {
|
|||
SNodeList* pProjections;
|
||||
bool mergeDataBlock;
|
||||
bool ignoreGroupId;
|
||||
bool inputIgnoreGroup;
|
||||
} SProjectPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SIndefRowsFuncPhysiNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -583,6 +595,7 @@ typedef SIntervalPhysiNode SMergeAlignedIntervalPhysiNode;
|
|||
typedef SIntervalPhysiNode SStreamIntervalPhysiNode;
|
||||
typedef SIntervalPhysiNode SStreamFinalIntervalPhysiNode;
|
||||
typedef SIntervalPhysiNode SStreamSemiIntervalPhysiNode;
|
||||
typedef SIntervalPhysiNode SStreamMidIntervalPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SFillPhysiNode {
|
||||
SPhysiNode node;
|
||||
|
|
@ -625,6 +638,14 @@ typedef struct SEventWinodwPhysiNode {
|
|||
|
||||
typedef SEventWinodwPhysiNode SStreamEventWinodwPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SCountWinodwPhysiNode {
|
||||
SWindowPhysiNode window;
|
||||
int64_t windowCount;
|
||||
int64_t windowSliding;
|
||||
} SCountWinodwPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef SCountWinodwPhysiNode SStreamCountWinodwPhysiNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SSortPhysiNode {
|
||||
SPhysiNode node;
|
||||
SNodeList* pExprs; // these are expression list of order_by_clause and parameter expression of aggregate function
|
||||
|
|
@ -709,8 +730,10 @@ typedef struct SSubplan {
|
|||
SNode* pTagCond;
|
||||
SNode* pTagIndexCond;
|
||||
bool showRewrite;
|
||||
int32_t rowsThreshold;
|
||||
bool isView;
|
||||
bool isAudit;
|
||||
bool dynamicRowThreshold;
|
||||
int32_t rowsThreshold;
|
||||
} SSubplan;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum EExplainMode { EXPLAIN_MODE_DISABLE = 1, EXPLAIN_MODE_STATIC, EXPLAIN_MODE_ANALYZE } EExplainMode;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -89,6 +89,7 @@ typedef struct SColumnNode {
|
|||
|
||||
typedef struct SColumnRefNode {
|
||||
ENodeType type;
|
||||
SDataType resType;
|
||||
char colName[TSDB_COL_NAME_LEN];
|
||||
} SColumnRefNode;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -127,6 +128,8 @@ typedef enum EHintOption {
|
|||
HINT_BATCH_SCAN,
|
||||
HINT_SORT_FOR_GROUP,
|
||||
HINT_PARTITION_FIRST,
|
||||
HINT_PARA_TABLES_SORT,
|
||||
HINT_SMALLDATA_TS_SORT,
|
||||
} EHintOption;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SHintNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -277,6 +280,13 @@ typedef struct SEventWindowNode {
|
|||
SNode* pEndCond;
|
||||
} SEventWindowNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct SCountWindowNode {
|
||||
ENodeType type; // QUERY_NODE_EVENT_WINDOW
|
||||
SNode* pCol; // timestamp primary key
|
||||
int64_t windowCount;
|
||||
int64_t windowSliding;
|
||||
} SCountWindowNode;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum EFillMode {
|
||||
FILL_MODE_NONE = 1,
|
||||
FILL_MODE_VALUE,
|
||||
|
|
@ -532,6 +542,7 @@ int32_t nodesCollectColumnsFromNode(SNode* node, const char* pTableAlias, EColle
|
|||
|
||||
typedef bool (*FFuncClassifier)(int32_t funcId);
|
||||
int32_t nodesCollectFuncs(SSelectStmt* pSelect, ESqlClause clause, char* tableAlias, FFuncClassifier classifier, SNodeList** pFuncs);
|
||||
int32_t nodesCollectSelectFuncs(SSelectStmt* pSelect, ESqlClause clause, char* tableAlias, FFuncClassifier classifier, SNodeList* pFuncs);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t nodesCollectSpecialNodes(SSelectStmt* pSelect, ESqlClause clause, ENodeType type, SNodeList** pNodes);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -86,8 +86,10 @@ typedef struct SParseContext {
|
|||
bool enableSysInfo;
|
||||
bool async;
|
||||
bool hasInvisibleCol;
|
||||
const char* svrVer;
|
||||
bool isView;
|
||||
bool isAudit;
|
||||
bool nodeOffline;
|
||||
const char* svrVer;
|
||||
SArray* pTableMetaPos; // sql table pos => catalog data pos
|
||||
SArray* pTableVgroupPos; // sql table pos => catalog data pos
|
||||
int64_t allocatorId;
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,7 +108,7 @@ int32_t qAnalyseSqlSemantic(SParseContext* pCxt, const struct SCatalogReq* pCata
|
|||
const struct SMetaData* pMetaData, SQuery* pQuery);
|
||||
int32_t qContinueParseSql(SParseContext* pCxt, struct SCatalogReq* pCatalogReq, const struct SMetaData* pMetaData,
|
||||
SQuery* pQuery);
|
||||
int32_t qContinueParsePostQuery(SParseContext* pCxt, SQuery* pQuery, void** pResRow);
|
||||
int32_t qContinueParsePostQuery(SParseContext* pCxt, SQuery* pQuery, SSDataBlock* pBlock);
|
||||
|
||||
void qDestroyParseContext(SParseContext* pCxt);
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,7 +152,7 @@ int32_t smlBindData(SQuery* handle, bool dataFormat, SArray* tags, SArray* colsS
|
|||
STableMeta* pTableMeta, char* tableName, const char* sTableName, int32_t sTableNameLen, int32_t ttl,
|
||||
char* msgBuf, int32_t msgBufLen);
|
||||
int32_t smlBuildOutput(SQuery* handle, SHashObj* pVgHash);
|
||||
int rawBlockBindData(SQuery *query, STableMeta* pTableMeta, void* data, SVCreateTbReq* pCreateTb, TAOS_FIELD *fields, int numFields, bool needChangeLength);
|
||||
int rawBlockBindData(SQuery *query, STableMeta* pTableMeta, void* data, SVCreateTbReq** pCreateTb, TAOS_FIELD *fields, int numFields, bool needChangeLength);
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t rewriteToVnodeModifyOpStmt(SQuery* pQuery, SArray* pBufArray);
|
||||
SArray* serializeVgroupsCreateTableBatch(SHashObj* pVgroupHashmap);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,6 +32,8 @@ typedef struct SPlanContext {
|
|||
bool streamQuery;
|
||||
bool rSmaQuery;
|
||||
bool showRewrite;
|
||||
bool isView;
|
||||
bool isAudit;
|
||||
int8_t triggerType;
|
||||
int64_t watermark;
|
||||
int64_t deleteMark;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue