|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 6.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 2.5 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 4.5 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.3 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 3.7 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 3.7 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 12 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 12 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 13 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 13 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.8 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 6.9 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 125 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 119 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 26 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 11 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 14 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.1 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 12 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 62 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 63 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 6.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.7 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 9.5 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 16 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.8 KiB |
|
|
@ -167,6 +167,3 @@ ax.legend() ;
|
|||
- 请思考两种绘图模式的优缺点和各自适合的使用场景
|
||||
- 在第五节绘图模板中我们是以OO模式作为例子展示的,请思考并写一个pyplot绘图模式的简单模板
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考资料
|
||||
|
||||
[1.matplotlib官网用户指南](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/introductory/usage.html)
|
||||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ kernelspec:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
第五回详细介绍matplotlib中样式和颜色的使用,绘图样式和颜色是丰富可视化图表的重要手段,因此熟练掌握本章可以让可视化图表变得更美观,突出重点和凸显艺术性。
|
||||
关于绘图样式,常见的有4种方法,分别是修改预定义样式,自定义样式,rcparams和matplotlibrc文件。
|
||||
关于绘图样式,常见的有3种方法,分别是修改预定义样式,自定义样式和rcparams。
|
||||
关于颜色使用,本章介绍了常见的5种表示单色颜色的基本方法,以及colormap多色显示的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
## 一、matplotlib的绘图样式(style)
|
||||
|
|
@ -135,24 +135,6 @@ plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[2,3,4,5]);
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.修改matplotlibrc文件
|
||||
|
||||
由于matplotlib是使用matplotlibrc文件来控制样式的,也就是上一节提到的rc setting,所以我们还可以通过修改matplotlibrc文件的方式改变样式。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
# 查找matplotlibrc文件的路径
|
||||
mpl.matplotlib_fname()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
找到路径后,就可以直接编辑样式文件了,打开后看到的文件格式大致是这样的,文件中列举了所有的样式参数,找到想要修改的参数,比如lines.linewidth: 8,并将前面的注释符号去掉,此时再绘图发现样式以及生效了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 二、matplotlib的色彩设置(color)
|
||||
|
||||
在可视化中,如何选择合适的颜色和搭配组合也是需要仔细考虑的,色彩选择要能够反映出可视化图像的主旨。
|
||||
|
|
@ -265,21 +247,9 @@ plt.scatter(x,y,c=x,cmap='RdPu');
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在以下官网页面可以查询上述五种colormap的字符串表示和颜色图的对应关系
|
||||
[https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/colors/colormaps.html](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/colors/colormaps.html)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考资料
|
||||
[1.matplotlib官网样式使用指南](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/introductory/customizing.html?highlight=rcparams)
|
||||
[2.matplotlib官网色彩使用指南](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/colors/colors.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-colors-colors-py)
|
||||
|
||||
## 思考题
|
||||
- 学习如何自定义colormap,并将其应用到任意一个数据集中,绘制一幅图像,注意colormap的类型要和数据集的特性相匹配,并做简单解释
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,217 +9,211 @@ kernelspec:
|
|||
# 第四回:文字图例尽眉目
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
import matplotlib
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 一、Figure和Axes上的文本
|
||||
|
||||
Matplotlib具有广泛的文本支持,包括对数学表达式的支持、对栅格和矢量输出的TrueType支持、具有任意旋转的换行分隔文本以及Unicode支持。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.文本API示例
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令是介绍了通过pyplot API和objected-oriented API分别创建文本的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
| pyplot API | OO API | description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ------- | ------------ |
|
||||
| `text` | `text` | 在子图axes的任意位置添加文本|
|
||||
| `annotate` | `annotate` | 在子图axes的任意位置添加注解,包含指向性的箭头|
|
||||
| `xlabel` | `set_xlabel` | 为子图axes添加x轴标签 |
|
||||
| `ylabel` | `set_ylabel` | 为子图axes添加y轴标签 |
|
||||
| `title` | `set_title` | 为子图axes添加标题 |
|
||||
| `figtext` | `text` | 在画布figure的任意位置添加文本 |
|
||||
| `suptitle` | `suptitle` | 为画布figure添加标题 |
|
||||
|
||||
| pyplot API | OO API | description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ---------- | --------------------------- |
|
||||
| text | text | 在 Axes的任意位置添加text |
|
||||
| title | set_title | 在 Axes添加title |
|
||||
| figtext | text | 在Figure的任意位置添加text. |
|
||||
| suptitle | suptitle | 在 Figure添加title |
|
||||
| xlabel | set_xlabel | 在Axes的x-axis添加label |
|
||||
| ylabel | set_ylabel | 在Axes的y-axis添加label |
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.text
|
||||
pyplot API:matplotlib.pyplot.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
OO API:Axes.text(self, x, y, s, fontdict=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
**参数**:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
|
||||
s:此参数是要添加的文本。
|
||||
xy:此参数是放置文本的点(x,y)。
|
||||
fontdict:此参数是一个可选参数,并且是一个覆盖默认文本属性的字典。如果fontdict为None,则由rcParams确定默认值。
|
||||
**返回值**:此方法返回作为创建的文本实例的文本。
|
||||
|
||||
fontdict主要参数具体介绍,更多参数请参考[官网说明](https://matplotlib.org/api/text_api.html?highlight=text#matplotlib.text.Text):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| alpha | float or None 该参数指透明度,越接近0越透明,越接近1越不透明 |
|
||||
| backgroundcolor | color |
|
||||
| bbox | dict with properties for patches.FancyBboxPatch 这个是用来设置text周围的box外框 |
|
||||
| color or c | color 指的是字体的颜色 |
|
||||
| fontfamily or family | {FONTNAME, 'serif', 'sans-serif', 'cursive', 'fantasy', 'monospace'} 该参数指的是字体的类型 |
|
||||
| fontproperties or font or font_properties | font_manager.FontProperties or str or pathlib.Path |
|
||||
| fontsize or size | float or {'xx-small', 'x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large', 'xx-large'} 该参数指字体大小 |
|
||||
| fontstretch or stretch | {a numeric value in range 0-1000, 'ultra-condensed', 'extra-condensed', 'condensed', 'semi-condensed', 'normal', 'semi-expanded', 'expanded', 'extra-expanded', 'ultra-expanded'} 该参数是指从字体中选择正常、压缩或扩展的字体 |
|
||||
| fontstyle or style | {'normal', 'italic', 'oblique'} 该参数是指字体的样式是否倾斜等 |
|
||||
| fontweight or weight | {a numeric value in range 0-1000, 'ultralight', 'light', 'normal', 'regular', 'book', 'medium', 'roman', 'semibold', 'demibold', 'demi', 'bold', 'heavy', 'extra bold', 'black'} |
|
||||
| horizontalalignment or ha | {'center', 'right', 'left'} 该参数是指选择文本左对齐右对齐还是居中对齐 |
|
||||
| label | object |
|
||||
| linespacing | float (multiple of font size) |
|
||||
| position | (float, float) |
|
||||
| rotation | float or {'vertical', 'horizontal'} 该参数是指text逆时针旋转的角度,“horizontal”等于0,“vertical”等于90。我们可以根据自己设定来选择合适角度 |
|
||||
| verticalalignment or va | {'center', 'top', 'bottom', 'baseline', 'center_baseline'} |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
通过一个综合例子,以OO模式展示这些API是如何控制一个图像中各部分的文本,在之后的章节我们再详细分析这些api的使用技巧
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
||||
ax = fig.add_subplot()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 分别为figure和ax设置标题,注意两者的位置是不同的
|
||||
fig.suptitle('bold figure suptitle', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
|
||||
ax.set_title('axes title')
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置x和y轴标签
|
||||
ax.set_xlabel('xlabel')
|
||||
ax.set_ylabel('ylabel')
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置x和y轴显示范围均为0到10
|
||||
ax.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
|
||||
|
||||
# 在子图上添加文本
|
||||
ax.text(3, 8, 'boxed italics text in data coords', style='italic',
|
||||
bbox={'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10})
|
||||
|
||||
# 在画布上添加文本,一般在子图上添加文本是更常见的操作,这种方法很少用
|
||||
fig.text(0.4,0.8,'This is text for figure')
|
||||
|
||||
ax.plot([2], [1], 'o')
|
||||
# 添加注解
|
||||
ax.annotate('annotate', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 4),arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.text - 子图上的文本
|
||||
|
||||
text的调用方式为`Axes.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, **kwargs) `
|
||||
其中`x`,`y`为文本出现的位置,默认状态下即为当前坐标系下的坐标值,
|
||||
`s`为文本的内容,
|
||||
`fontdict`是可选参数,用于覆盖默认的文本属性,
|
||||
`**kwargs`为关键字参数,也可以用于传入文本样式参数
|
||||
|
||||
重点解释下fontdict和\*\*kwargs参数,这两种方式都可以用于调整呈现的文本样式,最终效果是一样的,不仅text方法,其他文本方法如set_xlabel,set_title等同样适用这两种方式修改样式。通过一个例子演示这两种方法是如何使用的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#fontdict学习的案例
|
||||
#学习的过程中请尝试更换不同的fontdict字典的内容,以便于更好的掌握
|
||||
#---------设置字体样式,分别是字体,颜色,宽度,大小
|
||||
font1 = {'family': 'SimSun',#华文楷体
|
||||
'alpha':0.7,#透明度
|
||||
'color': 'purple',
|
||||
'weight': 'normal',
|
||||
'size': 16,
|
||||
}
|
||||
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
|
||||
'color': 'red',
|
||||
'weight': 'normal',
|
||||
'size': 16,
|
||||
}
|
||||
font3 = {'family': 'serif',
|
||||
'color': 'blue',
|
||||
'weight': 'bold',
|
||||
'size': 14,
|
||||
}
|
||||
font4 = {'family': 'Calibri',
|
||||
'color': 'navy',
|
||||
'weight': 'normal',
|
||||
'size': 17,
|
||||
}
|
||||
#-----------四种不同字体显示风格-----
|
||||
|
||||
#-------建立函数----------
|
||||
x = np.linspace(0.0, 5.0, 100)
|
||||
y = np.cos(2*np.pi*x) * np.exp(-x/3)
|
||||
#-------绘制图像,添加标注----------
|
||||
plt.plot(x, y, '--')
|
||||
plt.title('震荡曲线', fontdict=font1)
|
||||
#------添加文本在指定的坐标处------------
|
||||
plt.text(2, 0.65, r'$\cos(2 \pi x) \exp(-x/3)$', fontdict=font2)
|
||||
#---------设置坐标标签
|
||||
plt.xlabel('Y=time (s)', fontdict=font3)
|
||||
plt.ylabel('X=voltage(mv)', fontdict=font4)
|
||||
|
||||
# 调整图像边距
|
||||
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.15)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
|
||||
axes = fig.subplots(1,2)
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用关键字参数修改文本样式
|
||||
axes[0].text(0.3, 0.8, 'modify by **kwargs', style='italic',
|
||||
bbox={'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10});
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用fontdict参数修改文本样式
|
||||
font = {'bbox':{'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10}, 'style':'italic'}
|
||||
axes[1].text(0.3, 0.8, 'modify by fontdict', fontdict=font);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.title和set_title
|
||||
pyplot API:matplotlib.pyplot.title(label, fontdict=None, loc=None, pad=None, \*, y=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
OO API:Axes.set_title(self, label, fontdict=None, loc=None, pad=None, \*, y=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
该命令是用来设置axes的标题。
|
||||
**参数**:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
|
||||
label:str,此参数是要添加的文本
|
||||
fontdict:dict,此参数是控制title文本的外观,默认fontdict如下:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
{'fontsize': rcParams['axes.titlesize'],
|
||||
'fontweight': rcParams['axes.titleweight'],
|
||||
'color': rcParams['axes.titlecolor'],
|
||||
'verticalalignment': 'baseline',
|
||||
'horizontalalignment': loc}
|
||||
```
|
||||
loc:str,{'center', 'left', 'right'}默认为center
|
||||
pad:float,该参数是指标题偏离图表顶部的距离,默认为6。
|
||||
y:float,该参数是title所在axes垂向的位置。默认值为1,即title位于axes的顶部。
|
||||
kwargs:该参数是指可以设置的一些奇特文本的属性。
|
||||
**返回值**:此方法返回作为创建的title实例的文本。
|
||||
matplotlib中所有支持的样式参数请参考[官网文档说明](https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.axes.Axes.text.html#matplotlib.axes.Axes.text),大多数时候需要用到的时候再查询即可。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.figtext和text
|
||||
pyplot API:matplotlib.pyplot.figtext(x, y, s, fontdict=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
OO API:text(self, x, y, s, fontdict=None,\*\*kwargs)
|
||||
**参数**:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
|
||||
x,y:float,此参数是指在figure中放置文本的位置。一般取值是在\[0,1\]范围内。使用transform关键字可以更改坐标系。
|
||||
s:str,此参数是指文本
|
||||
fontdict:dict,此参数是一个可选参数,并且是一个覆盖默认文本属性的字典。如果fontdict为None,则由rcParams确定默认值。
|
||||
**返回值**:此方法返回作为创建的文本实例的文本。
|
||||
下表列举了一些常用的参数供参考。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.suptitle
|
||||
pyplot API:matplotlib.pyplot.suptitle(t, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
OO API:suptitle(self, t, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
**参数**:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
|
||||
t: str,标题的文本
|
||||
x:float,默认值是0.5.该参数是指文本在figure坐标系下的x坐标
|
||||
y:float,默认值是0.95.该参数是指文本在figure坐标系下的y坐标
|
||||
horizontalalignment, ha:该参数是指选择文本水平对齐方式,有三种选择{'center', 'left', right'},默认值是 'center'
|
||||
verticalalignment, va:该参数是指选择文本垂直对齐方式,有四种选择{'top', 'center', 'bottom', 'baseline'},默认值是 'top'
|
||||
fontsize, size:该参数是指文本的大小,默认值是依据rcParams的设置:rcParams["figure.titlesize"] (default: 'large')
|
||||
fontweight, weight:该参数是用来设置字重。默认值是依据rcParams的设置:rcParams["figure.titleweight"] (default: 'normal')
|
||||
fontproperties:None or dict,该参数是可选参数,如果该参数被指定,字体的大小将从该参数的默认值中提取。
|
||||
**返回值**:此方法返回作为创建的title实例的文本。
|
||||
| Property | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | :-------------------------- |
|
||||
| `alpha` |float or None 透明度,越接近0越透明,越接近1越不透明 |
|
||||
| `backgroundcolor` | color 文本的背景颜色 |
|
||||
| `bbox` | dict with properties for patches.FancyBboxPatch 用来设置text周围的box外框 |
|
||||
| `color` or c | color 字体的颜色 |
|
||||
| `fontfamily` or family | {FONTNAME, 'serif', 'sans-serif', 'cursive', 'fantasy', 'monospace'} 字体的类型|
|
||||
| `fontsize` or size | float or {'xx-small', 'x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large', 'xx-large'} 字体大小|
|
||||
| `fontstyle` or style | {'normal', 'italic', 'oblique'} 字体的样式是否倾斜等 |
|
||||
| `fontweight` or weight | {a numeric value in range 0-1000, 'ultralight', 'light', 'normal', 'regular', 'book', 'medium', 'roman', 'semibold', 'demibold', 'demi', 'bold', 'heavy', 'extra bold', 'black'} 文本粗细|
|
||||
| `horizontalalignment` or ha | {'center', 'right', 'left'} 选择文本左对齐右对齐还是居中对齐 |
|
||||
| `linespacing` | float (multiple of font size) 文本间距 |
|
||||
| `rotation` | float or {'vertical', 'horizontal'} 指text逆时针旋转的角度,“horizontal”等于0,“vertical”等于90 |
|
||||
| `verticalalignment` or va | {'center', 'top', 'bottom', 'baseline', 'center_baseline'} 文本在垂直角度的对齐方式 |
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.xlabel和ylabel
|
||||
|
||||
pyplot API:matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel(xlabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None, \*, loc=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
     matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel(ylabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None,\*, loc=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
OO API:  Axes.set_xlabel(self, xlabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None, \*, loc=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
     Axes.set_ylabel(self, ylabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None,\*, loc=None, \*\*kwargs)
|
||||
**参数**:此方法接受以下描述的参数:
|
||||
xlabel或者ylabel:label的文本
|
||||
labelpad:设置label距离轴(axis)的距离
|
||||
loc:{'left', 'center', 'right'},默认为center
|
||||
\*\*kwargs:[文本](https://matplotlib.org/api/text_api.html#matplotlib.text.Text)属性
|
||||
**返回值**:此方法返回作为创建的xlabel和ylabel实例的文本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.xlabel和ylabel - 子图的x,y轴标签
|
||||
|
||||
xlabel的调用方式为`Axes.set_xlabel(xlabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None, *, loc=None, **kwargs)`
|
||||
ylabel方式类似,这里不重复写出。
|
||||
其中`xlabel`即为标签内容,
|
||||
`fontdict`和`**kwargs`用来修改样式,上一小节已介绍,
|
||||
`labelpad`为标签和坐标轴的距离,默认为4,
|
||||
`loc`为标签位置,可选的值为'left', 'center', 'right'之一,默认为居中
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#文本属性的输入一种是通过**kwargs属性这种方式,一种是通过操作 matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties 方法
|
||||
#该案例中对于x_label采用**kwargs调整字体属性,y_label则采用 matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties 方法调整字体属性
|
||||
#该链接是FontProperties方法的介绍 https://matplotlib.org/api/font_manager_api.html#matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties
|
||||
x1 = np.linspace(0.0, 5.0, 100)
|
||||
y1 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * x1) * np.exp(-x1)
|
||||
# 观察labelpad和loc参数的使用效果
|
||||
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
|
||||
axes = fig.subplots(1,2)
|
||||
axes[0].set_xlabel('xlabel',labelpad=20,loc='left')
|
||||
|
||||
font = FontProperties()
|
||||
font.set_family('serif')
|
||||
font.set_name('Times New Roman')
|
||||
font.set_style('italic')
|
||||
|
||||
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 3))
|
||||
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15, left=0.2)
|
||||
ax.plot(x1, y1)
|
||||
ax.set_xlabel('time [s]', fontsize='large', fontweight='bold')
|
||||
ax.set_ylabel('Damped oscillation [V]', fontproperties=font)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
# loc参数仅能提供粗略的位置调整,如果想要更精确的设置标签的位置,可以使用position参数+horizontalalignment参数来定位
|
||||
# position由一个元组过程,第一个元素0.2表示x轴标签在x轴的位置,第二个元素对于xlabel其实是无意义的,随便填一个数都可以
|
||||
# horizontalalignment='left'表示左对齐,这样设置后x轴标签就能精确定位在x=0.2的位置处
|
||||
axes[1].set_xlabel('xlabel', position=(0.2, _), horizontalalignment='left');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.title和suptitle - 子图和画布的标题
|
||||
|
||||
title的调用方式为`Axes.set_title(label, fontdict=None, loc=None, pad=None, *, y=None, **kwargs)`
|
||||
其中label为子图标签的内容,`fontdict`,`loc`,`**kwargs`和之前小节相同不重复介绍
|
||||
`pad`是指标题偏离图表顶部的距离,默认为6
|
||||
`y`是title所在子图垂向的位置。默认值为1,即title位于子图的顶部。
|
||||
|
||||
suptitle的调用方式为`figure.suptitle(t, **kwargs)`
|
||||
其中`t`为画布的标题内容
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
# 观察pad参数的使用效果
|
||||
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
|
||||
fig.suptitle('This is figure title',y=1.2) # 通过参数y设置高度
|
||||
axes = fig.subplots(1,2)
|
||||
axes[0].set_title('This is title',pad=15)
|
||||
axes[1].set_title('This is title',pad=6);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.annotate - 子图的注解
|
||||
|
||||
annotate的调用方式为`Axes.annotate(text, xy, *args, **kwargs)`
|
||||
其中`text`为注解的内容,
|
||||
`xy`为注解箭头指向的坐标,
|
||||
其他常用的参数包括:
|
||||
`xytext`为注解文字的坐标,
|
||||
`xycoords`用来定义xy参数的坐标系,
|
||||
`textcoords`用来定义xytext参数的坐标系,
|
||||
`arrowprops`用来定义指向箭头的样式
|
||||
annotate的参数非常复杂,这里仅仅展示一个简单的例子,更多参数可以查看[官方文档中的annotate介绍](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/text/annotations.html#plotting-guide-annotation)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
||||
ax = fig.add_subplot()
|
||||
ax.annotate("",
|
||||
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
|
||||
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
|
||||
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3,rad=0.2")
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.字体的属性设置
|
||||
字体设置一般有全局字体设置和自定义局部字体设置两种方法。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#首先可以查看matplotlib所有可用的字体
|
||||
from matplotlib import font_manager
|
||||
font_family = font_manager.fontManager.ttflist
|
||||
font_name_list = [i.name for i in font_family]
|
||||
for font in font_name_list[:10]:
|
||||
print(f'{font}\n')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[为方便在图中加入合适的字体,可以尝试了解中文字体的英文名称,该链接告诉了常用中文的英文名称](https://www.cnblogs.com/chendc/p/9298832.html)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#该block讲述如何在matplotlib里面,修改字体默认属性,完成全局字体的更改。
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimSun'] # 指定默认字体为新宋体。
|
||||
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像时 负号'-' 显示为方块和报错的问题。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -227,111 +221,20 @@ plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像时 负号'-
|
|||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#局部字体的修改方法1
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import matplotlib.font_manager as fontmg
|
||||
|
||||
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
|
||||
plt.plot(x, label='小示例图标签')
|
||||
|
||||
# 直接用字体的名字。
|
||||
# 直接用字体的名字
|
||||
plt.xlabel('x 轴名称参数', fontproperties='Microsoft YaHei', fontsize=16) # 设置x轴名称,采用微软雅黑字体
|
||||
plt.ylabel('y 轴名称参数', fontproperties='Microsoft YaHei', fontsize=14) # 设置Y轴名称
|
||||
plt.title('坐标系的标题', fontproperties='Microsoft YaHei', fontsize=20) # 设置坐标系标题的字体
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='lower right', prop={"family": 'Microsoft YaHei'}, fontsize=10); # 小示例图的字体设置
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='lower right', prop={"family": 'Microsoft YaHei'}, fontsize=10) ; # 小示例图的字体设置
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#局部字体的修改方法2
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import matplotlib.font_manager as fontmg
|
||||
|
||||
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
|
||||
plt.plot(x, label='小示例图标签')
|
||||
#fname为你系统中的字体库路径
|
||||
my_font1 = fontmg.FontProperties(fname=r'C:\Windows\Fonts\simhei.ttf') # 读取系统中的 黑体 字体。
|
||||
my_font2 = fontmg.FontProperties(fname=r'C:\Windows\Fonts\simkai.ttf') # 读取系统中的 楷体 字体。
|
||||
# fontproperties 设置中文显示,fontsize 设置字体大小
|
||||
plt.xlabel('x 轴名称参数', fontproperties=my_font1, fontsize=16) # 设置x轴名称
|
||||
plt.ylabel('y 轴名称参数', fontproperties=my_font1, fontsize=14) # 设置Y轴名称
|
||||
plt.title('坐标系的标题', fontproperties=my_font2, fontsize=20) # 标题的字体设置
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='lower right', prop=my_font1, fontsize=10); # 小示例图的字体设置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 7.数学表达式
|
||||
在文本标签中使用数学表达式。有关MathText的概述,请参见 [写数学表达式](https://matplotlib.org/tutorials/text/mathtext.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-text-mathtext-py),但由于数学表达式的练习想必我们都在markdown语法和latex语法中多少有接触,故在此不继续展开,愿意深入学习的可以参看官方文档.下面是一个官方案例,供参考了解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
t = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
|
||||
s = np.sin(2*np.pi*t)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.plot(t, s)
|
||||
plt.title(r'$\alpha_i > \beta_i$', fontsize=20)
|
||||
plt.text(1, -0.6, r'$\sum_{i=0}^\infty x_i$', fontsize=20)
|
||||
plt.text(0.6, 0.6, r'$\mathcal{A}\mathrm{sin}(2 \omega t)$',
|
||||
fontsize=20)
|
||||
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
|
||||
plt.ylabel('volts (mV)')
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#这是对前七节学习内容的总结案例
|
||||
import matplotlib
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
||||
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
|
||||
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
|
||||
|
||||
# 分别在figure和subplot上设置title
|
||||
fig.suptitle('bold figure suptitle', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
|
||||
ax.set_title('axes title')
|
||||
|
||||
ax.set_xlabel('xlabel')
|
||||
ax.set_ylabel('ylabel')
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置x-axis和y-axis的范围都是[0, 10]
|
||||
ax.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
|
||||
|
||||
ax.text(3, 8, 'boxed italics text in data coords', style='italic',
|
||||
bbox={'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10})
|
||||
|
||||
ax.text(2, 6, r'an equation: $E=mc^2$', fontsize=15)
|
||||
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
|
||||
'color': 'purple',
|
||||
'weight': 'normal',
|
||||
'size': 10,
|
||||
}
|
||||
ax.text(3, 2, 'unicode: Institut für Festkörperphysik',fontdict=font1)
|
||||
ax.text(0.95, 0.01, 'colored text in axes coords',
|
||||
verticalalignment='bottom', horizontalalignment='right',
|
||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
||||
color='green', fontsize=15)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 二、Tick上的文本
|
||||
|
|
@ -343,9 +246,6 @@ plt.show()
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import matplotlib
|
||||
x1 = np.linspace(0.0, 5.0, 100)
|
||||
y1 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * x1) * np.exp(-x1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -356,12 +256,13 @@ y1 = np.cos(2 * np.pi * x1) * np.exp(-x1)
|
|||
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(5, 3), tight_layout=True)
|
||||
axs[0].plot(x1, y1)
|
||||
axs[1].plot(x1, y1)
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticks(np.arange(0., 10.1, 2.))
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticks(np.arange(0., 10.1, 2.));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -373,11 +274,13 @@ axs[1].plot(x1, y1)
|
|||
ticks = np.arange(0., 8.1, 2.)
|
||||
tickla = [f'{tick:1.2f}' for tick in ticks]
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticks(ticks)
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticklabels(tickla)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticklabels(tickla);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -397,12 +300,16 @@ axs[1].set_xticks([0,1,2,3,4,5,6])#要将x轴的刻度放在数据范围中的
|
|||
axs[1].set_xticklabels(['zero','one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five','six'],#设置刻度对应的标签
|
||||
rotation=30, fontsize='small')#rotation选项设定x刻度标签倾斜30度。
|
||||
axs[1].xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')#set_ticks_position()方法是用来设置刻度所在的位置,常用的参数有bottom、top、both、none
|
||||
print(axs[1].xaxis.get_ticklines())
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
print(axs[1].xaxis.get_ticklines());
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.Tick Locators and Formatters
|
||||
|
|
@ -428,13 +335,13 @@ formatter = matplotlib.ticker.FormatStrFormatter('-%1.1f')
|
|||
axs[1, 0].xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
|
||||
|
||||
formatter = matplotlib.ticker.FormatStrFormatter('%1.5f')
|
||||
axs[1, 1].xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
axs[1, 1].xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
|
|
@ -448,12 +355,13 @@ def formatoddticks(x, pos):
|
|||
|
||||
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 3), tight_layout=True)
|
||||
ax.plot(x1, y1)
|
||||
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatoddticks)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatoddticks);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### b) Tick Locators
|
||||
|
|
@ -486,21 +394,19 @@ axs[1, 0].xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
locator = matplotlib.ticker.FixedLocator([0,7,14,21,28])
|
||||
axs[1, 1].xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
axs[1, 1].xaxis.set_major_locator(locator);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
此外`matplotlib.dates` 模块还提供了特殊的设置日期型刻度格式和位置的方式
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
# 特殊的日期型locator和formatter
|
||||
locator = mdates.DayLocator(bymonthday=[1,15,25])
|
||||
formatter = mdates.DateFormatter('%b %d')
|
||||
|
|
@ -511,158 +417,117 @@ ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
|
|||
base = datetime.datetime(2017, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1)
|
||||
time = [base + datetime.timedelta(days=x) for x in range(len(x1))]
|
||||
ax.plot(time, y1)
|
||||
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=70)
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=70);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**其他进阶案例**
|
||||
## 三、legend(图例)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#这个案例中展示了如何进行坐标轴的移动,如何更改刻度值的样式
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
x = np.linspace(-3,3,50)
|
||||
y1 = 2*x+1
|
||||
y2 = x**2
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
plt.plot(x,y2)
|
||||
plt.plot(x,y1,color='red',linewidth=1.0,linestyle = '--')
|
||||
plt.xlim((-3,5))
|
||||
plt.ylim((-3,5))
|
||||
plt.xlabel('x')
|
||||
plt.ylabel('y')
|
||||
new_ticks1 = np.linspace(-3,5,5)
|
||||
plt.xticks(new_ticks1)
|
||||
plt.yticks([-2,0,2,5],[r'$one\ shu$',r'$\alpha$',r'$three$',r'four'])
|
||||
'''
|
||||
上一行代码是将y轴上的小标改成文字,其中,空格需要增加\,即'\ ',$可将格式更改成数字模式,如果需要输入数学形式的α,则需要用\转换,即\alpha
|
||||
如果使用面向对象的命令进行画图,那么下面两行代码可以实现与 plt.yticks([-2,0,2,5],[r'$one\ shu$',r'$\alpha$',r'$three$',r'four']) 同样的功能
|
||||
axs.set_yticks([-2,0,2,5])
|
||||
axs.set_yticklabels([r'$one\ shu$',r'$\alpha$',r'$three$',r'four'])
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ax = plt.gca()#gca = 'get current axes' 获取现在的轴
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ax = plt.gca()是获取当前的axes,其中gca代表的是get current axes。
|
||||
fig=plt.gcf是获取当前的figure,其中gcf代表的是get current figure。
|
||||
|
||||
许多函数都是对当前的Figure或Axes对象进行处理,
|
||||
例如plt.plot()实际上会通过plt.gca()获得当前的Axes对象ax,然后再调用ax.plot()方法实现真正的绘图。
|
||||
|
||||
而在本例中则可以通过ax.spines方法获得当前顶部和右边的轴并将其颜色设置为不可见
|
||||
然后将左边轴和底部的轴所在的位置重新设置
|
||||
最后再通过set_ticks_position方法设置ticks在x轴或y轴的位置,本示例中因所设置的bottom和left是ticks在x轴或y轴的默认值,所以这两行的代码也可以不写
|
||||
'''
|
||||
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
|
||||
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
|
||||
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data',0))
|
||||
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data',0))#axes 百分比
|
||||
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') #设置ticks在x轴的位置
|
||||
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') #设置ticks在y轴的位置
|
||||
plt.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 三、[legend](https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.legend.html#matplotlib.pyplot.legend)(图例)
|
||||
|
||||
图例的设置会使用一些常见术语,为了清楚起见,这些术语在此处进行说明:
|
||||
** legend entry(图例条目)**
|
||||
图例有一个或多个legend entries组成。一个entry由一个key和一个label组成。
|
||||
** legend key(图例键)**
|
||||
每个 legend label左面的colored/patterned marker(彩色/图案标记)
|
||||
** legend label(图例标签)**
|
||||
描述由key来表示的handle的文本
|
||||
** legend handle(图例句柄)**
|
||||
用于在图例中生成适当图例条目的原始对象
|
||||
在具体学习图例之前,首先解释几个术语:
|
||||
**legend entry(图例条目)**
|
||||
每个图例由一个或多个legend entries组成。一个entry包含一个key和其对应的label。
|
||||
**legend key(图例键)**
|
||||
每个legend label左面的colored/patterned marker(彩色/图案标记)
|
||||
**legend label(图例标签)**
|
||||
描述由key来表示的handle的文本
|
||||
**legend handle(图例句柄)**
|
||||
用于在图例中生成适当图例条目的原始对象
|
||||
|
||||
以下面这个图为例,右侧的方框中的共有两个legend entry;两个legend key,分别是一个蓝色和一个黄色的legend key;两个legend label,一个名为‘Line up’和一个名为‘Line Down’的legend label
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
常用的几个参数:
|
||||
|
||||
(1)设置图列位置
|
||||
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='upper center') 等同于plt.legend(loc=9),对应关系如下表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| loc by number | loc by text |
|
||||
| ------------- | -------------- |
|
||||
| 0 | 'best' |
|
||||
| 1 | 'upper right' |
|
||||
| 2 | 'upper left' |
|
||||
| 3 | 'lower left' |
|
||||
| 4 | 'lower right' |
|
||||
| 5 | 'right' |
|
||||
| 6 | 'center left' |
|
||||
| 7 | 'center right' |
|
||||
| 8 | 'lower center' |
|
||||
| 9 | 'upper center' |
|
||||
| 10 | 'center' |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(2)设置图例字体大小
|
||||
|
||||
fontsize : int or float or {‘xx-small’, ‘x-small’, ‘small’, ‘medium’, ‘large’, ‘x-large’, ‘xx-large’}
|
||||
|
||||
(3)设置图例边框及背景
|
||||
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='best',frameon=False) #去掉图例边框
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='best',edgecolor='blue') #设置图例边框颜色
|
||||
plt.legend(loc='best',facecolor='blue') #设置图例背景颜色,若无边框,参数无效
|
||||
|
||||
(4)设置图例标题
|
||||
|
||||
legend = plt.legend(["CH", "US"], title='China VS Us')
|
||||
|
||||
(5)设置图例名字及对应关系
|
||||
|
||||
legend = plt.legend([p1, p2], ["CH", "US"])
|
||||
图例的绘制同样有OO模式和pyplot模式两种方式,写法都是一样的,使用legend()即可调用。
|
||||
以下面的代码为例,在使用legend方法时,我们可以手动传入两个变量,句柄和标签,用以指定条目中的特定绘图对象和显示的标签值。
|
||||
当然通常更简单的操作是不传入任何参数,此时matplotlib会自动寻找合适的图例条目。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
line_up, = plt.plot([1, 2, 3], label='Line 2')
|
||||
line_down, = plt.plot([3, 2, 1], label='Line 1')
|
||||
plt.legend([line_up, line_down], ['Line Up', 'Line Down'],loc=5, title='line',frameon=False);#loc参数设置图例所在的位置,title设置图例的标题,frameon参数将图例边框给去掉
|
||||
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
|
||||
line_up, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3], label='Line 2')
|
||||
line_down, = ax.plot([3, 2, 1], label='Line 1')
|
||||
ax.legend(handles = [line_up, line_down], labels = ['Line Up', 'Line Down']);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
legend其他常用的几个参数如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**设置图例位置**
|
||||
loc参数接收一个字符串或数字表示图例出现的位置
|
||||
ax.legend(loc='upper center') 等同于ax.legend(loc=9)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Location String | Location Code |
|
||||
| --------------- | ------------- |
|
||||
| 'best' | 0 |
|
||||
| 'upper right' | 1 |
|
||||
| 'upper left' | 2 |
|
||||
| 'lower left' | 3 |
|
||||
| 'lower right' | 4 |
|
||||
| 'right' | 5 |
|
||||
| 'center left' | 6 |
|
||||
| 'center right' | 7 |
|
||||
| 'lower center' | 8 |
|
||||
| 'upper center' | 9 |
|
||||
| 'center' | 10 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
#这个案例是显示多图例legend
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
x = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 4)
|
||||
y = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 4)
|
||||
p1, = plt.plot([1,2,3])
|
||||
p2, = plt.plot([3,2,1])
|
||||
l1 = plt.legend([p2, p1], ["line 2", "line 1"], loc='upper left')
|
||||
|
||||
p3 = plt.scatter(x[0:2], y[0:2], marker = 'D', color='r')
|
||||
p4 = plt.scatter(x[2:], y[2:], marker = 'D', color='g')
|
||||
# 下面这行代码由于添加了新的legend,所以会将l1从legend中给移除
|
||||
plt.legend([p3, p4], ['label', 'label1'], loc='lower right', scatterpoints=1)
|
||||
# 为了保留之前的l1这个legend,所以必须要通过plt.gca()获得当前的axes,然后将l1作为单独的artist
|
||||
plt.gca().add_artist(l1);
|
||||
fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,4,figsize=(10,4))
|
||||
for i in range(4):
|
||||
axes[i].plot([0.5],[0.5])
|
||||
axes[i].legend(labels='a',loc=i) # 观察loc参数传入不同值时图例的位置
|
||||
fig.tight_layout()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**设置图例边框及背景**
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考资料
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
|
||||
axes = fig.subplots(1,3)
|
||||
for i, ax in enumerate(axes):
|
||||
ax.plot([1,2,3],label=f'ax {i}')
|
||||
axes[0].legend(frameon=False) #去掉图例边框
|
||||
axes[1].legend(edgecolor='blue') #设置图例边框颜色
|
||||
axes[2].legend(facecolor='gray'); #设置图例背景颜色,若无边框,参数无效
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[1.matplotlib官网文字使用指南](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/text/text_intro.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-text-text-intro-py
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**设置图例标题**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
fig,ax =plt.subplots()
|
||||
ax.plot([1,2,3],label='label')
|
||||
ax.legend(title='legend title');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 思考题
|
||||
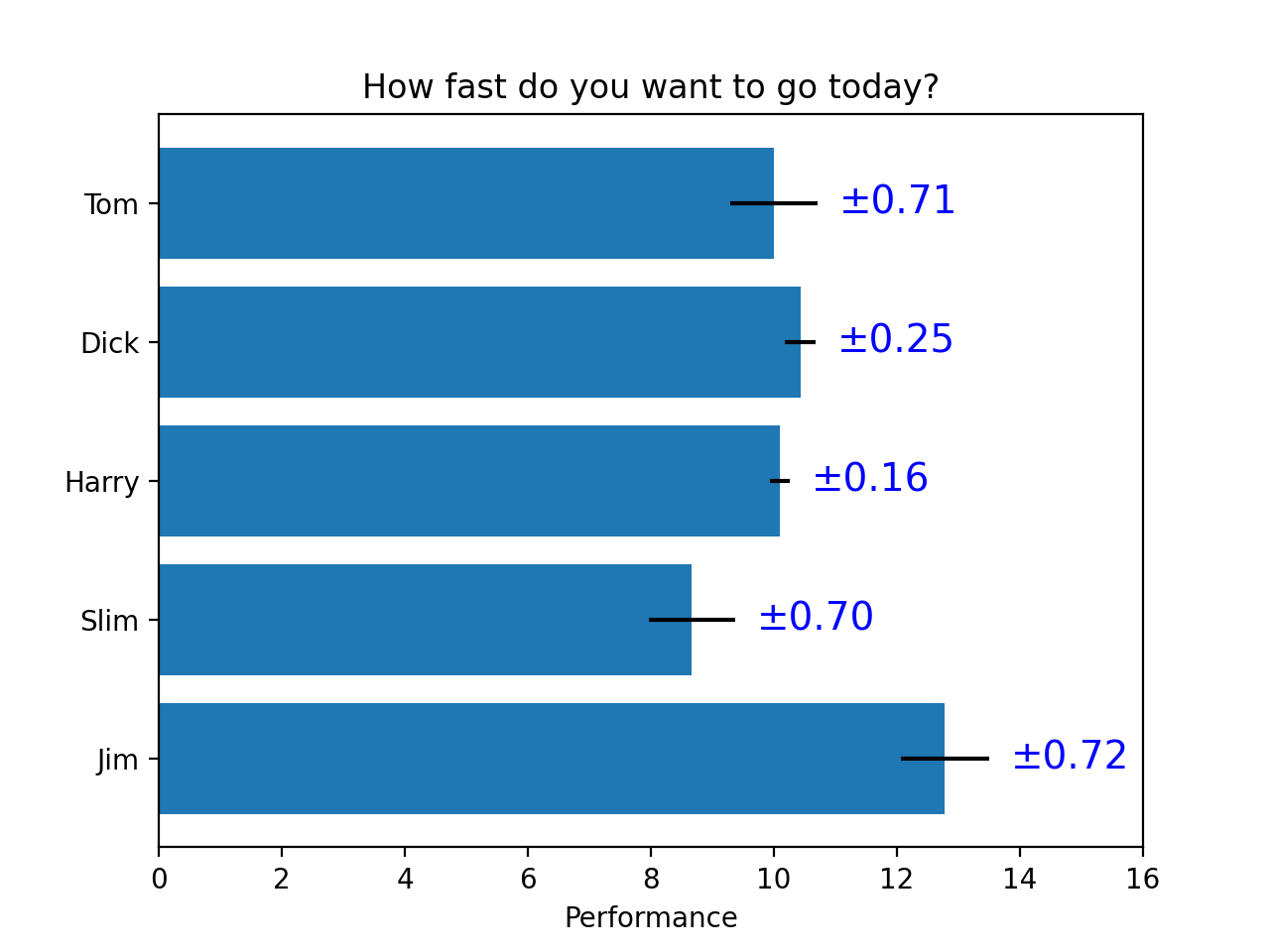
- 请尝试使用两种方式模仿画出下面的图表(重点是柱状图上的标签),本文学习的text方法和matplotlib自带的柱状图标签方法bar_label
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```{code-cell} ipython3
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -199,7 +199,6 @@
|
|||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9AMatplotlib%E5%88%9D%E7%9B%B8%E8%AF%86/index.html#id3">四、两种绘图接口</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9AMatplotlib%E5%88%9D%E7%9B%B8%E8%AF%86/index.html#id4">五、通用绘图模板</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9AMatplotlib%E5%88%9D%E7%9B%B8%E8%AF%86/index.html#id5">思考题</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9AMatplotlib%E5%88%9D%E7%9B%B8%E8%AF%86/index.html#id6">参考资料</a></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l1"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%8C%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E8%89%BA%E6%9C%AF%E7%94%BB%E7%AC%94%E8%A7%81%E4%B9%BE%E5%9D%A4/index.html">第二回:艺术画笔见乾坤</a><ul>
|
||||
|
|
@ -219,13 +218,13 @@
|
|||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E5%9B%9B%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97%E5%9B%BE%E4%BE%8B%E5%B0%BD%E7%9C%89%E7%9B%AE/index.html#figureaxes">一、Figure和Axes上的文本</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E5%9B%9B%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97%E5%9B%BE%E4%BE%8B%E5%B0%BD%E7%9C%89%E7%9B%AE/index.html#tick">二、Tick上的文本</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E5%9B%9B%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97%E5%9B%BE%E4%BE%8B%E5%B0%BD%E7%9C%89%E7%9B%AE/index.html#legend">三、legend(图例)</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E5%9B%9B%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97%E5%9B%BE%E4%BE%8B%E5%B0%BD%E7%9C%89%E7%9B%AE/index.html#id5">参考资料</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E5%9B%9B%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97%E5%9B%BE%E4%BE%8B%E5%B0%BD%E7%9C%89%E7%9B%AE/index.html#id4">思考题</a></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l1"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%94%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%B7%E5%BC%8F%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A7%80%E8%8A%B3%E5%8D%8E/index.html">第五回:样式色彩秀芳华</a><ul>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%94%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%B7%E5%BC%8F%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A7%80%E8%8A%B3%E5%8D%8E/index.html#matplotlib-style">一、matplotlib的绘图样式(style)</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%94%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%B7%E5%BC%8F%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A7%80%E8%8A%B3%E5%8D%8E/index.html#matplotlib-color">二、matplotlib的色彩设置(color)</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%94%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%B7%E5%BC%8F%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A7%80%E8%8A%B3%E5%8D%8E/index.html#id5">参考资料</a></li>
|
||||
<li class="toctree-l2"><a class="reference internal" href="%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%94%E5%9B%9E%EF%BC%9A%E6%A0%B7%E5%BC%8F%E8%89%B2%E5%BD%A9%E7%A7%80%E8%8A%B3%E5%8D%8E/index.html#id5">思考题</a></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -216,11 +216,6 @@
|
|||
思考题
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toc-h2 nav-item toc-entry">
|
||||
<a class="reference internal nav-link" href="#id6">
|
||||
参考资料
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
</nav>
|
||||
|
|
@ -383,10 +378,6 @@
|
|||
<li><p>在第五节绘图模板中我们是以OO模式作为例子展示的,请思考并写一个pyplot绘图模式的简单模板</p></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="section" id="id6">
|
||||
<h2>参考资料<a class="headerlink" href="#id6" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h2>
|
||||
<p><a class="reference external" href="https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/introductory/usage.html">1.matplotlib官网用户指南</a></p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -205,11 +205,6 @@
|
|||
3.设置rcparams
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toc-h3 nav-item toc-entry">
|
||||
<a class="reference internal nav-link" href="#matplotlibrc">
|
||||
4.修改matplotlibrc文件
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toc-h2 nav-item toc-entry">
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +246,7 @@
|
|||
</li>
|
||||
<li class="toc-h2 nav-item toc-entry">
|
||||
<a class="reference internal nav-link" href="#id5">
|
||||
参考资料
|
||||
思考题
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
|
@ -268,7 +263,7 @@
|
|||
<div class="section" id="id1">
|
||||
<h1>第五回:样式色彩秀芳华<a class="headerlink" href="#id1" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h1>
|
||||
<p>第五回详细介绍matplotlib中样式和颜色的使用,绘图样式和颜色是丰富可视化图表的重要手段,因此熟练掌握本章可以让可视化图表变得更美观,突出重点和凸显艺术性。<br />
|
||||
关于绘图样式,常见的有4种方法,分别是修改预定义样式,自定义样式,rcparams和matplotlibrc文件。<br />
|
||||
关于绘图样式,常见的有3种方法,分别是修改预定义样式,自定义样式和rcparams。<br />
|
||||
关于颜色使用,本章介绍了常见的5种表示单色颜色的基本方法,以及colormap多色显示的方法。</p>
|
||||
<div class="section" id="matplotlib-style">
|
||||
<h2>一、matplotlib的绘图样式(style)<a class="headerlink" href="#matplotlib-style" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h2>
|
||||
|
|
@ -398,25 +393,6 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="section" id="matplotlibrc">
|
||||
<h3>4.修改matplotlibrc文件<a class="headerlink" href="#matplotlibrc" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h3>
|
||||
<p>由于matplotlib是使用matplotlibrc文件来控制样式的,也就是上一节提到的rc setting,所以我们还可以通过修改matplotlibrc文件的方式改变样式。</p>
|
||||
<div class="cell docutils container">
|
||||
<div class="cell_input docutils container">
|
||||
<div class="highlight-ipython3 notranslate"><div class="highlight"><pre><span></span><span class="c1"># 查找matplotlibrc文件的路径</span>
|
||||
<span class="n">mpl</span><span class="o">.</span><span class="n">matplotlib_fname</span><span class="p">()</span>
|
||||
</pre></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<div class="output text_plain highlight-myst-ansi notranslate"><div class="highlight"><pre><span></span>'c:\\users\\skywater\\pycharmprojects\\personal\\demo\\lib\\site-packages\\matplotlib\\mpl-data\\matplotlibrc'
|
||||
</pre></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<p>找到路径后,就可以直接编辑样式文件了,打开后看到的文件格式大致是这样的,文件中列举了所有的样式参数,找到想要修改的参数,比如lines.linewidth: 8,并将前面的注释符号去掉,此时再绘图发现样式以及生效了。</p>
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201124005855980.PNG" /></p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="section" id="matplotlib-color">
|
||||
<h2>二、matplotlib的色彩设置(color)<a class="headerlink" href="#matplotlib-color" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h2>
|
||||
|
|
@ -446,7 +422,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_19_01.png" src="../_images/index_19_01.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_17_01.png" src="../_images/index_17_01.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
@ -461,7 +437,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_21_02.png" src="../_images/index_21_02.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_19_01.png" src="../_images/index_19_01.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<p>RGB颜色和HEX颜色之间是可以一一对应的,以下网址提供了两种色彩表示方法的转换工具。<br />
|
||||
|
|
@ -477,7 +453,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_23_01.png" src="../_images/index_23_01.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_21_02.png" src="../_images/index_21_02.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
@ -491,7 +467,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_25_01.png" src="../_images/index_25_01.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_23_01.png" src="../_images/index_23_01.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
|
@ -505,7 +481,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_27_01.png" src="../_images/index_27_01.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_25_01.png" src="../_images/index_25_01.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://matplotlib.org/3.1.0/_images/sphx_glr_named_colors_002.png" />
|
||||
|
|
@ -531,7 +507,7 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="cell_output docutils container">
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_29_0.png" src="../_images/index_29_0.png" />
|
||||
<img alt="../_images/index_27_01.png" src="../_images/index_27_01.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<p>在以下官网页面可以查询上述五种colormap的字符串表示和颜色图的对应关系<br />
|
||||
|
|
@ -539,9 +515,10 @@ ytick.labelsize : 16</p>
|
|||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="section" id="id5">
|
||||
<h2>参考资料<a class="headerlink" href="#id5" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h2>
|
||||
<p><a class="reference external" href="https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/introductory/customizing.html?highlight=rcparams">1.matplotlib官网样式使用指南</a><br />
|
||||
<a class="reference external" href="https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/colors/colors.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-colors-colors-py">2.matplotlib官网色彩使用指南</a></p>
|
||||
<h2>思考题<a class="headerlink" href="#id5" title="永久链接至标题">¶</a></h2>
|
||||
<ul class="simple">
|
||||
<li><p>学习如何自定义colormap,并将其应用到任意一个数据集中,绘制一幅图像,注意colormap的类型要和数据集的特性相匹配,并做简单解释</p></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -322,15 +322,6 @@
|
|||
"- 在第五节绘图模板中我们是以OO模式作为例子展示的,请思考并写一个pyplot绘图模式的简单模板"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## 参考资料\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"[1.matplotlib官网用户指南](https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/introductory/usage.html)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||